Introduction
Deep learning frameworks are the tools that turn theory into practice. Among the most popular are TensorFlow (developed by Google) and PyTorch (developed by Facebook). Both are widely used in industry and research, but each has distinct features, strengths, and learning curves.
At Curiosity Tech, learners in Nagpur start their AI journey with small datasets, building neural networks using both frameworks. This approach ensures they understand how the framework works, not just how to copy code.
Whether you want to work on image recognition, NLP, or reinforcement learning, mastering these frameworks is essential for a career as a Deep Learning Engineer.
1. Why TensorFlow and PyTorch?
| Feature | TensorFlow | PyTorch |
| Developer | Facebook/Meta | |
| Ease of Learning | Moderate | Beginner-friendly |
| Dynamic vs Static Graphs | Static (TF 2.x has Eager Execution) | Dynamic (eager execution default) |
| Deployment | TensorFlow Serving, TFLite, TensorFlow.js | ONNX, TorchServe |
| Community & Ecosystem | Large, enterprise-oriented | Large, research-oriented |
| Use Case Examples | Production, mobile AI apps | Research, prototyping, GANs |
Career Tip: At CuriosityTech, students start with PyTorch for research projects and transition to TensorFlow for deployment projects. This dual knowledge is highly valued in the job market.
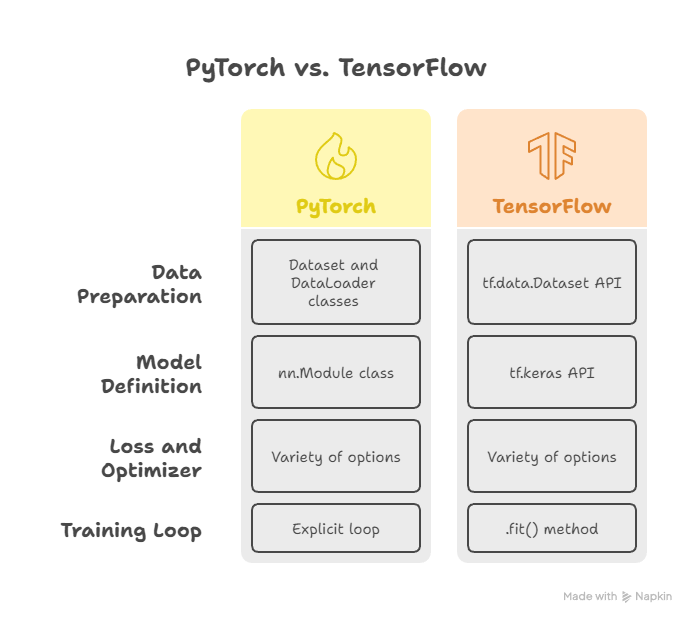
2. Basic Workflow of Both Frameworks
Deep learning frameworks follow a similar workflow, but the syntax and approach differ:
1 – Data Preparation
- PyTorch: Uses Dataset and DataLoader classes for batch processing.
- TensorFlow: Uses tf.data.Dataset API for efficient data pipelines.
2 – Define Model
- PyTorch: Define nn.Module class. Dynamic and flexible.
- TensorFlow: Use tf.keras.Sequential or Functional API. Ideal for beginners.
3 – Define Loss and Optimizer
- Both frameworks provide a variety of loss functions (cross-entropy, MSE) and optimizers (Adam, SGD).
4 – Training Loop
- PyTorch: Explicit loop over epochs and batches. Gives full control.
- TensorFlow: .fit() method simplifies training.
Workflow Diagram (Text Representation):
3. Code Comparison Example: Simple Neural Network
PyTorch
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
class SimpleNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SimpleNN, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(4, 8)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(8, 3)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.fc2(x)
return x
model = SimpleNN()
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
TensorFlow
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
model = Sequential([
Dense(8, input_dim=4, activation=’relu’),
Dense(3, activation=’softmax’)
])
model.compile(optimizer=’adam’, loss=’sparse_categorical_crossentropy’, metrics=[‘accuracy’])
Observation: PyTorch offers more flexibility and is preferred in research, while TensorFlow is production-ready with easier deployment options.
4. Key Differences for Beginners
| Aspect | TensorFlow | PyTorch |
| Learning Curve | Slightly steeper | Easier to start |
| Debugging | Requires understanding TF graph | Pythonic, easier to debug |
| Community Support | Enterprise-focused | Research & prototyping focused |
| Deployment | Strong (TFLite, TF Serving) | Moderate (ONNX, TorchServe) |
CuriosityTech Insight: Beginners often start with PyTorch in labs to visualize gradients and activation functions, then switch to TensorFlow for mobile and cloud deployment projects.
5. Applications in Real-World Projects
At CuriosityTech learners use these frameworks for:
- Image Recognition: CNN models for classifying X-ray images
- Natural Language Processing: RNNs, LSTMs, and Transformers for sentiment analysis
- Generative AI: GANs to generate synthetic images or data
- Reinforcement Learning: Deep Q-Learning agents
Career Tip: Employers often expect hands-on experience with at least one of these frameworks for AI and ML positions.
6. How to Become an Expert
- Start Small: Build simple networks on datasets like MNIST or CIFAR-10.
- Visualize Everything: Use tools like TensorBoard (TensorFlow) or matplotlib (PyTorch).
- Experiment: Change activation functions, optimizers, and layers to see their impact.
- Deploy: Learn TensorFlow Serving, TorchServe, or cloud AI platforms like AWS AI, Google Vertex AI, Azure Cognitive Services.
- Projects Portfolio: Show real projects (CuriosityTech mentors guide this) in your portfolio to attract recruiters.
7. Humanized Experience
During a workshop at CuriosityTech Park, a beginner exclaimed:– “I thought PyTorch was too complex, but after building my first model and seeing the loss decrease, I felt like I was training a real brain!”
This kind of hands-on, guided learning ensures students internalize concepts instead of memorizing code, which is crucial for AI careers.
Conclusion
Mastering TensorFlow and PyTorch is non-negotiable for AI engineers in 2025. PyTorch is excellent for research and prototyping, TensorFlow excels in deployment. Combining both, with hands-on practice on real datasets (as done at CuriosityTech.in), allows learners to become well-rounded AI professionals capable of tackling both industry and research challenges.