Introduction
Building and training machine learning models is only part of the journey. Deploying ML models to production enables real-world applications such as recommendation systems, spam detection, and predictive analytics.
At CuriosityTech.in (Nagpur, Wardha Road, Gajanan Nagar), we emphasize hands-on deployment training. By integrating Flask and FastAPI, ML engineers can serve models as APIs, making them accessible to web and mobile applications.
1. Understanding Model Deployment
Definition: Deployment is the process of making a trained ML model available for real-time or batch predictions in production.
Benefits of Deployment:
- Real-time predictions for users or systems
- Integration with web and mobile applications
- Continuous monitoring and updates
- Scalable and reproducible solutions
CuriosityTech Insight: Many beginners build models but struggle with deployment. Deployment is mandatory for ML engineers who want to create end-to-end solutions.
2. Deployment Options
| Deployment Type | Description | Use Case |
| Local Deployment | Run on local machine | Testing and development |
| Cloud Deployment | AWS, GCP, Azure | Scalable production applications |
| Dockerized Deployment | Containerize models | Reproducibility and scalability |
| Microservices | Deploy as API | Integrate multiple models into applications |
3. Flask vs FastAPI
| Feature | Flask | FastAPI |
| Speed | Moderate | High (async support) |
| API Documentation | Manual | Automatic Swagger UI |
| Learning Curve | Beginner-friendly | Slightly advanced |
| Use Case | Small-scale projects | High-performance APIs, modern apps |
At CuriosityTech.in, learners often start with Flask for hands-on practice and then move to FastAPI for scalable and performant APIs.
4. Stepwise Deployment Workflow
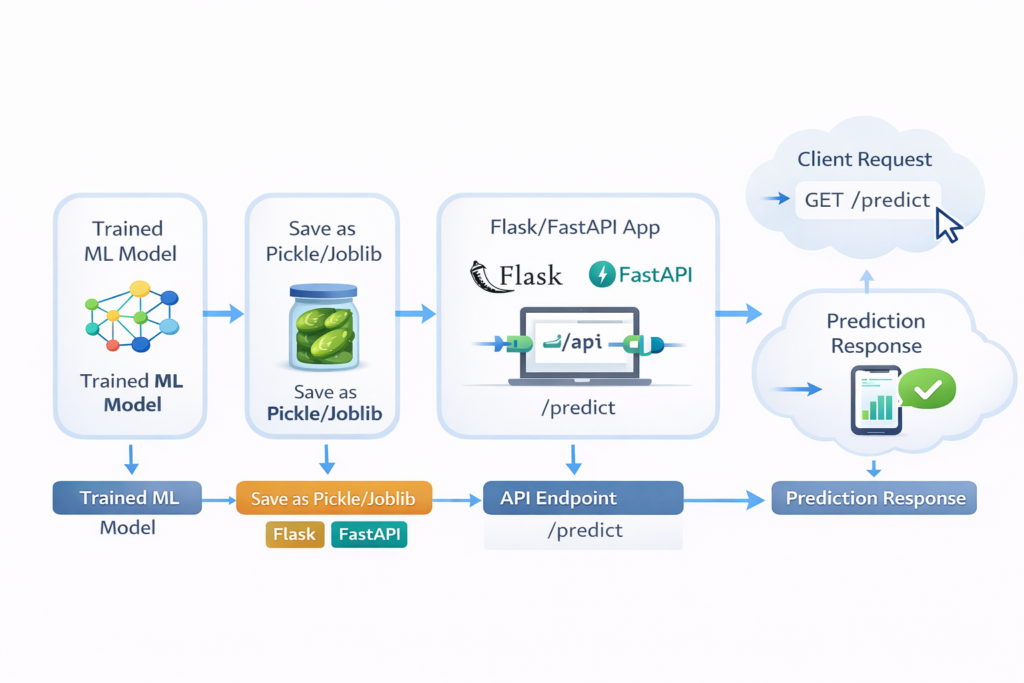
Diagram Description: Trained ML Model → Save as Pickle/Joblib → Flask/FastAPI App → API Endpoint → Client Request → Prediction Response
Workflow Stages:
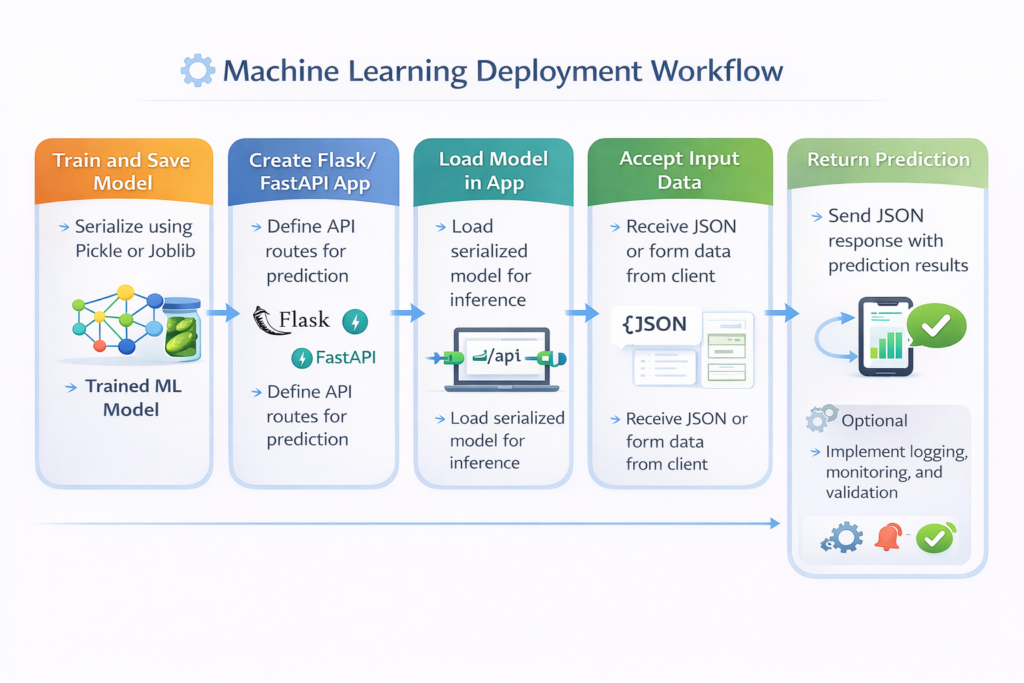
- Train and Save Model: Serialize using Pickle or Joblib
- Create Flask/FastAPI App: Define API routes for prediction
- Load Model in App: Load serialized model for inference
- Accept Input Data: Receive JSON or form data from client
- Return Prediction: Send JSON response with prediction results
- Optional: Implement logging, monitoring, and validation
5. Example: Deploying a Spam Detection Model
- Step 1: Save the Model
- import joblib
- joblib.dump(model, ‘spam_model.pkl’)
- Step 2: Create Flask App
- from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
- import joblib
- app = Flask(__name__)
- model = joblib.load(‘spam_model.pkl’)
- @app.route(‘/predict’, methods=[‘POST’])
- def predict():
- data = request.get_json()
- message = data[‘message’]
- vect = vectorizer.transform([message])
- prediction = model.predict(vect)[0]
