Introduction
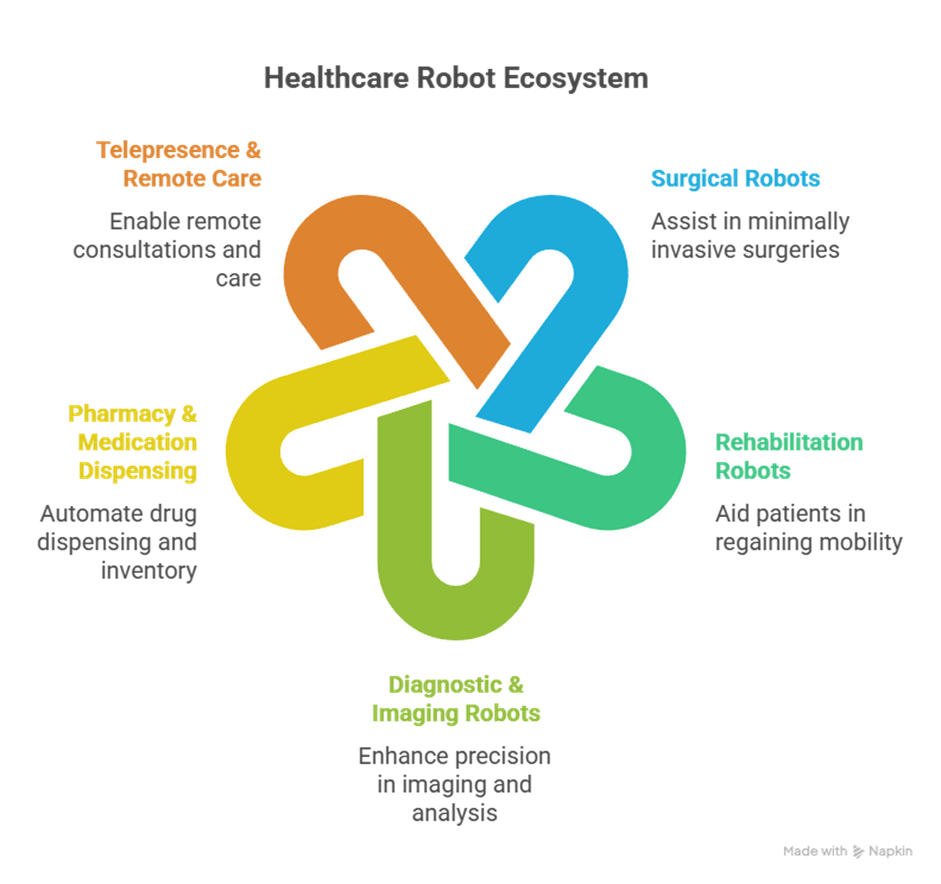
Robotics in healthcare has redefined patient care, surgical precision, and operational efficiency. From robotic-assisted surgeries to rehabilitation robots and pharmacy automation, robots enhance accuracy, reduce human errors, and improve patient outcomes.
At Curiosity Tech, learners explore real-world healthcare robotics systems, surgical workflows, and project-based learning to understand how robotic technologies integrate into clinical environments.
1. Applications of Robotics in Healthcare
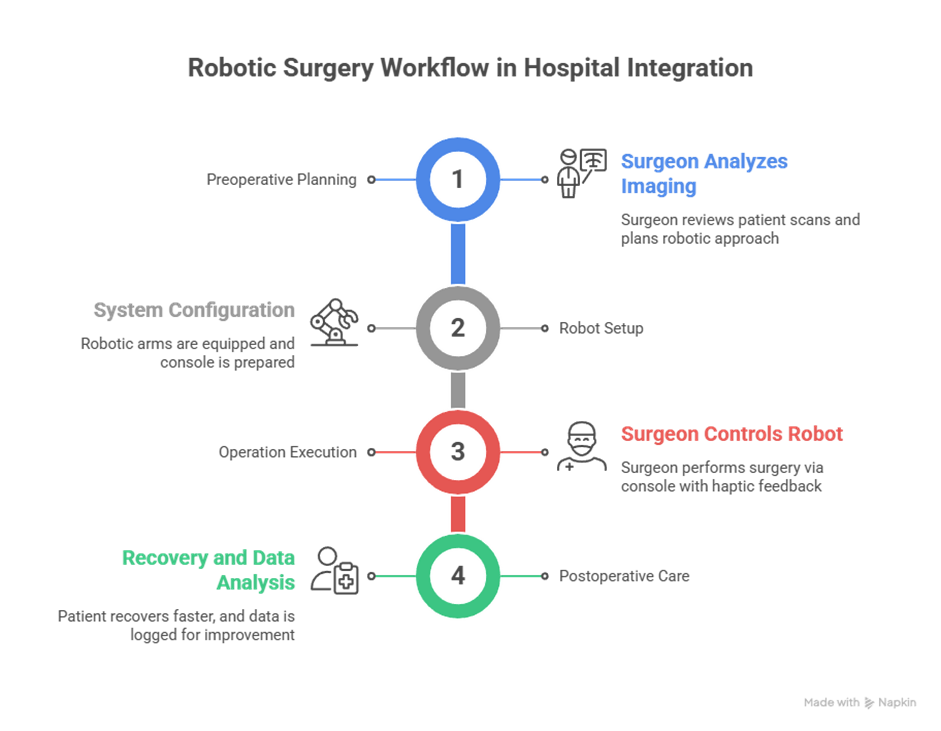
2. Case Study: Robotic-Assisted Surgery
3. Rehabilitation & Assistive Robotics
Applications:
- Exoskeletons: Aid mobility for paraplegic or post-stroke patients.
