Introduction
Modern DevOps heavily relies on cloud platforms to provide scalable, flexible, and automated infrastructure. AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are the three dominant cloud providers, each offering unique tools and services for DevOps workflows. At Curiosity Tech, we focus on helping engineers understand the strengths, differences, and practical applications of each platform for building robust DevOps pipelines.
Why Cloud Platforms are Essential for DevOps
Cloud platforms provide:
- On-Demand Infrastructure – Spin up VMs, containers, or serverless resources instantly.
- Scalability & Flexibility – Auto-scale applications based on demand.
- Integrated DevOps Tools – CI/CD, monitoring, security, and IaC tools built-in.
- Global Availability – Deploy applications closer to users for low latency.
- Cost Efficiency – Pay-as-you-go models reduce capital expenditure.
Cloud platforms eliminate manual hardware setup, enabling rapid experimentation, deployment, and automation in DevOps pipelines.
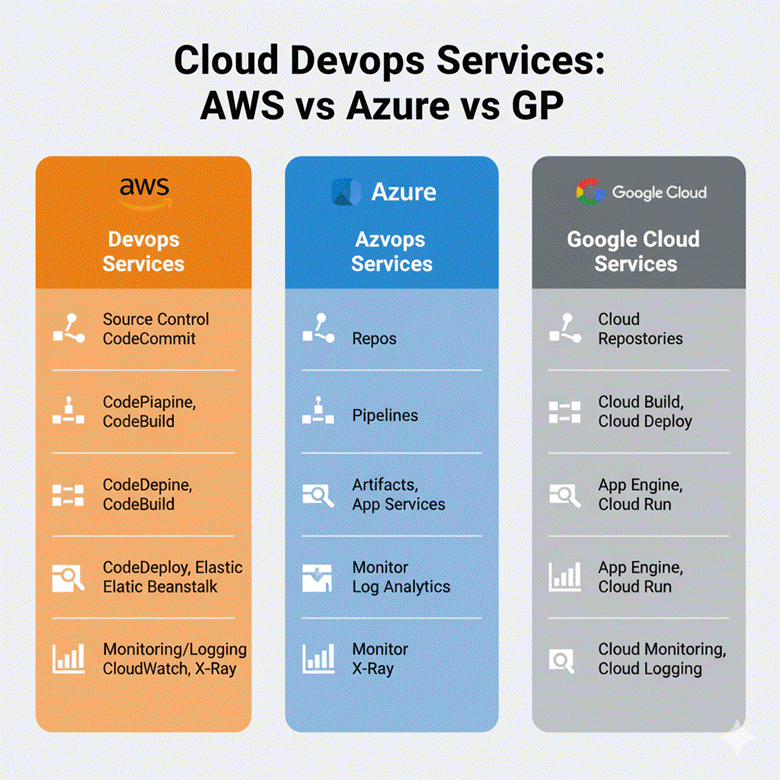
Comparative Table: AWS vs Azure vs GCP for DevOps
| Feature | AWS | Azure | GCP |
| Compute Services | EC2, ECS, EKS, Lambda | VMs, AKS, Azure Functions | Compute Engine, GKE, Cloud Functions |
| Storage | S3, EBS, EFS | Blob Storage, Disk Storage | Cloud Storage, Persistent Disk |
| CI/CD Tools | CodePipeline, CodeBuild, CodeDeploy | Azure DevOps, Pipelines | Cloud Build, Cloud Deploy |
| IaC Support | Terraform, CloudFormation | Terraform, ARM Templates | Terraform, Deployment Manager |
| Monitoring & Logging | CloudWatch, CloudTrail | Azure Monitor, Log Analytics | Stackdriver (Cloud Monitoring & Logging) |
| Security & IAM | IAM, KMS, GuardDuty | Azure AD, Key Vault, Security Center | IAM, KMS, Security Command Center |
| Serverless Support | Lambda | Azure Functions | Cloud Functions |
| Global Reach | 30+ regions | 60+ regions | 35+ regions |
Architecture Diagram: Multi-Cloud DevOps Workflow

DevOps Services on Each Cloud
1. AWS for DevOps
- CodePipeline & CodeBuild – Automate CI/CD pipelines.
- EKS & ECS – Managed Kubernetes and container orchestration.
- CloudFormation – IaC for infrastructure provisioning.
- CloudWatch & CloudTrail – Monitoring, logging, and auditing.
Best Practices:
- Use Lambda functions for serverless automation.
- Leverage auto-scaling groups for dynamic workloads.
- Combine Terraform + CloudFormation for hybrid IaC management.
2. Azure for DevOps
- Azure DevOps & Pipelines – End-to-end CI/CD automation.
- AKS – Managed Kubernetes service.
- ARM Templates & Terraform – Declarative infrastructure provisioning.
- Azure Monitor & Log Analytics – Centralized monitoring and logging.
Best Practices:
- Integrate Azure Functions for serverless automation.
- Use Azure Key Vault for secrets management.
- Utilize policy-as-code for governance.
3. GCP for DevOps
- Cloud Build & Cloud Deploy – CI/CD services for automated delivery.
- GKE – Google-managed Kubernetes orchestration.
- Deployment Manager & Terraform – Declarative infrastructure provisioning.
- Cloud Monitoring & Logging – Unified observability platform.
Best Practices:
- Use Cloud Functions for lightweight automation.
- Integrate Stackdriver alerts for proactive monitoring.
- Adopt IaC + containerization for scalable deployments.
- Integrate Stackdriver alerts for proactive monitoring.
- Adopt IaC + containerization for scalable deployments.
Challenges in Multi-Cloud DevOps
| Challenge | Solution |
| Tool Differences | Standardize CI/CD with Terraform and Jenkins across clouds |
| Security & Compliance | Implement unified IAM, encryption, and monitoring policies |
| Cost Management | Use budgeting, alerts, and auto-scaling policies |
| Observability | Centralize logs and metrics in Grafana/ELK for all clouds |
Practical Workflow Example
Scenario: Deploy a containerized microservice to AWS, Azure, and GCP simultaneously:
- Containerize Application – Docker image for microservice.
- Push to Container Registry – ECR (AWS), ACR (Azure), GCR (GCP).
- CI/CD Pipeline – Jenkins triggers deployments to all three clouds.
- IaC Provisioning – Terraform creates infrastructure in each cloud.
- Monitoring & Logging – Unified dashboards in Grafana using Prometheus + Cloud metrics.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners practice real multi-cloud deployments, mastering portability, scalability, and cross-platform observability.
Infographic Content:
Conclusion
Cloud platforms are the backbone of modern DevOps, providing automation, scalability, and flexibility. AWS, Azure, and GCP each offer robust services to implement CI/CD pipelines, monitoring, IaC, and serverless workflows. Understanding multi-cloud strategies allows DevOps engineers to deliver resilient, high-performance applications while optimizing costs and compliance.
At Curiosity Tech, learners are trained to leverage AWS, Azure, and GCP for end-to-end DevOps pipelines, gaining hands-on experience with multi-cloud deployments, monitoring, and automation—preparing them for enterprise-grade DevOps roles.



