Introduction
Microservices architecture allows applications to be broken into smaller, independent services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled individually. .NET developers can leverage ASP.NET Core and Docker to build, containerize, and deploy microservices efficiently.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners gain practical knowledge of building scalable, containerized FullStack applications, ensuring they are industry-ready.
1. Understanding Microservices
Monolithic vs Microservices:
| Aspect | Monolithic | Microservices |
| Architecture | Single, large codebase | Independent, modular services |
| Deployment | Single deployment | Independent deployment per service |
| Scaling | Vertical | Horizontal (per service) |
| Technology Stack | Single | Multiple stacks per service |
Advantages of Microservices:
- Scalability of individual services
- Independent deployment and development
- Resilience and fault isolation
- Technology flexibility
Diagram: Microservices Architecture
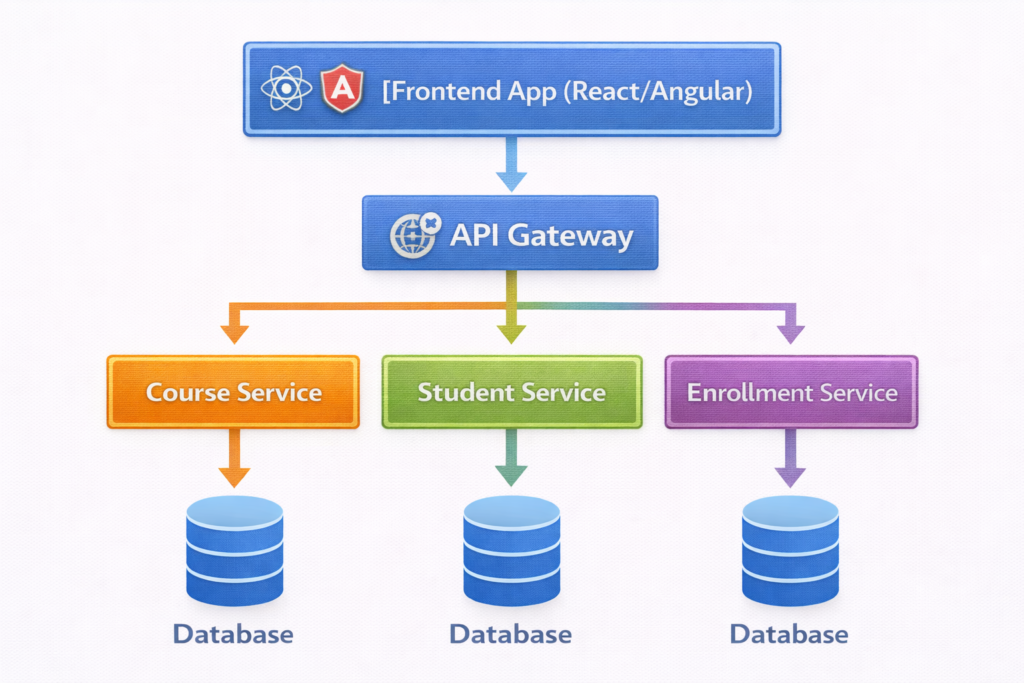
2. Creating a Simple Microservice in .NET
CourseService Example (ASP.NET Core Web API):
[ApiController]
[Route(“api/[controller]”)]
public class CoursesController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ICourseRepository _repository;
public CoursesController(ICourseRepository repository)
{
_repository = repository;
}
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult GetCourses() => Ok(_repository.GetAllCourses());
}
Key Points:
- Each microservice is self-contained
- Own database and API endpoints
- Can be tested and deployed independently
3. Dockerizing .NET Microservices
Dockerfile Example:
# Use official .NET SDK image for build
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/sdk:7.0 AS build
WORKDIR /app
# Copy csproj and restore as distinct layers
COPY *.csproj .
RUN dotnet restore
# Copy everything else and build
COPY . .
RUN dotnet publish -c Release -o out
# Runtime image
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/aspnet:7.0
WORKDIR /app
COPY –from=build /app/out .
