When I began consulting nearly two decades ago, companies handled identity and access with just passwords and role-lists. In today’s 2025 landscape of hybrid cloud, remote work, and IoT, that old approach is obsolete. Attackers no longer just target your firewall—they target identities. If they steal an admin login or trick a user into approving a malicious session, they bypass all your security investments.
That’s why Identity & Access Management (IAM) is one of the most critical disciplines in cybersecurity today.
At CuriosityTech.in Nagpur, when training fresh engineers, we emphasize IAM not as “just user logins,” but as the security spine connecting every app, device, and system.
What is IAM?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is the framework of technologies and policies ensuring the right person or system has the right level of access to the right resources at the right time.
Think of it like airport security:
- Identity = passport & boarding pass check.
- Access = permission to enter only your assigned flight gate.
- IAM adds continuous checks to ensure no impostor sneaks in even after boarding.
IAM Core Principles
1. Authentication (Who are you?)
- Passwords, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), biometrics.
2. Authorization (What can you do?)
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC).
3. Accountability (What did you do?)
- Logging, auditing, compliance reporting.
4. Governance (Should you still have access?)
- Lifecycle management, periodic reviews.
IAM Visual Architecture
Architecture Diagram Description:
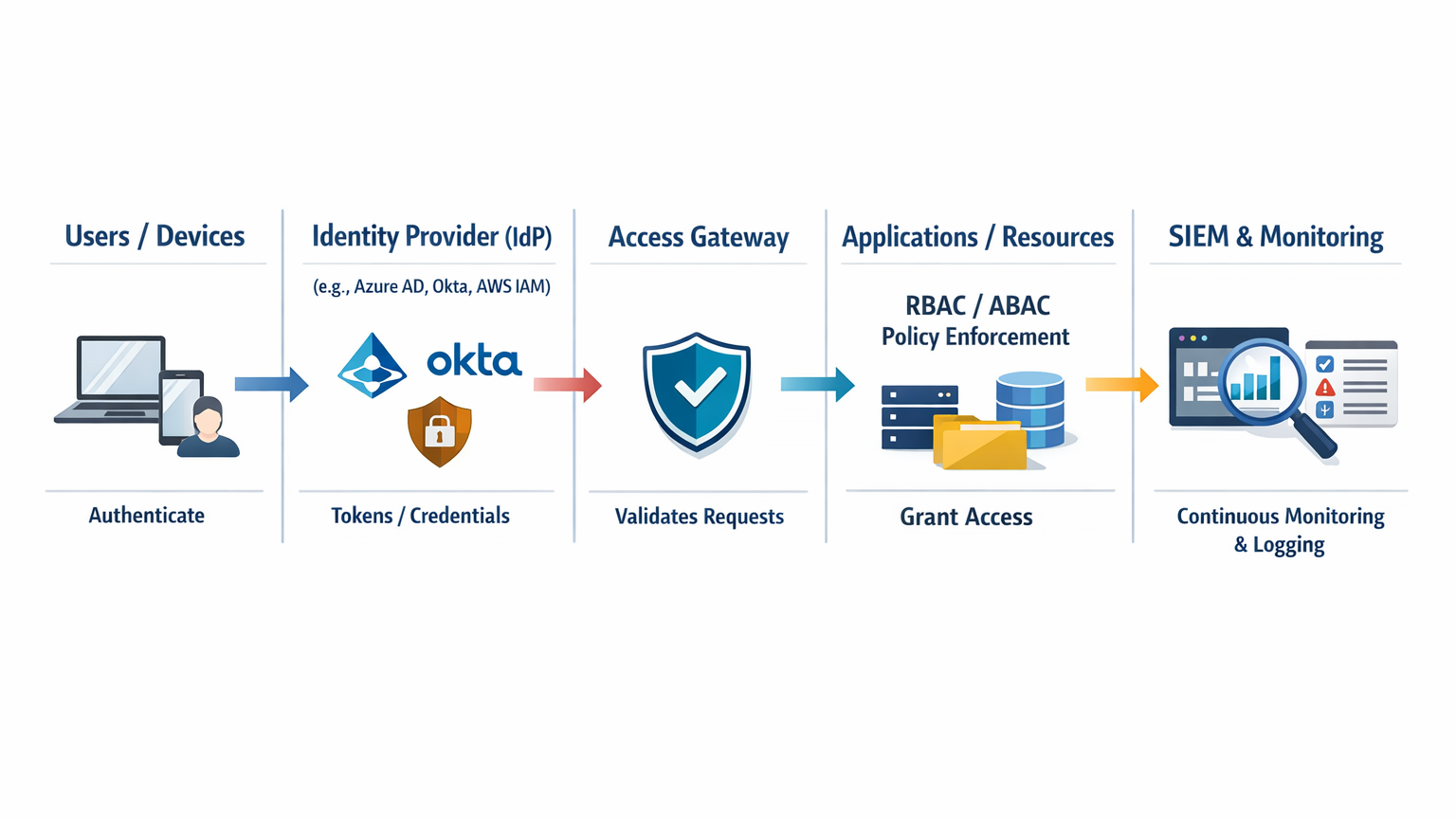
Users/Devices → Authenticate through Identity Provider (IdP) (e.g., Azure AD, Okta, AWS IAM). → IdP issues tokens/credentials. → Access Gateway validates requests. → Applications/Resources grant access based on RBAC/ABAC. → Continuous monitoring logs activities into SIEM.
This architecture shows IAM as the center hub controlling trust across cloud, apps, and devices.
IAM in the Zero Trust Model
In 2025, all major security frameworks endorse Zero Trust IAM.
Concept: Never trust; always verify.
- No user/device automatically trusted—even inside corporate LAN.
