Introduction
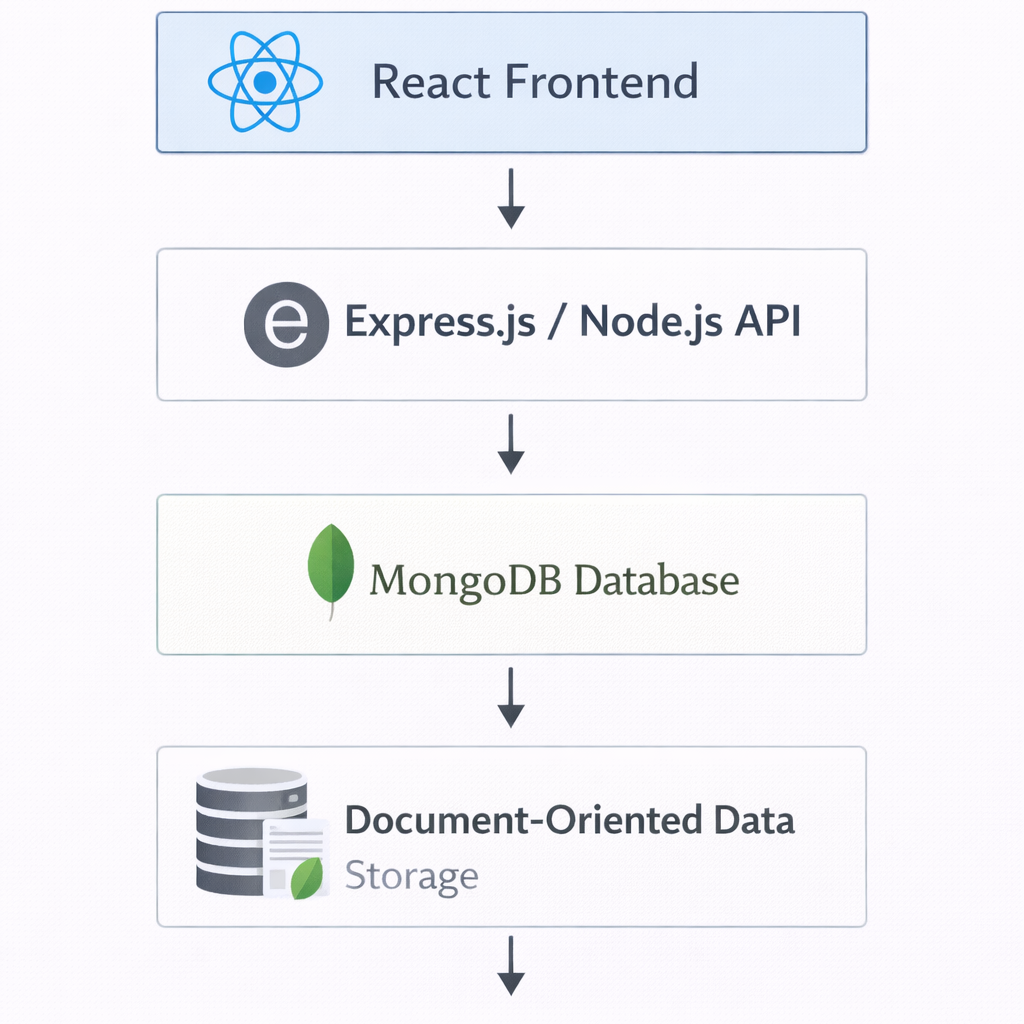
MongoDB is a NoSQL database widely used in MERN stack development. Unlike traditional relational databases, MongoDB stores data in JSON-like documents rather than tables, allowing flexibility, scalability, and high performance. For MERN developers, understanding MongoDB is crucial because it forms the backbone of data storage and retrieval in modern web applications.
At Curiosity Tech, learners are trained to handle complex datasets and design efficient database schemas, bridging theory with real-world MERN applications.
What is NoSQL and Why MongoDB?
NoSQL stands for “Not Only SQL”, a type of database designed to handle large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data.
