Introduction
ASP.NET Core MVC is the framework of choice for modern web development with .NET. It allows developers to build dynamic, scalable, and maintainable web applications by separating concerns into Model, View, and Controller (MVC).
At CuriosityTech.in, we help FullStack developers turn theory into real-world applications through guided projects, ensuring learners understand not just how MVC works, but why it matters in professional development.
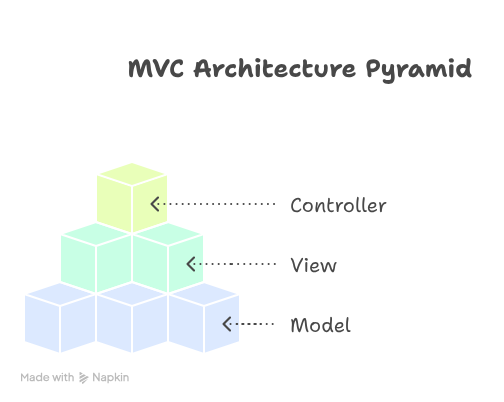
1. Understanding MVC Architecture
MVC Architecture divides an application into three interconnected components:
| Component | Role | Example |
| Model | Represents data and business logic | Course class with properties like Name, Duration |
| View | Handles UI and presentation | Razor pages showing course details |
| Controller | Handles user requests and updates the model/view | CourseController processing enrollments |
Diagram:
User Request
|
V
Controller ——–> Model (Data/Business Logic)
|
V
View (UI/Presentation)
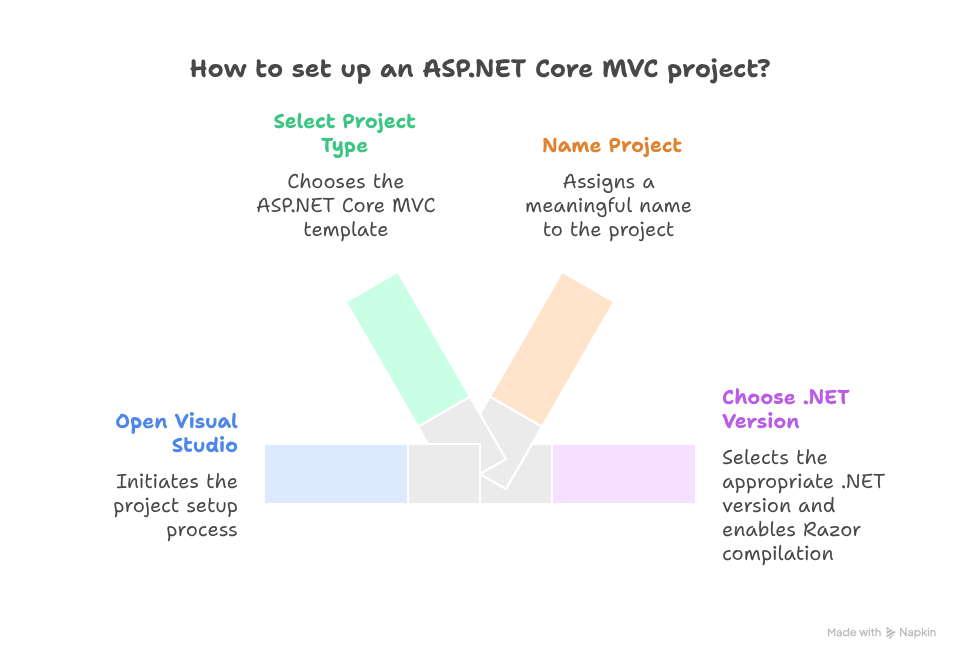
2. Setting Up ASP.NET Core MVC Project
- Open Visual Studio 2022
- Select Create a new project → ASP.NET Core Web App (Model-View-Controller)
- Name your project: CuriosityTechPortal
- Choose .NET 7 (or latest LTS) and enable Razor Runtime Compilation
3. Creating Models
Example: Course Model
public class Course
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Instructor { get; set; }
public int DurationInHours { get; set; }
}
Tip: Use Data Annotations for validation:
[Required(ErrorMessage = “Course Name is required”)]
public string Name { get; set; }
4. Building Controllers
Controllers manage user input and application logic.
public class CourseController : Controller
{
private static List<Course> Courses = new List<Course>();
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View(Courses);
}
public IActionResult AddCourse()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult AddCourse(Course course)
{
Courses.Add(course);
return RedirectToAction(“Index”);
}
}
5. Creating Views with Razor
Razor syntax combines HTML and C# for dynamic UI.
Index.cshtml
@model List<Course>
<h2>Available Courses</h2>
<table>
<tr><th>Name</th><th>Instructor</th><th>Duration</th></tr>
@foreach(var course in Model)
{
<tr>
<td>@course.Name</td>
<td>@course.Instructor</td>
<td>@course.DurationInHours hrs</td>
</tr>
}
</table>
6. Routing and Navigation
- Default Route: /Controller/Action/Id
- Customize routes in Program.cs:
app.MapControllerRoute(
name: “default”,
pattern: “{controller=Course}/{action=Index}/{id?}”);
7. Practical Example: CuriosityTech Course Portal
At CuriosityTech.in, learners can build a mini course portal with:
- CRUD operations: Add, view, edit, delete courses
- Model validation: Ensure correct input from users
- Dynamic UI: Display real-time course lists
- R outing: Navigate between pages seamlessly
Architecture Diagram:
[User]
|
V
[Browser] –> [Controller] –> [Model] –> [Database]
|
V
[View]
8. Advanced Tips
- Use ViewModels for complex data presentation
- Implement partial views for reusable UI components
- Leverage Tag Helpers for cleaner Razor syntax
- Integrate Entity Framework Core for database management
9. CuriosityTech.in Mentorship Insights
- Hands-on projects: Learners get guided steps to build real-world web applications.
- Stepwise learning: MVC concepts are explained and implemented progressively.
- Career-ready skills: Projects replicate industry standards, preparing learners for jobs and freelance projects.
Conclusion
ASP.NET Core MVC is a must-learn framework for FullStack .NET developers. By mastering Models, Views, and Controllers and integrating real-world projects like the Curiosity tech’s course portal learners develop both technical skills and problem-solving mindset.
The next step in your journey is Day 9 – RESTful API Development with ASP.NET Core Web API, where you’ll learn how to make your applications communicate seamlessly with clients and other systems.