ENTRYPOINT [“dotnet”, “CourseService.dll”]
Docker Commands:
# Build Docker image
docker build -t courseservice:latest .
# Run container
docker run -d -p 5001:80 courseservice:latest
4. Real-World Project: CuriosityTech Microservices Portal
Scenario: Split the course portal into microservices:
- CourseService – Handles course management
- StudentService – Manages student data
- EnrollmentService – Manages course enrollment
- API Gateway – Routes requests to appropriate services
- Database per service – Independent SQL Server or PostgreSQL
Benefits:
- Services can be scaled independently
- Faster development and deployment cycles
- Resilient architecture for high-traffic applications
Architecture Diagram:
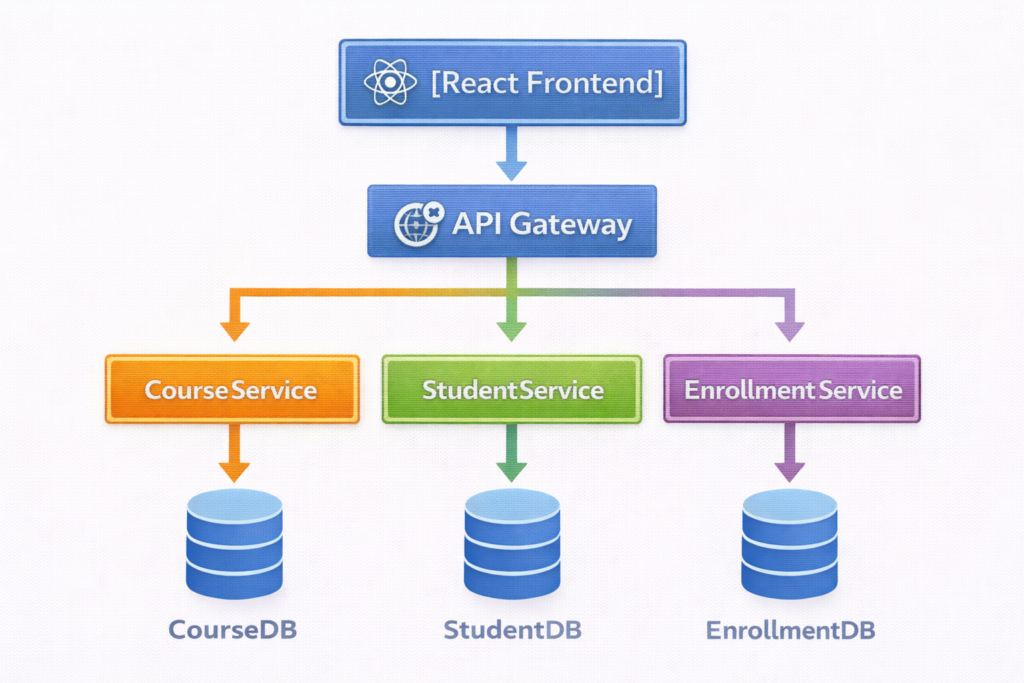
5. Best Practices
- Keep services small and focused
- Use API Gateway for routing, authentication, and logging
- Store state in databases, not in-memory
- Use Docker Compose for local development of multiple services
- Implement logging and monitoring per service
Docker Compose Example:
version: ‘3.8’
services:
courseservice:
build: ./CourseService
ports:
– “5001:80”
studentservice:
build: ./StudentService
ports:
– “5002:80”
enrollmentservice:
build: ./EnrollmentService
ports:
– “5003:80”
6. CuriosityTech.in Mentorship Insights
- Prepares learners for enterprise-level microservices development
Conclusion
Building microservices with .NET and Docker empowers developers to create scalable, independent, and resilient applications. At CuriosityTech.in, learners practice real-world microservices projects, learning containerization, deployment, and best practices that are highly demanded in the industry.
The next step is Day 18 – Securing .NET Applications: Identity, OAuth, and JWT, focusing on advanced security practices for microservices and APIs.