- Adaptive, continuous authentication (checking risk signals like device posture, location, behavior).
- Least privilege enforcement.
Zero Trust Workflow Example:
- User tries to access payroll app.
- IAM checks device posture (Is laptop patched?).
- Challenge with MFA if high risk (login from unusual location).
- Session monitored; abnormal behavior triggers re-authentication.
IAM Components Across Major Providers
| Provider | IAM System | Key Features |
| AWS | AWS IAM & IAM Identity Center | Fine-grained roles, temporary credentials, federated SSO. |
| Azure | Azure Active Directory (AAD) | Conditional access, MFA, identity governance, seamless Microsoft integration. |
| GCP | Google Cloud IAM & Identity-Aware Proxy | Role-granular controls, Zero Trust, service account governance. |
| Okta (3rd party) | Universal Identity Provider | Multi-cloud federated SSO, lifecycle management, adaptive MFA. |
Practical IAM Scenarios
Scenario 1: Stopping Lateral Movement
- Problem: Attacker compromises marketing user account.
- IAM Defense: Role-based access ensures no access to finance or HR systems.
- Outcome: Attack isolated, damage minimized.
Scenario 2: Cloud Console Protection
- Problem: Engineer’s laptop stolen with cached cloud console session.
- IAM Defense: Session expires quickly, requires MFA re-authentication.
- Outcome: Stolen laptop useless.
Scenario 3: Insider Misuse
- Problem: Employee downloads sensitive files before resigning.
- IAM Defense: Governance triggers role deactivation upon HR update, logs reviewed in SIEM.
- Outcome: Unauthorized access prevented in real time.
IAM Lab Exercises (CuriosityTech-Style Training)
- SSO Setup:- Connect a sample web app to Azure AD for Single Sign-On.
- MFA Enforcement :- Configure conditional policy to require OTP for logins outside India.
- RBAC Test :- Create roles for Developers vs HR team. Developers restricted from HR DB.
- Simulated Attack :- Run brute-force login attempt on a test system. Observe SIEM alert and MFA block.
Hands-on labs like this transform IAM from documents into lived defensive power.
Common IAM Mistakes
- Overusing admin accounts instead of enforcing least privilege.
- Relying on passwords only (phishing steals them easily).
