Introduction
Embedded systems are the brain of modern robots, allowing them to process information, make decisions, and control actuators. Microcontrollers like Arduino and single-board computers like Raspberry Pi are widely used in robotics because they offer flexibility, compactness, and efficient real-time control.
At Curiosity Tech, learners can access detailed tutorials, project guides, and simulation exercises to master embedded systems and integrate them seamlessly into robotic designs.
1. What is an Embedded System?
An embedded system is a specialized computing system that performs dedicated tasks within a larger mechanical or electrical system. Unlike general-purpose computers, embedded systems are designed for specific functionalities in real-time.
Key Characteristics:
- Dedicated functionality (robot motion control, sensor data processing).
- Real-time operation for immediate response.
- Compact and energy-efficient design.
2. Microcontrollers in Robotics
Microcontrollers (MCUs) are small, integrated circuits with a CPU, memory, and input/output peripherals for controlling robots.
Popular Microcontrollers:
- Arduino Uno: Beginner-friendly, ideal for small robots and sensor-based projects.
- Arduino Mega: More I/O pins, suitable for complex projects like robotic arms.
- ESP32: Wi-Fi/Bluetooth enabled, ideal for IoT-connected robots.
Applications in Robotics:
- Reading sensor data (IR, ultrasonic, LiDAR).
- Controlling motors and actuators via PWM.
- Handling communication between multiple devices.
Pros: Low cost, real-time control, easy programming.
Cons: Limited processing power for complex algorithms or AI applications.
3. Raspberry Pi in Robotics
Raspberry Pi is a single-board computer capable of running Linux and high-level software, making it suitable for AI, vision processing, and advanced computation tasks.
Applications:
- Real-time image processing for machine vision.
- Running ROS nodes for autonomous navigation.
- Multi-sensor integration and data logging.
Pros:
- High computational power.
- Supports Python, C++, ROS, and OpenCV.
- Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and USB connectivity.
Cons:
- Not a real-time controller (use with microcontrollers for critical timing).
- Slightly higher power consumption compared to MCUs.
4. Comparison: Microcontroller vs Raspberry Pi
| Feature | Microcontroller (Arduino) | Raspberry Pi |
| Processing Power | Low | High |
| Real-Time Operation | Yes | Limited |
| Programming Language | C/C++ | Python, C++, Java |
| Operating System | None | Linux (Raspbian) |
| Sensor & Actuator Control | Direct I/O pins | Via GPIO or external MCU |
| Use Case in Robotics | Motor control, sensors, simple tasks | Machine vision, AI, ROS, data processing |
Practical Tip: Use a hybrid approach — Arduino for real-time actuator control and Raspberry Pi for vision or path planning.
5. Embedded System Architecture in Robotics
Block Diagram of Embedded Robotics System:
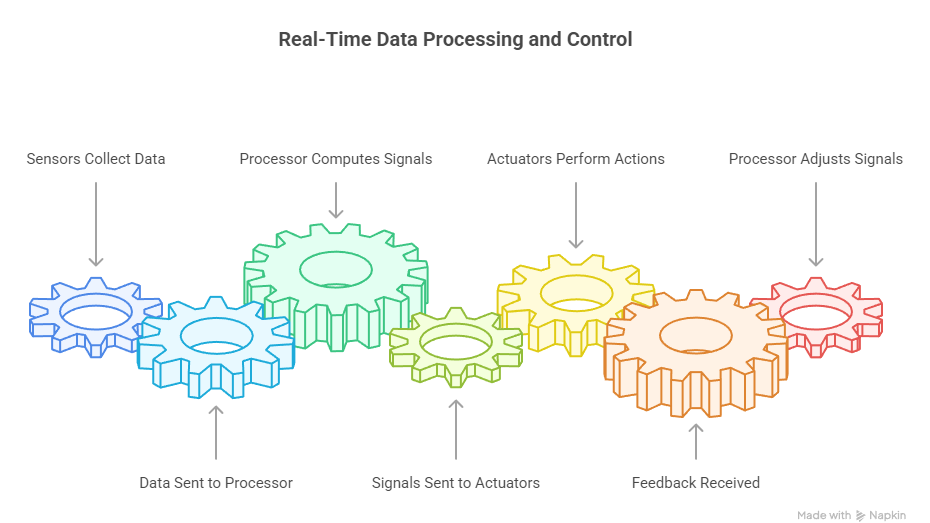
Description: Sensors feed real-time data to the embedded processor, which computes control signals for actuators. Feedback from actuators or sensors ensures accurate operation.
6. Beginner Project Example: Line Following Robot with Embedded Systems
Objective: Build a robot that follows a black line using embedded systems.
Components:
- Sensors: IR sensors for line detection.
- Controller: Arduino Uno for motor control.
- Actuators: DC motors with motor driver.
- Optional: Raspberry Pi for logging data or adding camera vision.
Implementation Steps:
- Connect IR sensors to Arduino and calibrate line detection.
- Program Arduino to read sensor input and generate motor PWM signals.
- Connect DC motors via H-Bridge driver.
- Optionally, integrate Raspberry Pi to capture robot movement and log data.

Curiosity Tech provides schematics, wiring diagrams, and example Arduino/Python code for this project.
7. Advanced Applications
- Robotic Arm Control: Arduino for servo control, Raspberry Pi for object recognition using camera.
- Autonomous Mobile Robots: Pi for ROS navigation and LiDAR processing, Arduino for motor actuation.
- IoT Robots: ESP32 or Pi for Wi-Fi enabled robots reporting data to cloud platforms.
- AI-Enabled Robotics: Raspberry Pi for image classification using TensorFlow or OpenCV, controlling MCU-driven actuators.
8. Tips for Mastering Embedded Systems in Robotics
- Understand I/O pin control and PWM for actuators.
- Learn sensor interfacing and signal processing.
- Use microcontrollers for real-time tasks and Pi for computation-heavy tasks.
- Experiment with hybrid systems for complex robots.
- Simulate robot behavior using Gazebo/V-REP before deploying hardware.
Conclusion
Embedded systems form the core intelligence of robots, bridging the gap between sensors and actuators. Mastering microcontrollers and Raspberry Pi empowers robotics engineers to build autonomous, intelligent, and efficient robotic systems. Platforms like CuriosityTech.in provide project-based tutorials, practical wiring guides, and simulation exercises that make learning embedded robotics accessible and hands-on.