Advantages of MongoDB in MERN:
- Schema flexibility – No rigid table structures
- Horizontal scalability – Handles large datasets efficiently
- JSON-style documents – Seamlessly integrates with JavaScript and Node.js
- Powerful querying – Aggregation framework for analytics
Diagram – MongoDB in MERN Stack:
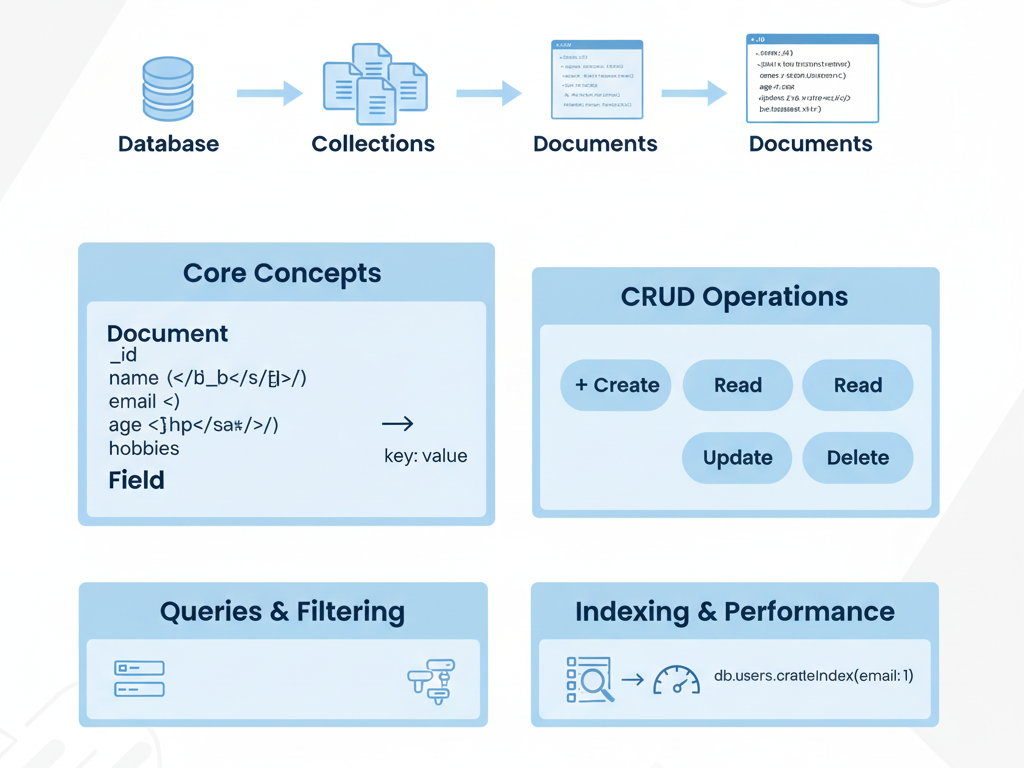
Core Concepts in MongoDB
- Database – Container for collections
- Collection – Equivalent to a table; stores documents
- Document – A JSON-like object representing a record
- Field – Key-value pair inside a document
Example Document – User Profile:
{
“_id”: “64f123abc4567890”,
“name”: “Alice”,
“email”: “alice@example.com”,
“age”: 28,
“hobbies”: [“reading”, “traveling”]
}
CRUD Operations in MongoDB
CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, Delete, the foundation of data manipulation in any application.
Table – MongoDB CRUD Operations:
| Operation | Command Example | Description |
| Create | db.users.insertOne({name: “Alice”}) | Add a new document to a collection |
| Read | db.users.find({age: {$gt: 20}}) | Fetch documents based on query conditions |
| Update | db.users.updateOne({name: “Alice”}, {$set:{age:29}}) | Modify existing documents |
| Delete | db.users.deleteOne({name: “Alice”}) | Remove documents from a collection |
MongoDB Queries and Filtering
MongoDB provides powerful query operators:
- Comparison: $eq, $ne, $gt, $lt
- Logical: $and, $or
- Array: $in, $all
- Element: $exists, $type
Example – Filter Users by Age and Hobbies:
db.users.find({
age: {$gte: 25},
hobbies: {$in: [“traveling”]}
})
Indexing and Performance Optimization
Indexes in MongoDB improve query performance by reducing search times:
Example – Creating an Index:
db.users.createIndex({email: 1}) // ascending order index
Best Practices:
- Use indexes on frequently queried field
- Avoid over-indexing, which increases write overhea
- Monitor query performance with explain()
MongoDB in MERN Stack Applications
- Integration with Node.js: Use Mongoose for schema modeling and validation
- Connecting to Express Routes: Define APIs that perform CRUD operations on MongoDB collections.
- Real-World Example: In a social media app, user data, posts, comments, and messages are stored in MongoDB, queried efficiently, and delivered to React frontend dynamically.
CuriosityTech.in projects focus on practical MERN applications where students design database schemas, write optimized queries, and implement backend functionality seamlessly.
How to Become a MongoDB Expert
- Master CRUD Operations: Build multiple sample datasets and practice queries.
- Learn Schema Design: Understand normalization vs denormalization, and design scalable collections.
- Use Aggregation Framework: Perform analytics and reporting on large datasets.
- Implement Indexing: Optimize query performance and database efficiency.
- Connect to MERN Stack: Build complete apps where MongoDB interacts with Express.js and React frontend.
Infographic Suggestion
Title: “MongoDB Architecture in MERN Stack”
Conclusion
MongoDB is a cornerstone of MERN stack development, offering flexibility, scalability, and seamless integration with JavaScript. By mastering collections, documents, queries, and indexing, developers can build high-performance applications. Curiosity Tech provides hands-on MERN projects to apply MongoDB skills in real-world scenarios, preparing learners for professional full-stack development.



