Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) is the backbone of modern DevOps workflows. Jenkins, one of the most widely adopted automation servers, enables engineers to automate builds, tests, and deployments, reducing manual errors and accelerating delivery cycles.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners gain hands-on experience building end-to-end CI/CD pipelines, integrating version control, automated testing, containerization, and deployment.
Why Jenkins for CI/CD?
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
| Open-Source | Community-driven with extensive plugin ecosystem | Highly customizable, cost-effective |
| Extensible | Supports 1000+ plugins for integrations | Connects with version control, cloud, containers, testing frameworks |
| Pipeline as Code | Declarative and scripted pipelines | Versioned, repeatable, and maintainable CI/CD processes |
| Automation | Build, test, deploy automation | Reduces human errors, accelerates release cycles |
| Monitoring | Real-time job monitoring and logging | Track pipeline execution and quickly troubleshoot failures |
CI/CD Pipeline Architecture Diagram
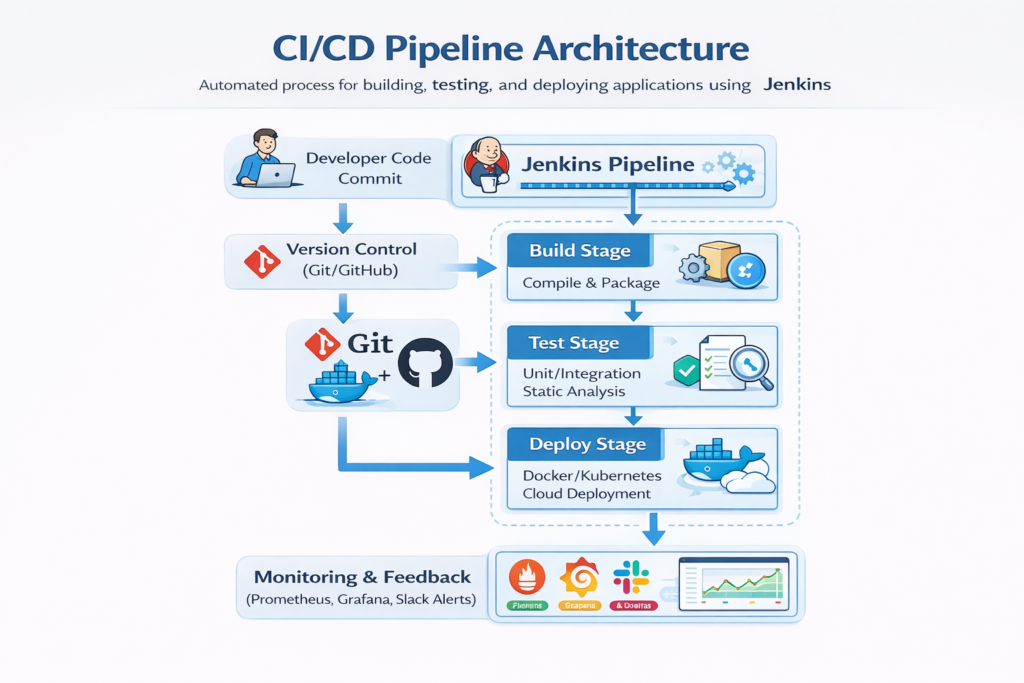
Description: Jenkins orchestrates the CI/CD process, executing build, test, and deployment stages with automated monitoring and feedback loops.
Step-by-Step Guide to Build Jenkins CI/CD Pipeline
Step 1: Set Up Jenkins Server
- Install Jenkins on Linux, Windows, or Docker container.
- Install essential plugins: Git, Docker, Kubernetes, Pipeline, Slack Notifications.
- Configure Jenkins credentials for version control, container registry, and cloud provider.
Step 2: Connect Version Control
- Integrate Git/GitHub repository with Jenkins.
- Enable webhooks to trigger builds on code commit.
Step 3: Define Pipeline Stages
- Build Stage: Compile code, package applications, and build Docker images.
- Test Stage: Run unit tests, integration tests, and static code analysis (SonarQube).
- Deploy Stage: Deploy to Kubernetes cluster, cloud instances, or staging environment.
- Post-Deployment: Notify teams via Slack/Teams and monitor application health.
Step 4: Implement Pipeline as Code
Jenkinsfile Example (Declarative Pipeline)
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage(‘Build’) {
steps {
echo ‘Building application…’
sh ‘mvn clean package’
sh ‘docker build -t myapp:${GIT_COMMIT} .’
} }
stage(‘Test’) {
steps {
echo ‘Running tests…’
sh ‘mvn test’
} }
stage(‘Deploy’) {
steps {
echo ‘Deploying to Kubernetes…’
sh ‘kubectl apply -f k8s/deployment.yaml’
} } }
post {
success {
slackSend(channel: ‘#devops-alerts’, message: “Deployment Successful!”)
}
failure {
slackSend(channel: ‘#devops-alerts’, message: “Deployment Failed!”)
} } }
Explanation: Jenkinsfile defines pipeline stages as code, enabling reproducible builds, testing, and deployments.
Best Practices for Jenkins CI/CD
| Best Practice | Implementation |
| Pipeline as Code | Use Jenkinsfile stored in repo for versioning and transparency |
| Automated Testing | Include unit, integration, and UI tests in pipeline |
| Containerization | Build Docker images for consistency across environments |
| Environment Separation | Deploy to dev, staging, and production with isolated pipelines |
| Notifications & Monitoring | Use Slack, email, or dashboards for pipeline status and alerts |
| Security | Secure credentials via Jenkins credentials store and Vault integration |
| Rollback Strategy | Maintain previous artifact versions to revert in case of failure |
Challenges & Solutions
| Challenge | Solution |
| Pipeline Failures | Implement automated notifications and logging |
| Dependency Management | Use containerized builds with consistent environments |
| Manual Intervention | Automate all stages including testing and deployment |
| Scaling Jenkins | Deploy Jenkins in master-agent architecture for high availability |
| Secret Management | Integrate HashiCorp Vault or AWS KMS for secure credential handling |
Practical Example: End-to-End Pipeline
- Code Commit: Developer pushes code to GitHub.
- Build: Jenkins builds Docker image for microservice.
- Test: Unit and integration tests executed automatically.
- Deploy to Staging: Kubernetes deployment applied, monitored with Prometheus/Grafana.
- Approval & Production Deployment: Manual or automated approval triggers production deployment.
- Feedback Loop: Slack notifications, monitoring alerts, and logs analyzed for continuous improvement.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners implement multi-stage Jenkins pipelines, integrating Docker, Kubernetes, automated testing, and monitoring dashboards to simulate enterprise-grade DevOps pipelines.
Conclusion
Building a CI/CD pipeline with Jenkins is a critical skill for modern DevOps engineers. Automating builds, tests, and deployments not only reduces human error but also accelerates software delivery and ensures high reliability.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners practice real-world CI/CD pipeline projects, integrating version control, testing, containerization, cloud deployment, and monitoring—preparing them for enterprise DevOps roles.



