Introduction
Building a Python Full Stack application is one thing; ensuring it works correctly across all scenarios, devices, and users is another. This is where testing becomes crucial.
At Curiosity Tech, we teach that writing tests is not optional—it’s the backbone of professional software development. Testing helps identify bugs, improve reliability, and deliver robust applications that users trust.
In this blog, we’ll explore unit testing with Pytest and end-to-end testing with Selenium, showing how Python Full Stack developers can achieve comprehensive application quality.
Why Testing Matters
| Type of Testing | Purpose | Example |
| Unit Testing | Test individual functions or modules | Validate a function that calculates discounts |
| Integration Testing | Test interactions between modules/APIs | API response triggers correct DB update |
| End-to-End Testing | Test the entire workflow from frontend to DB | User logs in, adds item, checks out |
| Regression Testing | Ensure new changes don’t break existing code | Update a library, ensure forms still work |
Think of testing as insurance for your code—it prevents disasters in production.
Pytest – Unit and Integration Testing
Pytest is a powerful Python testing framework that makes writing tests easy and readable.
Example: Testing a Flask API Function
app.py
def calculate_discount(price, discount):
if discount > 100 or discount < 0:
raise ValueError(“Invalid discount”)
return price – (price * discount / 100)
test_app.py
import pytest
from app import calculate_discount
def test_discount_valid():
assert calculate_discount(1000, 10) == 900
def test_discount_zero():
assert calculate_discount(500, 0) == 500
def test_discount_invalid():
with pytest.raises(ValueError):
calculate_discount(100, -5)
- Run tests with:
pytest test_app.py
Benefits: Quick feedback, automation, and confidence in code changes.
Selenium – End-to-End Testing
While Pytest validates backend logic, Selenium automates browser interactions to ensure the frontend works correctly.
Example: Selenium Test for Login Page
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.get(“http://localhost:5000/login”)
# Enter credentials
driver.find_element(By.NAME, “username”).send_keys(“admin”)
driver.find_element(By.NAME, “password”).send_keys(“password123”)
driver.find_element(By.ID, “login-btn”).click()
# Assert dashboard loads
assert “Dashboard” in driver.title
driver.quit()
- Automates login flow, checks page title, ensures frontend functionality.
- Can be integrated with CI/CD pipelines for continuous testing.
Combining Pytest & Selenium in Full Stack Workflow
- Backend Unit Tests: Pytest validates API endpoints, business logic, and database interactions.
- Frontend End-to-End Tests: Selenium ensures forms, buttons, navigation, and dynamic content work as expected.
- CI/CD Integration: Tests run automatically on GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Jenkins whenever code is pushed.
Hierarchical Diagram Idea:
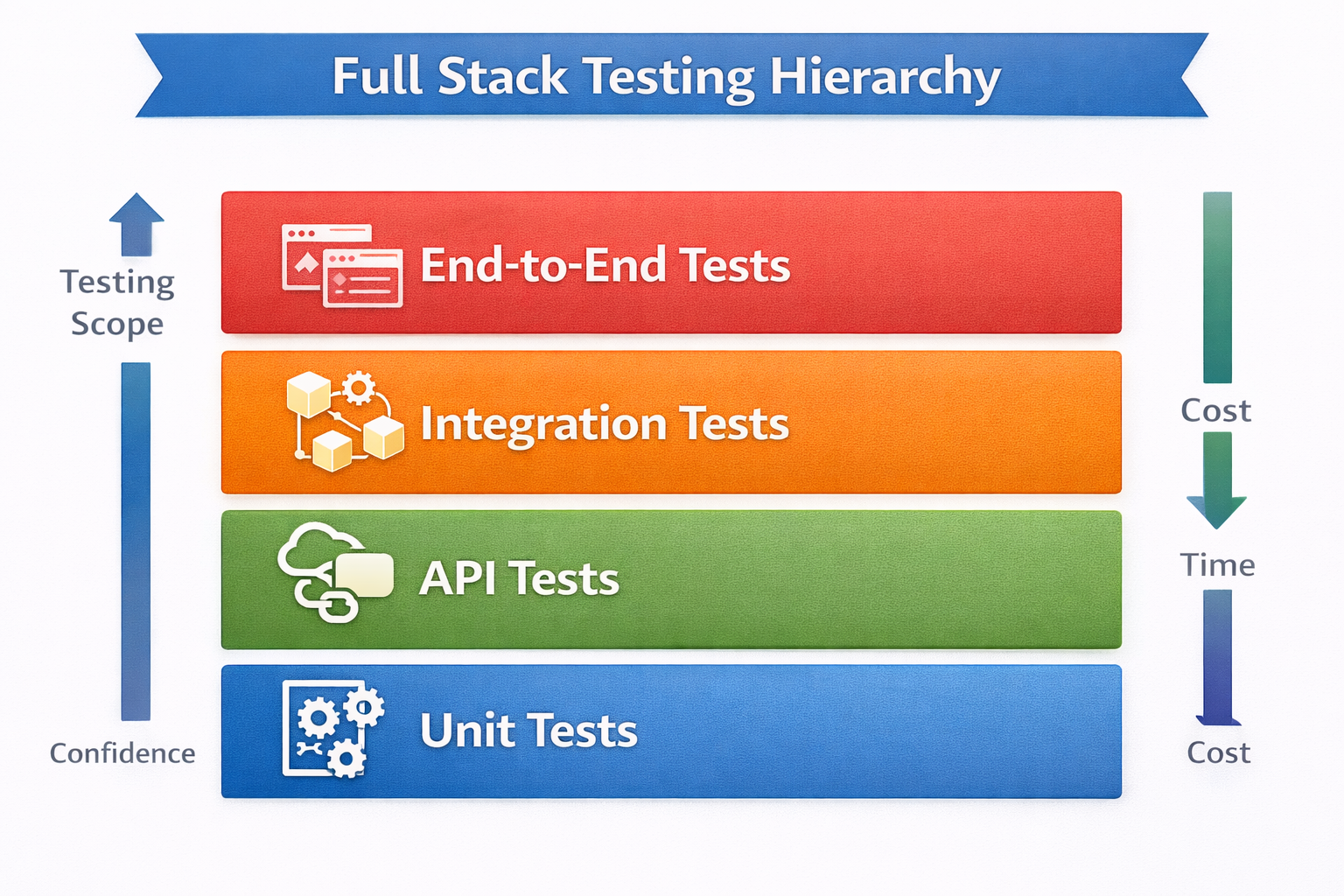
Best Practices for Testing
- Write tests early – Test-driven development (TDD) improves code quality.
