Introduction
When Netflix, Uber, or a bank suffers downtime, millions of users feel it instantly. In a world where digital services = lifelines, High Availability (HA) is no longer optional — it’s the baseline.
In single-cloud, HA is about zones and regions. But in multi-cloud, HA becomes a survival strategy:
- If AWS goes down, workloads failover to Azure.
- If Azure suffers an outage, GCP takes over.
- Users barely notice — business continues.
At CuriosityTech.in, we emphasize that HA in multi-cloud is not magic — it’s engineering discipline plus strategic planning.
Section 1 – The Pillars of High Availability
- Redundancy → Multiple instances/resources.
- Resilience → Survive failures without downtime.
- Recovery → Automated failover, not manual firefighting.
- Monitoring → Detect failures quickly.
- Testing → Chaos engineering to validate plans.
Section 2 – HA Levels in Multi-Cloud
Think of HA like layers of armor:
| Level | Description | Example in Multi-Cloud |
| Application-Level HA | Redundant instances, load balancing | Kubernetes clusters spanning AWS + GCP |
| Data-Level HA | Replication across DBs/clouds | AWS RDS → GCP Cloud SQL replica |
| Network-Level HA | Multi-cloud routing | BGP peering between Azure & AWS |
| Global HA | Cross-cloud failover policies | Traffic Director (GCP) + Route 53 (AWS) |
A true HA plan covers all levels, not just one.
Section 3 – Failover Strategies
1. Active-Passive
- One cloud runs workload.
- Another cloud is “warm” or “cold” standby.
- Failover only when primary fails.
- Pros: Cheaper, simple.
- Cons: Longer recovery (RTO higher).
2. Active-Active
- Workload runs simultaneously in multiple clouds.
- Load balancers route traffic across clouds.
- Pros: Low downtime, high performance.
- Cons: Expensive, complex synchronization.
3. Pilot Light
- Minimal copy (skeleton infra) in secondary cloud.
- Quickly scaled during outage.
- Pros: Cost-efficient middle ground.
- Cons: Some downtime during scale-up
4. Geo-Distributed HA
- Workloads split by geography (e.g., Asia → GCP, US → AWS).
- Acts as HA + performance optimization.
Section 4 – Multi-Cloud Failover Blueprint
Visual Diagram (Described):
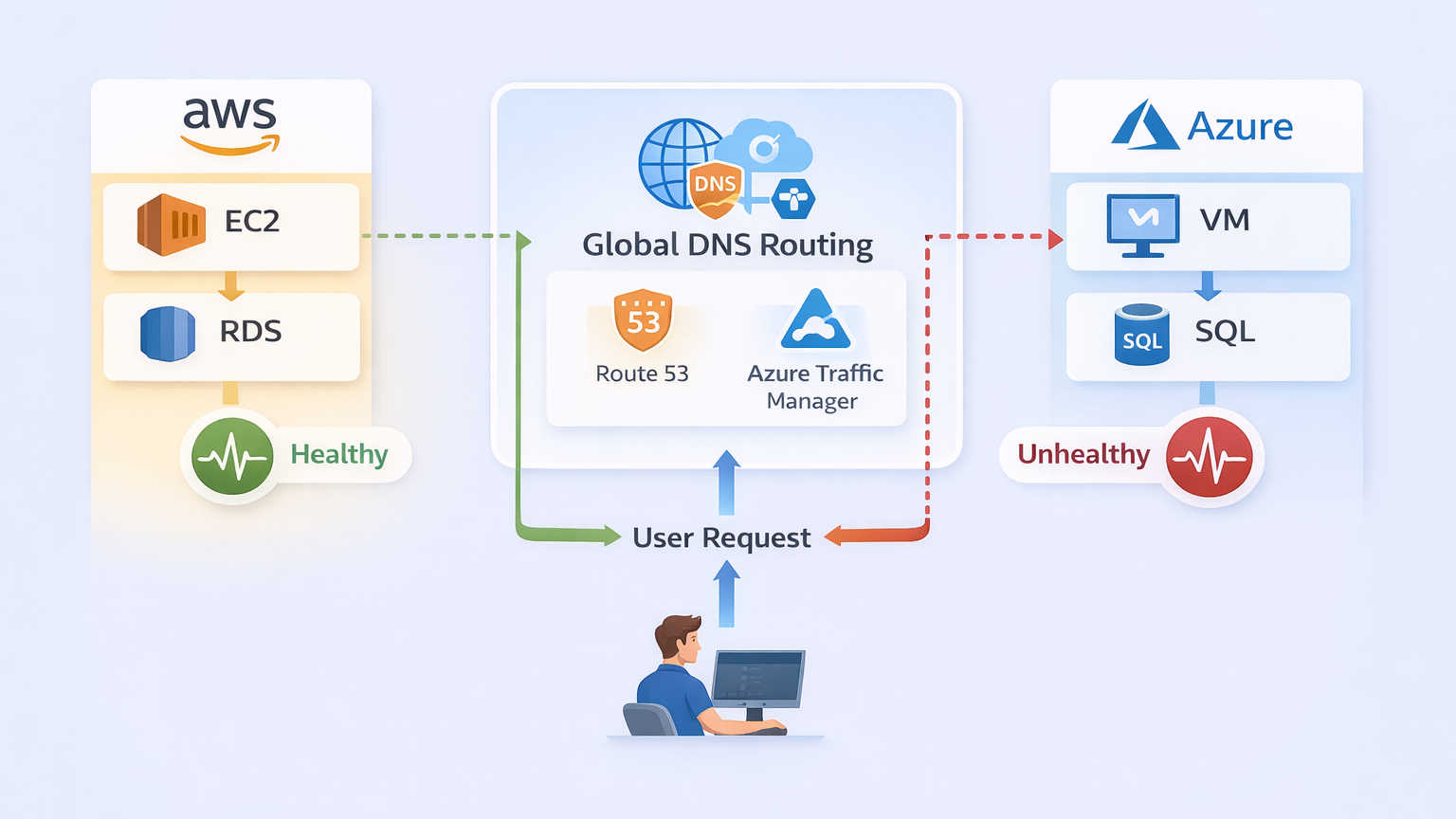
- Left: AWS (EC2 + RDS)
- Right: Azure (VM + SQL)
- Center: Global DNS (Route 53 + Azure Traffic Manager).
- Flow: User request → DNS → AWS (if healthy) → else route to Azure.
This represents DNS-based multi-cloud failover — the simplest and most common design.
