Introduction
In 2025, Natural Language Processing (NLP) has become a core component of AI applications, from chatbots and sentiment analysis to translation systems and content recommendation engines.
At CuriosityTech.in (Nagpur, Wardha Road, Gajanan Nagar), we train ML engineers to understand not just NLP algorithms but the end-to-end pipeline: from raw text to actionable insights. NLP combines linguistics, machine learning, and deep learning to enable machines to understand human language.
1. What is NLP?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the field of AI that enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
2. Core NLP Pipeline
A practical NLP workflow includes the following stages:
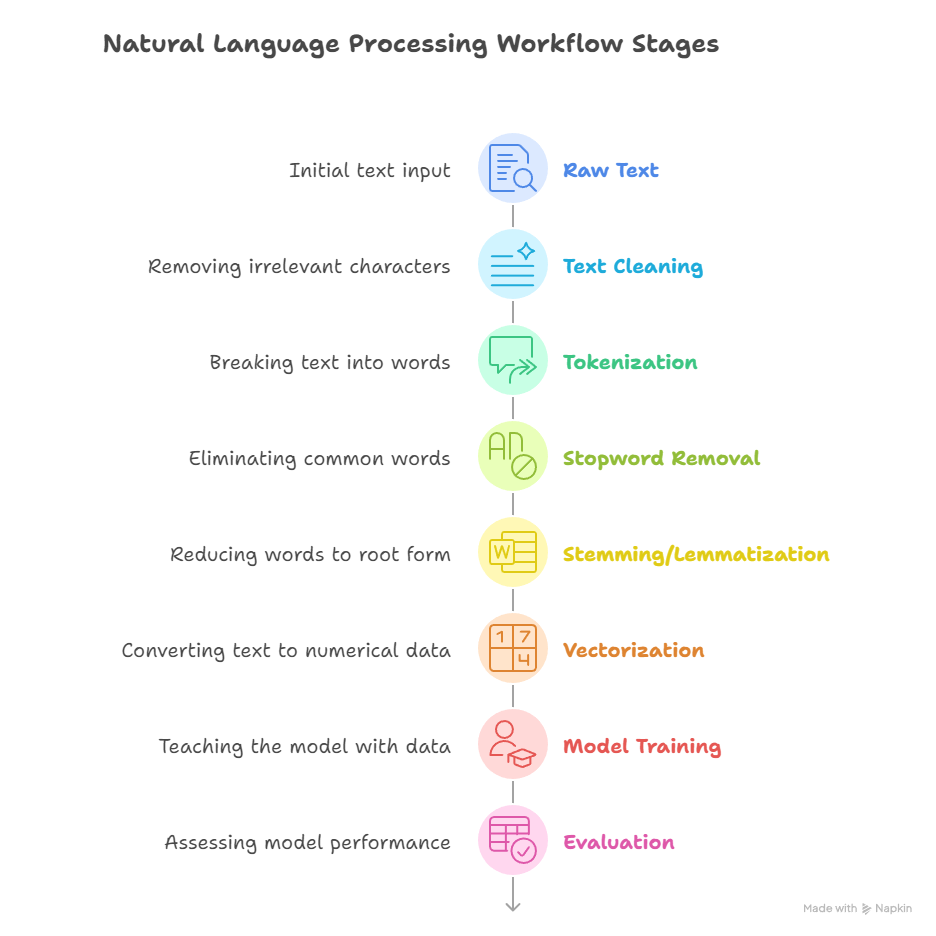
- Example: “Raw Text: ‘I love machine learning!’ → Tokens: [‘I’, ‘love’, ‘machine’, ‘learning’] → Vectorized → Input to classifier”
3. Text Preprocessing
Text preprocessing ensures consistency and reduces noise.
Key steps:
- Lowercasing:
Machine Learning→machine learning - Removing punctuation & special characters
- Stopword removal: Remove common words like “the”, “is”, “in”
- Stemming / Lemmatization: Reduce words to root forms
- Stemming:
- running→run - Lemmatization:-
better→good
- Stemming:
Practical Tip: At CuriosityTech.in, students implement preprocessing pipelines to standardize text for modeling.
4. Tokenization
Definition: Splitting text into smaller units (tokens), either words, subwords, or characters.
Type — Description — Example
- Word Tokenization — Split by words —
I love NLP→ [‘I’, ‘love’, ‘NLP’] - Subword Tokenization — Split by subword units —
machinelearning→ [‘machine’, ‘learning’] - Character Tokenization — Split by characters —
NLP→ [‘N’, ‘L’, ‘P’]
CuriosityTech Tip :- Tokenization is the first mandatory step before vectorization, ensuring ML models can process text numerically.
5. Text Representation (Vectorization)
Machines cannot process text directly; it must be converted into numerical form.
Technique — Description — Use Case
- Bag of Words (BoW) — Counts word occurrences — Simple classification
- TF-IDF — Considers word frequency & inverse document frequency — Spam detection, sentiment analysis
- Word Embeddings — Dense semantic vectors (Word2Vec, GloVe) — Deep learning NLP tasks
- Contextual Embeddings — Transformer-based (BERT, GPT) — Text understanding, Q&A, summarization
Scenario Example:– Riya at CuriosityTech Nagpur vectorizes movie reviews using TF-IDF and trains a logistic regression classifier achieving 88% accuracy.
6. NLP Models
Traditional ML Models:
- Logistic Regression
- SVM
- Random Forest
Deep Learning Models:
- RNN :- Processes sequences – Sentiment analysis
- LSTM / GRU :- Handles long dependencies – Translation, chatbots
- CNN :- Captures local text patterns – Text classification
- Transformers :- Attention-based – BERT, GPT, advanced NLP
CuriosityTech.in trains students in both traditional and deep learning NLP pipelines.
7. Real-World NLP Applications
Task — Model — Example
- Sentiment Analysis :- Logistic Regression, LSTM — Social media reviews
- Named Entity Recognition :- BiLSTM-CRF, Transformers — Extract names, locations
- Machine Translation :- Transformers (BERT, GPT) — English → French
- Text Summarization :- Seq2Seq + Attention — News summarization
- Spam Detection :- SVM, Naive Bayes — Email filtering
Hands-On Practice:– Students build spam classifiers or sentiment predictors, learning feature extraction, preprocessing, and evaluation.
8. Evaluation Metrics in NLP
Task — Metric — Description
- Classification :- Accuracy — Correct predictions / Total predictions
- Classification :- Precision, Recall, F1-score — For imbalanced datasets
- Sequence Generation :- BLEU Score — Measures similarity to reference text
- Clustering :- Silhouette Score — Measures cluster quality
Proper evaluation ensures NLP models are production-ready.
9. Advanced NLP Concepts
- Attention Mechanism: Focus on relevant text parts
- Transformers: Parallel processing and state-of-the-art performance
- Pretrained Models: BERT, GPT, RoBERTa
- Transfer Learning: Reduces data needs and improves performance
Scenario Example:– Arjun fine-tunes a BERT model on customer support data, achieving high accuracy in automated query classification.
10. Key Takeaways
- NLP is essential for modern AI applications
- Preprocessing and vectorization form the foundation
- Transformers dominate current NLP
- Hands-on practice is crucial for mastering real-world tasks
Conclusion
Natural Language Processing is a critical skill for ML engineers in 2025, powering applications in chatbots, sentiment analysis, translation, and more. Mastery of preprocessing, embeddings, and NLP models allows engineers to build production-ready language applications. For hands-on NLP training and real-world project work, contact: CuriosityTech.in +91-9860555369 contact @curiositytech.in