On Day 19, we explore AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), a fully managed service that simplifies deploying, managing, and scaling containerized applications using Kubernetes.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners understand that mastering container orchestration is critical for modern cloud-native applications, enabling scalability, automation, and resilience.
1. What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes (K8s) is an open-source platform for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Key Concepts:
- Pods: Smallest deployable unit, can contain one or more containers
- Deployments: Define desired state of pods
- Services: Expose pods internally or externally
- Namespaces: Logical grouping of resources
- ConfigMaps & Secrets: Store configuration and sensitive data
CuriosityTech.in Insight: Kubernetes is a complex but powerful system, and EKS abstracts much of the control plane management, allowing beginners to focus on application orchestration.
2. What is AWS EKS?
AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) is a fully managed Kubernetes service:
- AWS manages the control plane, including API servers and etcd database
- Users manage worker nodes (EC2 or Fargate)
- Fully integrated with IAM, VPC, CloudWatch, and ELB
- Supports auto-scaling, rolling updates, and high availability
Analogy: EKS is like having a pre-configured command center, where you control the operations, while AWS handles maintenance, security patches, and uptime.
3. EKS Architecture Diagram
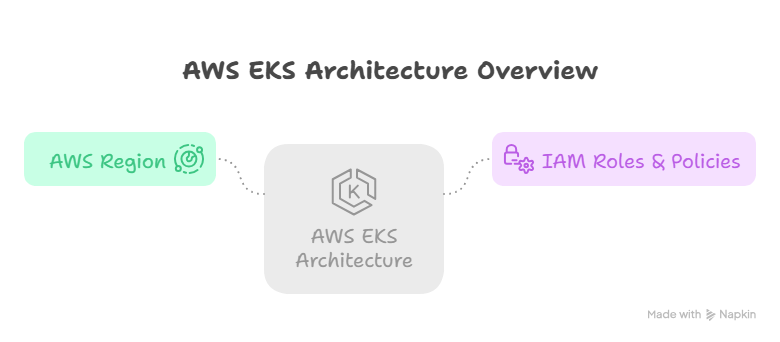
Explanation:
- Control plane is fully managed and spans multiple AZs
- Worker nodes run in private subnets for security
- ELB distributes traffic to pods
- IAM roles integrate with Kubernetes RBAC for fine-grained access control
4. Core EKS Components
| Component | Description | AWS Integration |
| Control Plane | API server, etcd, scheduler | Managed by AWS |
| Worker Nodes | EC2 instances / Fargate | Runs pods and containers |
| Kubelet | Node agent | Communicates with control plane |
| Kube-Proxy | Networking | Maintains network rules and load balancing |
| Cluster Autoscaler | Scaling | Adds/removes nodes automatically |