- return jsonify({‘prediction’: prediction})
- if __name__ == ‘__main__’:
- app.run(debug=True)
- Step 3: Testing API
- Use Postman or curl to send POST requests
- Receive real-time predictions
Practical Insight: Riya at CuriosityTech Park deploys a spam detection API, demonstrating how users can access model predictions via a web interface.
6. FastAPI Deployment Advantages
- Asynchronous Endpoints: Handle multiple requests concurrently
- Automatic Documentation: Swagger UI and ReDoc
- Input Validation: Pydantic models ensure structured data
FastAPI Example Snippet:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
import joblib
app = FastAPI()
model = joblib.load(‘spam_model.pkl’)
class Message(BaseModel):
message: str
@app.post(“/predict/”)
def predict_spam(data: Message):
vect = vectorizer.transform([data.message])
prediction = model.predict(vect)[0]
return {“prediction”: prediction}
Students at CuriosityTech.in appreciate automatic documentation, which allows stakeholders to test APIs without writing additional code.
7. Deployment Best Practices
- Version Control Models: Track multiple versions using MLflow
- Input Validation: Prevent errors and malicious input
- Logging & Monitoring: Record requests and responses for analysis
- Dockerize Applications: Ensure reproducibility and easier scaling
- Continuous Integration (CI/CD): Automate deployment pipelines
Scenario Storytelling: Arjun implements a Dockerized FastAPI deployment of a recommendation system. The model serves thousands of requests per day, and automatic logging helps identify when retraining is needed.
8. Real-World Applications
| Application | Deployment Type | Example |
| Spam Detection | Flask API | Web and mobile apps |
| Sentiment Analysis | FastAPI + Docker | Social media analytics |
| Image Recognition | Cloud API | Healthcare imaging |
| Predictive Maintenance | Microservices | IoT sensor data |
| Recommendation Systems | Flask/FastAPI | E-commerce and streaming |
9. Key Takeaways
- Deployment makes ML models accessible and actionable
- Flask is easy for beginners, FastAPI is ideal for performance and scalability
- Automation, validation, logging, and monitoring are mandatory for production-ready systems
- Hands-on practice bridges the gap between training models and creating usable ML services
CuriosityTech.in trains learners in end-to-end ML model deployment, preparing them for real-world applications.
Conclusion
Deploying ML models with Flask and FastAPI equips ML engineers to turn models into usable services, accessible by web or mobile applications. Mastery of deployment ensures:
- Scalable production solutions
- Real-time predictions for users
- Smooth integration with enterprise systems
Contact CuriosityTech.in at +91-9860555369 or contact@curiositytech.in to learn hands-on deployment and API integration for ML projects.