- Keep tests independent – Avoid shared state between tests.
- Mock external APIs – Ensure tests are reliable and not dependent on external services.
- Use fixtures in Pytest for reusable setup.
- Automate test execution in CI/CD pipelines.
Real-World Project – CuriosityTech Example
At CuriosityTech, students built a Python Full Stack e-commerce application:
- Backend: Django REST Framework
- Frontend: React SPA
- Testing:
- Pytest tested product CRUD, authentication and API endpoint.
- Selenium automated user flows like login, cart addition and checkout.
- Outcome: Students could deploy confidently, knowing their app passed both unit and end-to-end tests
Infographic Idea – “Full Stack Testing Layers”
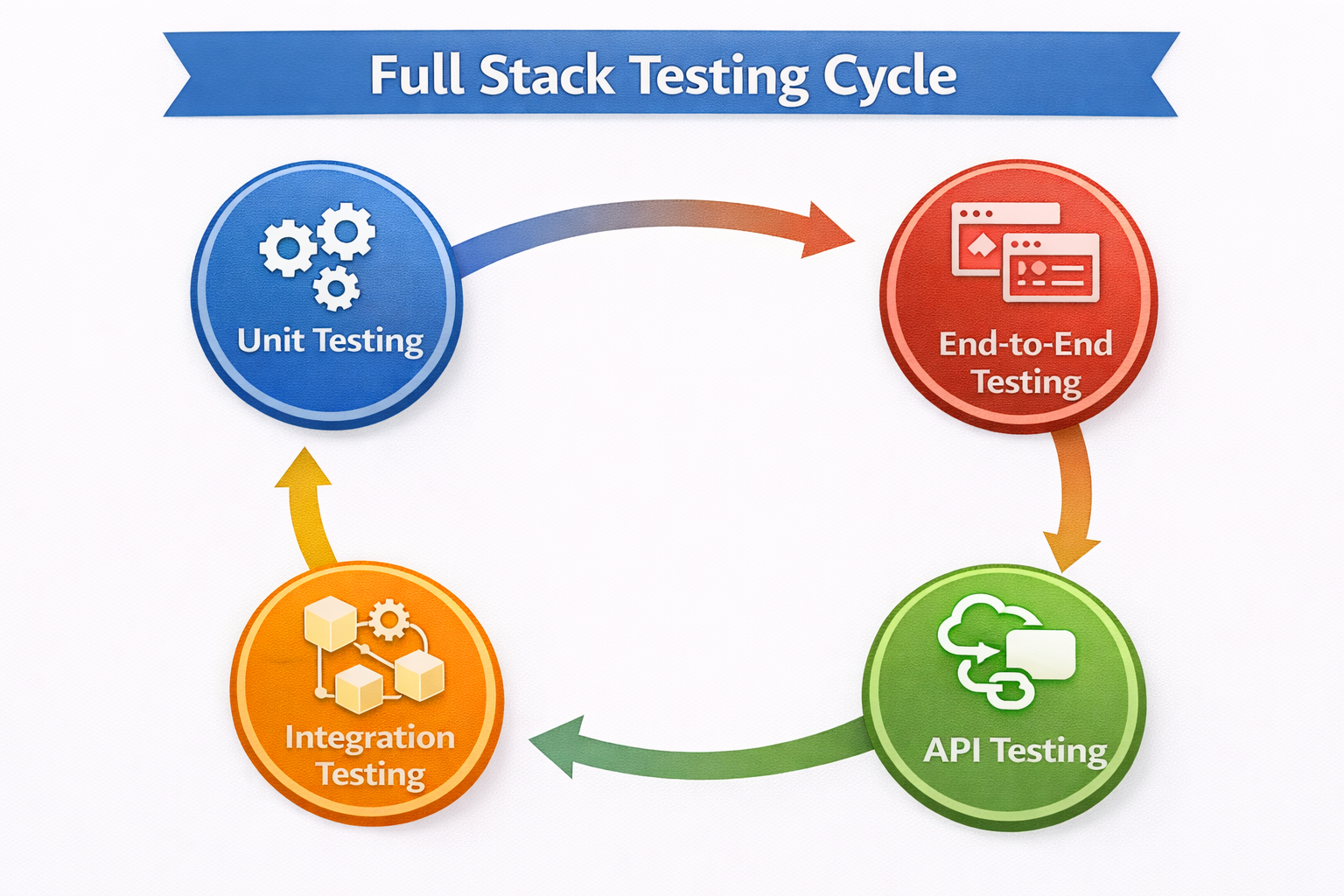
Each layer ensures robust application reliability, reducing bugs and downtime.
Conclusion
Testing is the unsung hero of Full Stack development. With Pytest for backend logic and Selenium for frontend workflows, Python developers can deliver stable, high-quality, and user-friendly applications.
At Curiosity Tech, students are trained to implement complete testing strategies, ensuring they don’t just build applications—they build trustworthy, production-ready software.