- Gait Trainers: Robots assist in physical therapy for walking rehabilitation.
- Assistive Robots: Help patients with daily tasks such as feeding or mobility.
- Key Features:
- Sensor-based feedback to adjust movement.
- Adaptive control for individual patient needs.
- Data collection for therapy progress monitoring.
- Table: Popular Rehabilitation Robots
| Robot Name | Function | Key Advantage |
| ReWalk Exoskeleton | Enables walking | Adjustable for patient height |
| Lokomat | Gait training | Interactive feedback control |
| iArm Assistive | Daily task support | Reduces caregiver dependency |
4. Telepresence & Remote Healthcare Robotics
- Telepresence robots allow doctors to consult patients remotely.
- Used in hospitals, elder care homes, and quarantine scenarios.
- Features include HD cameras, microphones, mobility control, and patient monitoring sensors.
Practical Example: Remote robotic consultation for COVID-19 patients in isolation wards, reducing infection risk for healthcare staff.
5. Robotics in Diagnostics
- Robotic imaging systems enhance precision in MRI, CT, and X-ray procedures.
- Robots ensure exact positioning of patients, reducing repeated scans and exposure to radiation.
- AI integration allows automated anomaly detection in imaging data.
6. Advantages of Robotics in Healthcare
- Precision & Accuracy: Reduces surgical errors and enhances treatment outcomes.
- Efficiency: Faster procedures, optimized workflows, and reduced recovery times.
- Safety: Minimally invasive surgery reduces infection risk.
- Accessibility: Telepresence extends healthcare access to remote areas.
- Data & Analytics: Robots log operation and therapy data for continuous improvement.
7. Challenges in Healthcare Robotics
- High cost of acquisition and maintenance.
- Training healthcare professionals for robot-assisted procedures.
- Regulatory approvals and compliance with medical standards.
- Integration with existing hospital IT infrastructure.
Tip: Hospitals often implement hybrid teams combining human expertise with robotic precision for optimal results.
8. Learning Robotics for Healthcare
- Study robotic anatomy, kinematics and surgical workflow.
- Gain expertise in robotic control systems, sensors and AI integration.
- Explore simulation platforms for surgical and rehabilitation robots.
- Understand medical safety regulations and standards (FDA, ISO 13485).
- Work on project-based learning to implement real-world robotic solutions.
CuriosityTech.in provides tutorials on medical robotics simulation, AI-assisted surgery workflows, and project guides for hands-on experience.
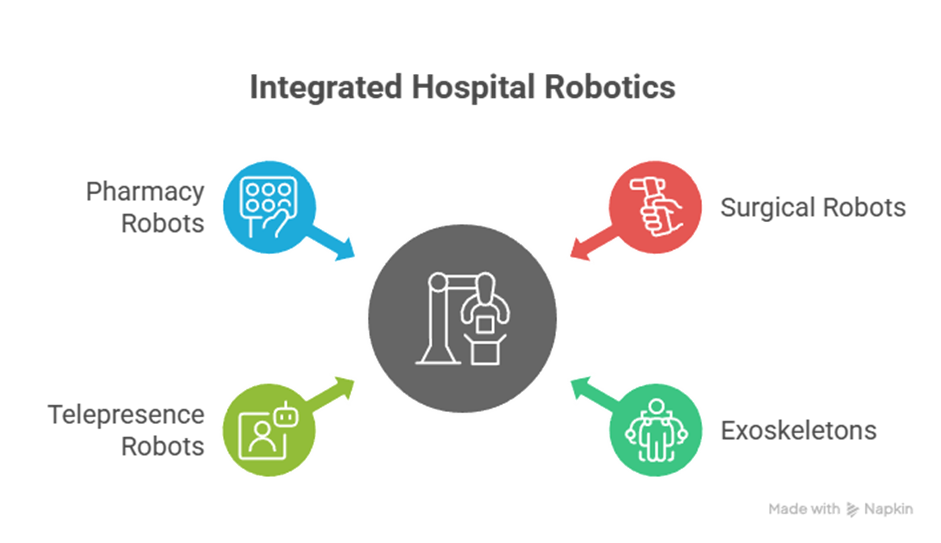
9. Real-World Example: Hospital Robotics Integration
Conclusion
Robotics in healthcare is transforming the medical field by improving precision, patient care, and operational efficiency. By mastering robotics applications in surgery, rehabilitation, diagnostics, and telepresence, engineers can develop innovative solutions that save lives and improve patient outcomes. Platforms like CuriosityTech.in provide project-based tutorials, real-world case studies, and simulation exercises to bridge theory and practical healthcare robotics.