| IAM for Service Accounts (IRSA) | Security | Fine-grained pod-level permissions |
5. Step-by-Step Lab: Deploying an Application on EKS
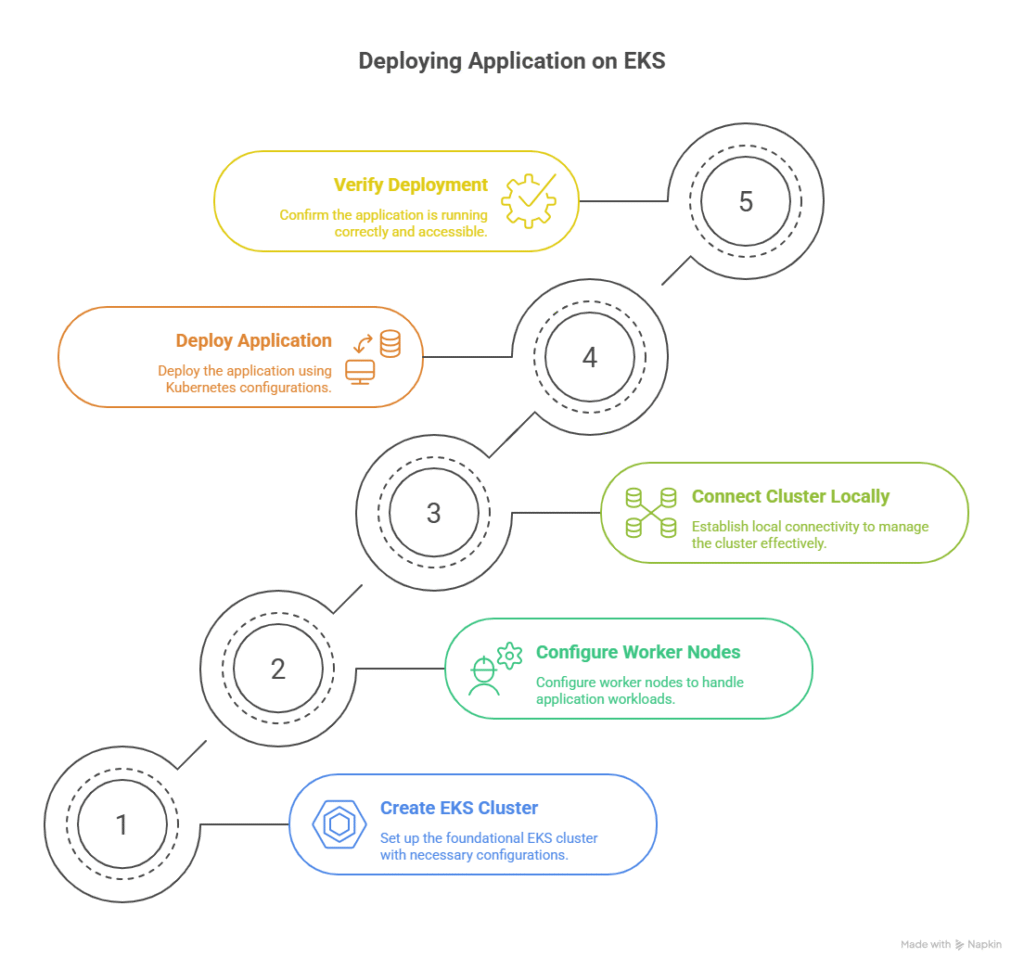
CuriosityTech.in Insight: Hands-on labs allow learners to understand pod scheduling, scaling, and service exposure in real Kubernetes clusters.
6. Scaling & High Availability
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA): Automatically scales pods based on CPU/memory usage
- Cluster Autoscaler: Adds/removes worker nodes automatically
- Multi-AZ Deployment: Ensures pods run across multiple AZs for fault tolerance
7. Security Best Practices
| Practice | Reason |
| Use IAM Roles for Service Accounts (IRSA) | Fine-grained pod permissions |
| Enable Private Endpoints for control plane | Restrict public access |
| Network policies | Control pod-to-pod communication |
| Kubernetes RBAC | Assign roles based on least privilege |
| Encrypt secrets using AWS KMS | Protect sensitive data |
8. Common Beginner Mistakes
- Deploying all pods in one AZ → single point of failure
- Not configuring worker node IAM roles → pod failures
- Using default Kubernetes namespaces for all apps → difficult resource isolation
- Ignoring auto-scaling → underutilized or overloaded nodes
- Not monitoring cluster with CloudWatch Container Insights → missed performance issues
9. Path to Expertise
- Start with single cluster, small applications
- Explore deployment, service, and pod scaling
- Use auto-scaling, managed node groups, and multi-AZ setups
- Implement security best practices with IRSA and network policies
- Integrate CI/CD pipelines for automated container deployment
At CuriosityTech.in, learners gain hands-on EKS experience, mastering container orchestration, scaling, and secure deployment, preparing them for cloud-native application engineering roles.
Conclusion
AWS EKS simplifies Kubernetes management, allowing cloud engineers to focus on application deployment and scaling while AWS handles control plane operations.
Through CuriosityTech.in practical labs, learners understand container orchestration, HA design, scaling, and security, becoming proficient in deploying modern cloud-native applications in production-ready environments.