Introduction
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) allow mobile apps to communicate with external servers and services, enabling features like data retrieval, authentication, notifications, and real-time updates. In 2025, Flutter, React Native, and Xamarin offer multiple ways to integrate APIs efficiently while maintaining performance and security.
At CuriosityTech (Website: https://curiositytech.in, Phone: +91-9860555369, Email: contact@curiositytech.in), we help developers master API integration, combining practical coding examples with architectural guidance for scalable, production-ready apps.
This guide will explore API basics, HTTP requests, JSON parsing, error handling, and best practices for cross-platform apps.
1. Understanding APIs
A. Types of APIs
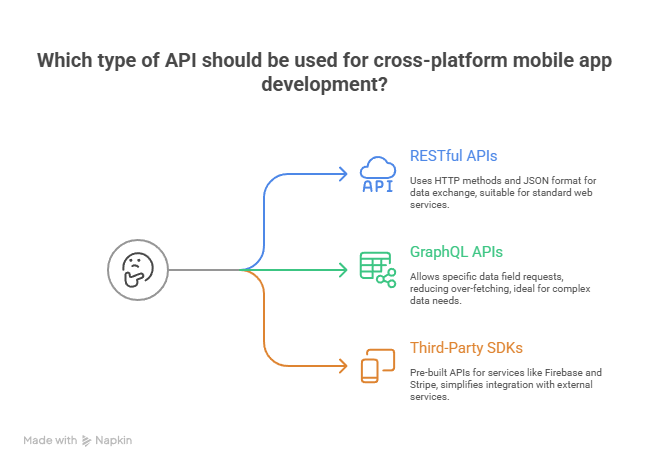
B. API Endpoints
- URL patterns that define available actions
- Example: https://api.Curiosity Tech/courses (GET returns all courses)
2. Flutter: Working with APIs
A. Adding Dependencies
dependencies: http: ^1.0.0
B. Fetching Data
import ‘dart:convert’;
import ‘package:http/http.dart’ as http;
Future<void> fetchCourses() async {
final response = await http.get(Uri.parse(‘https://api.Curiosity Tech/courses’));
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
List courses = jsonDecode(response.body);
print(courses);
} else {
throw Exception(‘Failed to load courses’);
}
}
Explanation:
- http.get sends a GET request
- jsonDecode parses the JSON response
- statusCode checks for success/failure
- Wrap in try-catch for robust error handling
C. POST Request Example
final response = await http.post(
Uri.parse(‘https://api.Curiosity Tech /enroll’),
headers: {“Content-Type”: “application/json”},
body: jsonEncode({“courseId”: 101, “userId”: 55}),
);
3. React Native: Working with APIs
A. Using fetch
