In the evolving world of web development, frontend security is often overlooked. Developers focus on UI/UX, performance, and responsiveness—but a website that looks amazing can still be dangerously vulnerable. For businesses and developers alike, understanding frontend security threats and proactively protecting against them is crucial. At CuriosityTech.in, we emphasize not just creating beautiful interfaces, but also building secure, trustworthy web experiences.
Why Frontend Security Matters
Frontend security ensures that user data and client interactions remain safe. Unlike backend security, which focuses on databases and servers, frontend security tackles vulnerabilities that happen in the browser, on user inputs, and through third-party scripts. A single unprotected input field can expose an entire system to attacks, potentially harming your users and brand reputation.
Common Frontend Threats
Here’s a deep dive into the most common frontend security threats:
| Threat | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | Malicious scripts injected into webpages, affecting users’ browsers | Input validation, Content Security Policy (CSP), sanitizing user inputs |
| Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) | Attackers trick users into performing unwanted actions | Use anti-CSRF tokens, SameSite cookies |
| Clickjacking | Overlaying malicious UI elements over legitimate buttons | Implement X-Frame-Options, Content Security Policy frame-ancestors |
| Insecure JavaScript Libraries | Outdated or vulnerable libraries open attack vectors | Regular updates, dependency scanning, using trusted libraries |
| Sensitive Data Exposure | Storing API keys or tokens in frontend code | Environment variables, secure backend proxies, encryption |
Practical Frontend Security Measures
1. Input Validation & Sanitization
Always treat user input as untrusted. Whether it’s form data, URL parameters, or file uploads, validate and sanitize everything. Frameworks like React and Angular provide built-in mechanisms to prevent XSS attacks.
2. Secure Communication
Use HTTPS with TLS for all frontend-backend communication. Avoid transmitting sensitive information over unsecured connections.
3. Content Security Policies (CSP)
CSP headers help prevent injection attacks by specifying trusted sources for scripts, styles, and media. For instance, a properly configured CSP can block malicious inline scripts.
4. Cookie Security
Set cookies with attributes like HttpOnly, Secure, and SameSite to prevent CSRF and session hijacking.
5. Regular Dependency Audits
Modern web apps often rely on dozens of third-party packages. Tools like npm audit or Snyk can detect vulnerabilities before they affect your users.
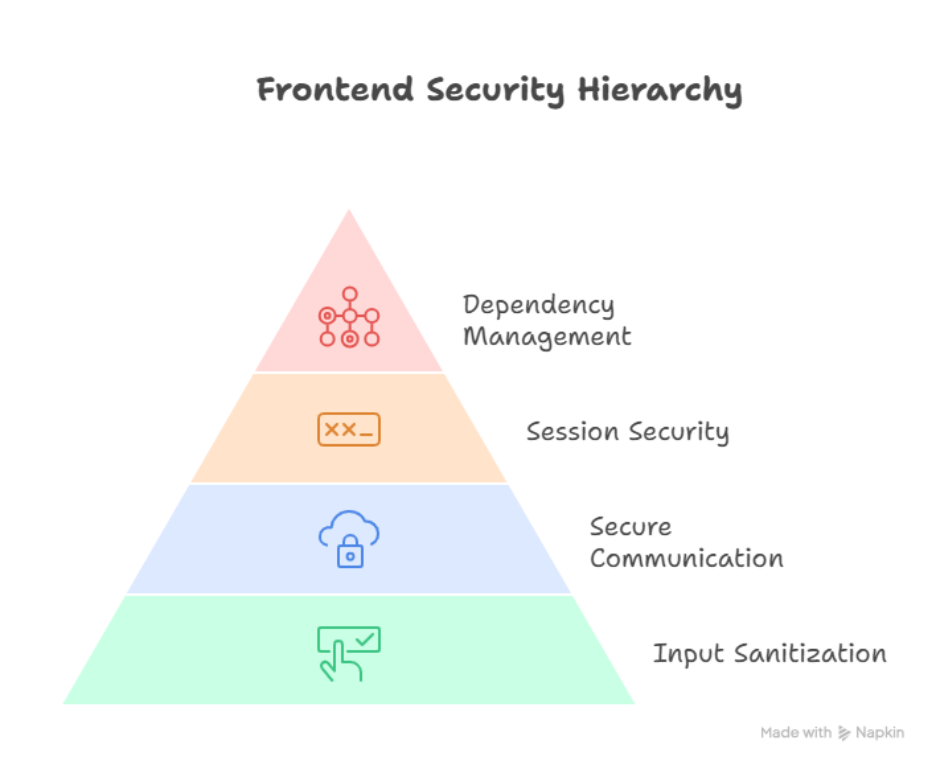
Infographic: Frontend Security Hierarchy
Integrating Security in Development Workflow
At CuriosityTech.in, we implement security as an integral part of the frontend development lifecycle:
- Design Phase: Incorporate secure design principles from the beginning.
- Development Phase: Use secure coding standards, avoid inline scripts, and implement CSP.
- Testing Phase: Conduct security audits and penetration tests before deployment.
- Deployment & Maintenance: Monitor logs, update libraries, and apply patches regularly.
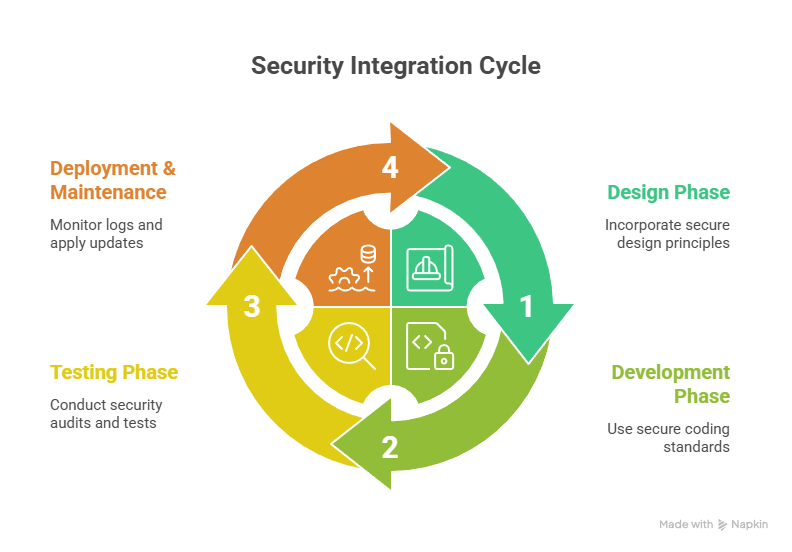
This approach ensures users enjoy seamless experiences without risking sensitive information.
Conclusion
Frontend security isn’t just a technical obligation; it’s a responsibility toward your users. By understanding common threats, applying layered protections, and integrating security into the development workflow, developers can create websites that are not only visually stunning but also safe and reliable. Remember, the web is only as secure as its weakest link—often, that’s the frontend.
At CuriosityTech.in, we combine creativity, performance, and security to craft modern web experiences. Whether you’re building e-commerce platforms, SaaS applications, or personal portfolios, keeping your frontend secure should always be a priority.



