In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations are constantly seeking methodologies to improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and accelerate delivery. But choosing the right approach—whether DevOps, Agile, or Traditional IT—can be daunting. Each methodology comes with its own philosophy, processes, and tools. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses and IT professionals alike.
At Curiosity Tech, we’ve helped countless organizations navigate these transitions, blending technology expertise with strategic guidance to drive innovation and operational excellence.
Understanding Traditional IT
Traditional IT, often referred to as the Waterfall model, is the legacy approach that has been dominant for decades.
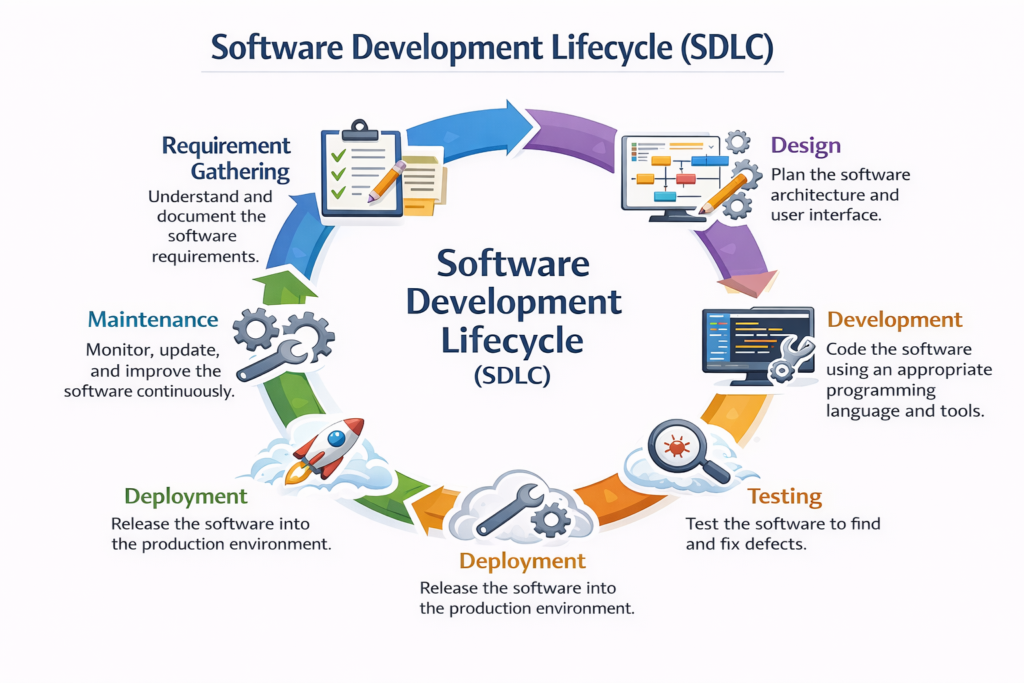
It follows a sequential process: requirement gathering → design → development → testing → deployment → maintenance.
Key Features:
- Linear Process: Each phase must be completed before the next begins.
- Rigid Planning: Changes mid-project are difficult and costly.
- Siloed Teams: Development, operations, and QA often operate independently.
While this approach has been reliable for structured projects, it struggles to accommodate rapid changes or iterative development. At Curiosity Tech, we observe that enterprises relying solely on traditional IT often face delays in responding to market demands, highlighting the need for more adaptive methodologies.
The Agile Approach
Agile emerged as a response to the rigidity of traditional IT. It emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer-centric development. Agile divides projects into small, manageable units called sprints, usually lasting 2–4 weeks.
Key Features:
- Iterative Development: Continuous feedback and improvements.
- Collaborative Teams: Developers, QA, and stakeholders work closely.
- Adaptive to Change: Agile welcomes changing requirements even late in the process.
Agile is widely used in software development but has applications across industries. For example, Curiosity Tech leverages Agile principles in client projects, ensuring faster delivery cycles and higher customer satisfaction.
DevOps – Bridging Development and Operations
DevOps takes Agile a step further by integrating development (Dev) and operations (Ops) to create a seamless, automated workflow. The goal is to reduce the time between code development and deployment while maintaining high quality.
Key Features:
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Automated testing and deployment pipelines.
- Collaboration Across Teams: Breaks down silos between developers and IT operations.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Automates environment provisioning, increasing scalability and reliability.
Unlike Agile, which focuses mainly on iterative development, DevOps emphasizes end-to-end delivery, ensuring applications run smoothly from development to production.
DevOps vs Agile vs Traditional IT – A Comparative Table
| Feature/Methodology | Traditional IT | Agile | DevOps |
| Approach | Sequential | Iterative & Incremental | Continuous & Collaborative |
| Flexibility | Low | High | Very High |
| Team Collaboration | Siloed | Cross-functional | Integrated Dev + Ops Teams |
| Delivery Cycle | Long | Short | Very Short (CI/CD) |
| Response to Change | Difficult | Adaptive | Rapid & Automated |
| Tooling | Manual Processes | Agile Tools (Jira, Trello) | Automation Tools (Jenkins, Ansible, Docker) |
| Best For | Stable, well-defined projects | Projects requiring flexibility | Fast-paced, scalable deployments |
This table clearly illustrates why modern organizations, including Curiosity Tech, often combine Agile and DevOps practices to accelerate innovation while maintaining stability.
Infographic Suggestion

Real-World Implications
Transitioning from Traditional IT to Agile or DevOps is more than adopting new tools—it’s a cultural shift. Organizations need leadership buy-in, training programs, and a mindset that embraces experimentation, collaboration, and accountability.
At Curiosity Tech, we’ve seen companies cut release cycles from months to weeks by embracing Agile and DevOps principles. Our expert team ensures that the adoption process is smooth, minimizing resistance while maximizing efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between Traditional IT, Agile, and DevOps is essential for modern businesses. While Traditional IT provides structure, Agile introduces flexibility, and DevOps ensures rapid, continuous delivery. Choosing the right approach—or a hybrid strategy—can significantly impact efficiency, collaboration, and customer satisfaction.
Organizations aiming to stay competitive in the fast-paced tech landscape must embrace modern practices while learning from traditional foundations. With the guidance of experts like Curiosity Tech, companies can navigate this journey seamlessly, achieving both speed and quality in their digital transformation efforts.



