Introduction
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a branch of AI where agents learn to make decisions by interacting with an environment. Unlike supervised learning, RL focuses on reward-based learning, making it ideal for robotics, gaming, autonomous systems, and optimization problems.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners explore Deep Q-Learning (DQL) to train agents in simulated environments, building hands-on experience that combines theory, algorithmic thinking, and coding skills, preparing them for AI careers in 2025 and beyond.
1. What is Reinforcement Learning?
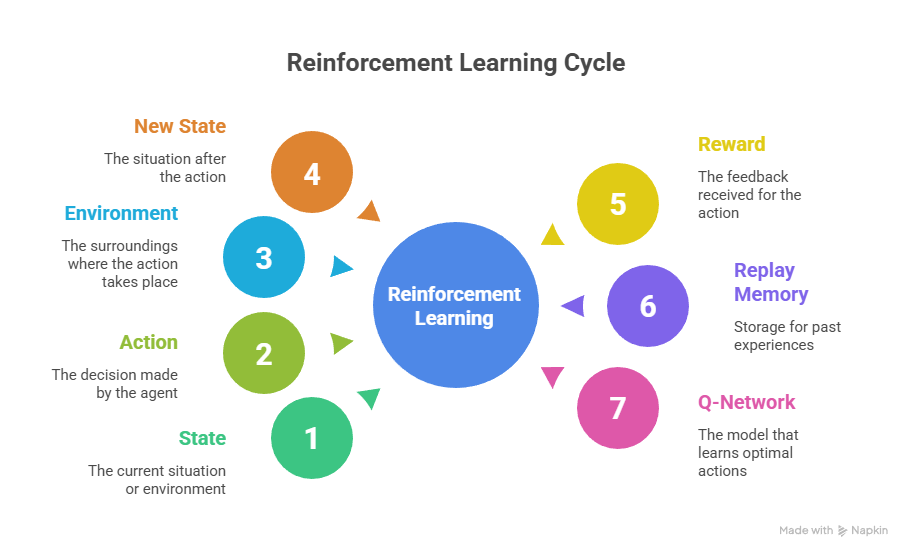
In RL, an agent interacts with an environment using the Markov Decision Process (MDP) framework.
Core Components:
| Component | Description |
| Agent | Learner that takes actions |
| Environment | The system or game the agent interacts with |
| State (s) | Current representation of the environment |
| Action (a) | Decision made by the agent |
| Reward (r) | Feedback received after action |
| Policy (π) | Strategy used to select actions |
| Value Function (V) | Expected cumulative reward |
Analogy: A student learning chess receives feedback (winning/losing) after each move, gradually improving strategy.
2. Deep Q-Learning (DQL)
Deep Q-Learning combines Q-Learning with deep neural networks to approximate the Q-function, enabling RL to work in high-dimensional state spaces.
Q-Function:
Q(s,a)=Expected cumulative reward for taking action a in state sQ(s, a) = \text{Expected cumulative reward for taking action } a \text{ in state } sQ(s,a)=Expected cumulative reward for taking action a in state s
Key Idea:
- The agent uses a neural network to predict Q-values for all possible actions in a given state
- Chooses the action with the highest Q-value (exploitation) or random action (exploration)
Algorithm Steps (Simplified):
- Initialize Replay Memory and Q-Network
- For each episode:
- Observe current state s
- Choose action a (ε-greedy strategy: exploration vs exploitation)
- Perform action, observe reward r and new state s’
- Store (s, a, r, s’) in replay memory
- Sample mini-batch from memory
- Update Q-network using loss:
Loss=(r+γmaxa′Q(s′,a′)−Q(s,a))2\text{Loss} = (r + \gamma \max_{a’} Q(s’, a’) – Q(s, a))^2Loss=(r+γa′maxQ(s′,a′)−Q(s,a))2
- Observe current state s
- Repeat until the agent maximizes cumulative reward
3. Visual Representation (Textual)
4. Practical Example: CartPole Simulation
Objective: Train an agent to balance a pole on a cart using Deep Q-Learning.
Steps for Beginners at CuriosityTech:
- Import OpenAI Gym environment (CartPole-v1)
- Initialize Deep Q-Network with input = state size, output = number of actions
- Train agent using ε-greedy policy
- Evaluate performance by plotting cumulative rewards per episode
Observation: Beginners witness the agent learning balance over time, demonstrating trial-and-error learning, which is the essence of reinforcement learning.
5. Key Concepts to Master
- Exploration vs Exploitation: Balancing random actions vs optimal strategy
- Discount Factor (γ): How much future rewards matter
- Replay Memory: Stabilizes learning by sampling past experiences
- Target Network: Helps avoid oscillations during training
CuriosityTech Tip: Students start with small environments like CartPole or MountainCar, then progress to Atari games or robotic simulations for real-world applications.
6. Applications of Deep Q-Learning
| Domain | Application |
| Robotics | Training robots to navigate, grasp, or manipulate objects |
| Gaming | Agents playing Atari or Chess/Go autonomously |
| Autonomous Vehicles | Decision-making in dynamic driving environments |
| Finance | Portfolio optimization and trading strategies |
| Resource Management | Smart grid energy allocation, traffic signal control |
Portfolio Tip: CuriosityTech students often include CartPole and custom simulations in their portfolios to demonstrate algorithmic and coding skills in RL.
7. Career Insights
- RL expertise is highly valued in robotics, gaming, autonomous systems, and research roles
- Employers expect understanding of:
- Q-Learning, Deep Q-Networks, Policy Gradients
- Gym environments and simulation-based experiments
- Algorithm tuning for exploration/exploitation balance
- Q-Learning, Deep Q-Networks, Policy Gradients
Mentorship Approach: CuriosityTech.in guides students to document RL experiments, visualize rewards, and explain agent behavior, making them interview-ready.
8. Human Story
A student struggled to balance the CartPole in initial episodes. After experimenting with learning rate, ε-decay strategy, and replay memory size, the agent could balance the pole consistently for 200 steps. This hands-on trial and error highlighted the iterative nature of reinforcement learning and the importance of parameter tuning for real-world AI problems.
Conclusion
Deep Q-Learning equips AI engineers to solve complex sequential decision-making problems, from robotics to autonomous driving. By combining simulation experiments, stepwise algorithm understanding, and deployment insights, learners at CuriosityTech.in acquire both practical skills and career readiness, preparing them for advanced roles in AI and reinforcement learning domains.