Section 5 – Tools & Services for HA
| Cloud | HA Services | Failover Tools |
| AWS | Route 53, Global Accelerator, RDS Multi-AZ | Elastic Disaster Recovery |
| Azure | Traffic Manager, Front Door, Availability Sets | Azure Site Recovery |
| GCP | Cloud DNS, Global Load Balancer, Spanner | Backup & DR Service |
Many enterprises use third-party multi-cloud DNS/load balancers like Cloudflare, F5, or Akamai for neutral failover control.
Section 6 – Data Replication Approaches
- Synchronous Replication → Zero data loss (RPO=0), but high latency.
- Asynchronous Replication → Low latency, but risk of minor data loss.
- Hybrid Replication → Mix: critical tables synchronous, analytics asynchronous.
At CuriosityTech labs, learners configure PostgreSQL replication across AWS and GCP, practicing both modes.
Section 7 – Testing HA with Chaos Engineering
Theory is useless unless tested.
- Simulate AWS region outage → validate Azure failover.
- Cut network links → test rerouting.
- Kill database nodes → check replication.
Inspired by Netflix’s Chaos Monkey, CuriosityTech trains engineers to break things on purpose and validate resilience.
Section 8 – Case Example
Banking App (CuriosityTech Scenario):
- Primary: AWS (EC2, RDS).
- Secondary: Azure (VM, SQL).
- Failover via Route 53 health checks.
- Database replication async (5 sec lag).
- Chaos drill: Disable AWS region → Azure takes over in 60 seconds.
Result: Customers continue transactions with minimal disruption.
Section 9 – Becoming an Expert in HA & Failover
An expert cloud engineer:
- Designs multi-layer HA (app, data, network).
- Chooses failover model (active-active, pilot light).
- Practices disaster drills regularly.
- Balances cost vs resilience for business needs.
At CuriosityTech.in Nagpur center, HA capstone projects involve building active-active web apps across AWS and GCP, with DNS-based traffic failover.
Conclusion
Multi-cloud HA is not about avoiding downtime entirely — it’s about engineering for graceful failure. With redundancy, replication, failover, and chaos testing, organizations can transform outages into non-events for users, At CuriosityTech, we teach that HA is less about tools and more about discipline, testing, and foresight.
Tags: Multi-Cloud High Availability, Failover Strategies, Resilience Engineering, CuriosityTech Training
Keywords: Multi-Cloud HA Failover, AWS Azure GCP Resilience, CuriosityTech Resilience Training, Active-Active Multi-Cloud