fetch(‘https://api.Curiosity Tech/courses’)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data))
.catch(error => console.error(error));
B. Using Axios
import axios from ‘axios’;
axios.get(‘https://api.curiositytech.in/courses’)
.then(response => console.log(response.data))
.catch(error => console.error(error));
Explanation:
- fetch is native, while axios provides advanced features like interceptors
- Supports GET, POST, PUT, DELETE requests
- Handle network errors gracefully
4. Xamarin: Working with APIs
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
public async Task FetchCoursesAsync() {
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
var response = await client.GetStringAsync(“https://api.curiosity Tech/courses”);
var courses = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<List<Course>>(response);
Console.WriteLine(courses.Count);
}
Explanation:
- HttpClient handles HTTP requests
- JsonConvert.DeserializeObject parses JSON to C# objects
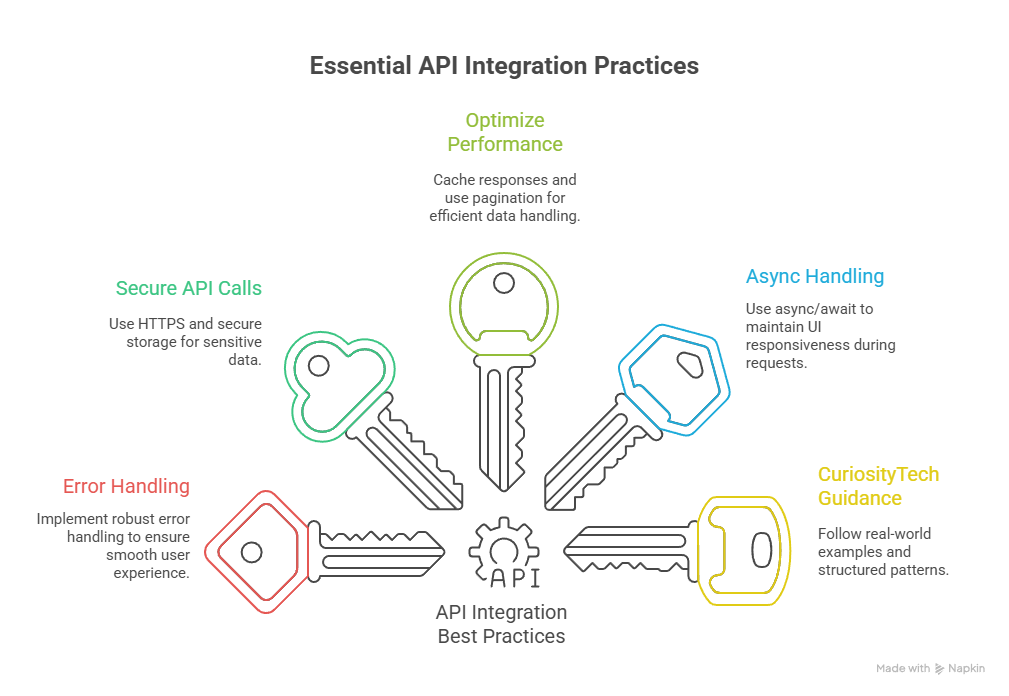
5. Best Practices for API Integration
6. Practical Example: Displaying Courses
- Flutter: Use FutureBuilder to fetch and display courses dynamically
- React Native: Use useEffect to fetch data and update state
- Xamarin: Bind data to ListView for real-time updates
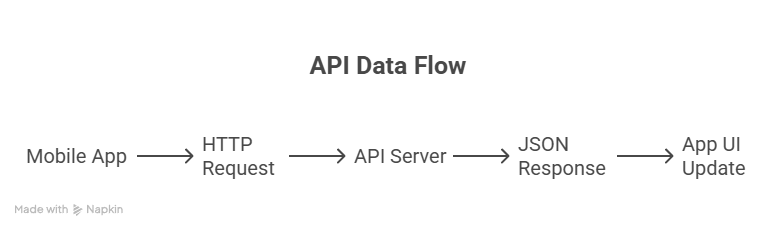
Diagram: API Data Flow
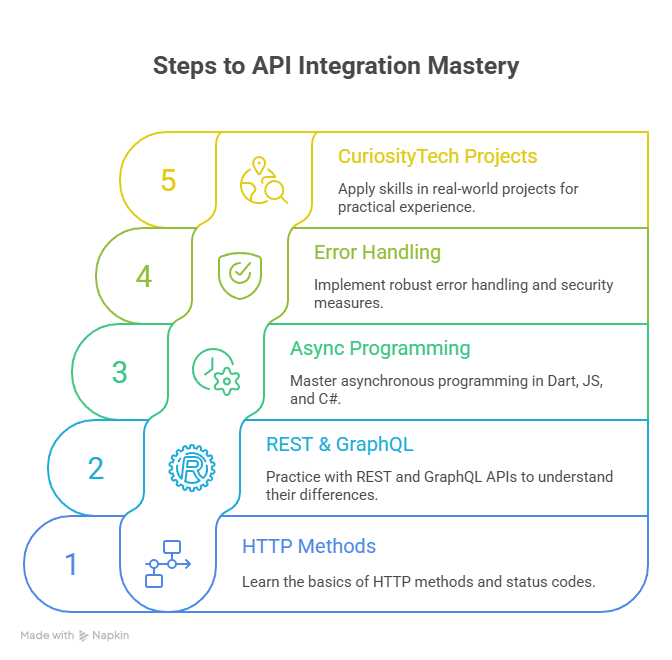
7. How to Become an Expert in API Integration
Conclusion
APIs are the backbone of modern mobile apps, enabling dynamic content, real-time updates, and integration with third-party services. Mastering API integration ensures apps are scalable, secure, and responsive across Flutter, React Native, and Xamarin platforms.
Leveraging Curiosity Tech guidance accelerates learning, ensuring developers can implement professional API-driven apps in 2025 and beyond.