- Not rotating API/service account keys in cloud.
- Failing to de-provision users after resignation.
- Storing credentials in code repositories (dangerously common).
Infographic Description
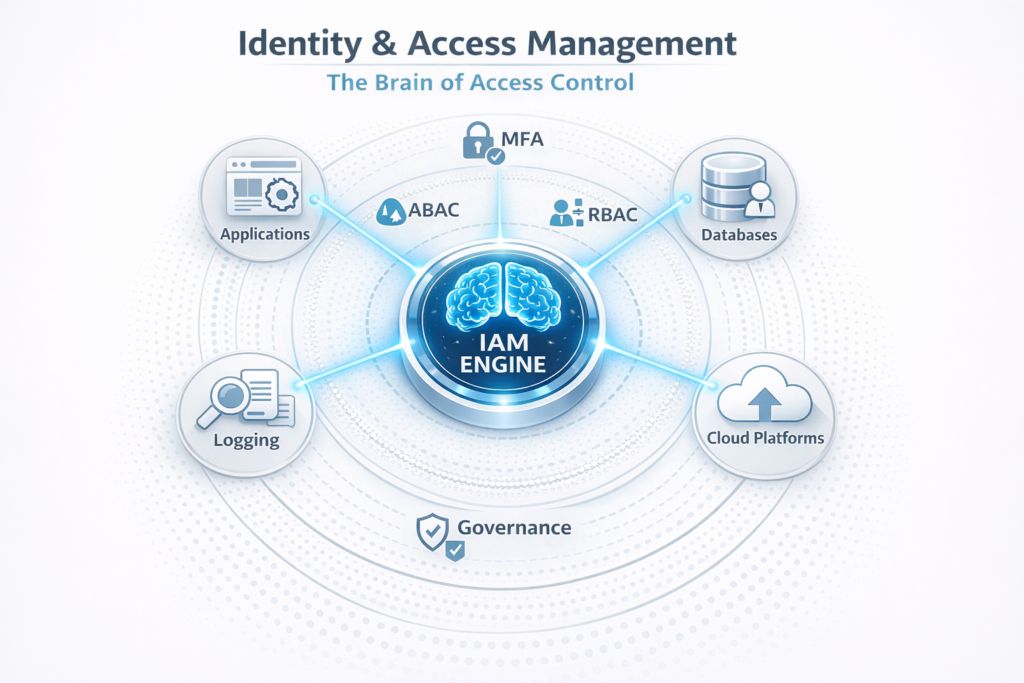
- Center hub = IAM Engine.
- Spokes = Applications, Databases, Cloud Platforms, Networks.
- Around hub, security layers: MFA, RBAC, ABAC, Logging, Governance.
Visual message: IAM is the brain of access control.
Personal Real-World Incident
One memorable 2020 case involved a retailer in central India. An attacker used stolen contractor credentials to access their cloud. But because IAM had conditional access enabled, the login attempt from Singapore triggered forced MFA. Since the attacker didn’t have the OTP, intrusion failed.
The company later told me: “That single OTP policy saved us millions.”
Conclusion
In 2025, IAM isn’t just another IT function—it’s the foundation of Zero Trust security. Engineers must master IAM workflows, policy design, and integrations across AWS, Azure, GCP, and third-party providers. A single misconfigured identity could mean the collapse of entire digital defenses.
At CuriosityTech.in (Address: Wardha Rd, Gajanan Nagar, Nagpur | Phone: +91-9860555369 | Email: contact@curiositytech.in | Instagram: @curiositytechpark | LinkedIn/Facebook: Curiosity Tech), our IAM labs train engineers to think in Zero Trust mode—never trust blindly, monitor continuously, and enforce access by design. Because when identities are armor, systems remain safe.
Tags
Identity and Access Management, IAM Explained 2025, Zero Trust Security, CuriosityTech Cyber Training
Keywords
IAM Basics 2025, Identity Access in Cybersecurity, Zero Trust Explained, IAM Lab Training Nagpur, CuriosityTech Training



