Introduction
When building Android applications, one of the most foundational concepts every developer must understand is the Activity Lifecycle. An Android app is composed of multiple activities—essentially the screens that users interact with. Each activity transitions through different states such as created, started, resumed, paused, stopped, and destroyed. Understanding these states is critical for creating apps that are efficient, responsive, and bug-free.
For both beginners and seasoned developers, mastering the activity lifecycle is a stepping stone toward writing robust, high-performance Android apps. At CuriosityTech.in, our courses emphasize this concept, integrating real-world examples and hands-on practice to help learners solidify their understanding.
Main Content
What is an Activity in Android?
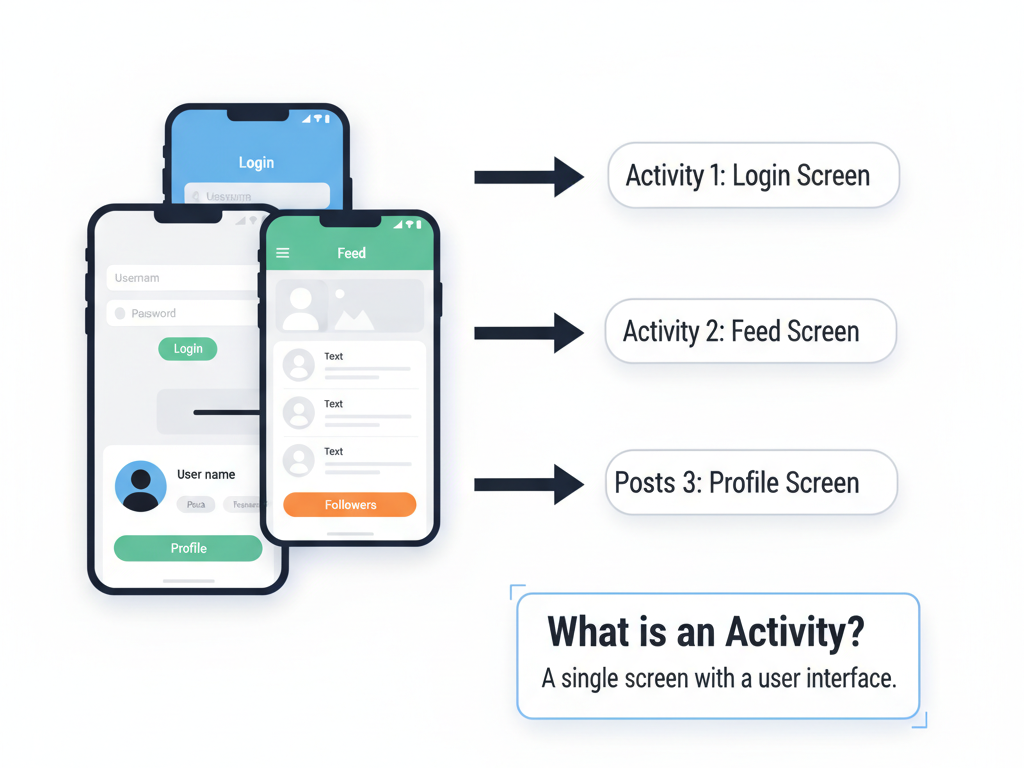
An Activity represents a single screen with a user interface. For example, in a social media app, the login screen, feed screen, and profile screen can each be separate activities. Each activity must respond to system events and user interactions, which are managed through the activity lifecycle.
Understanding the Activity Lifecycle
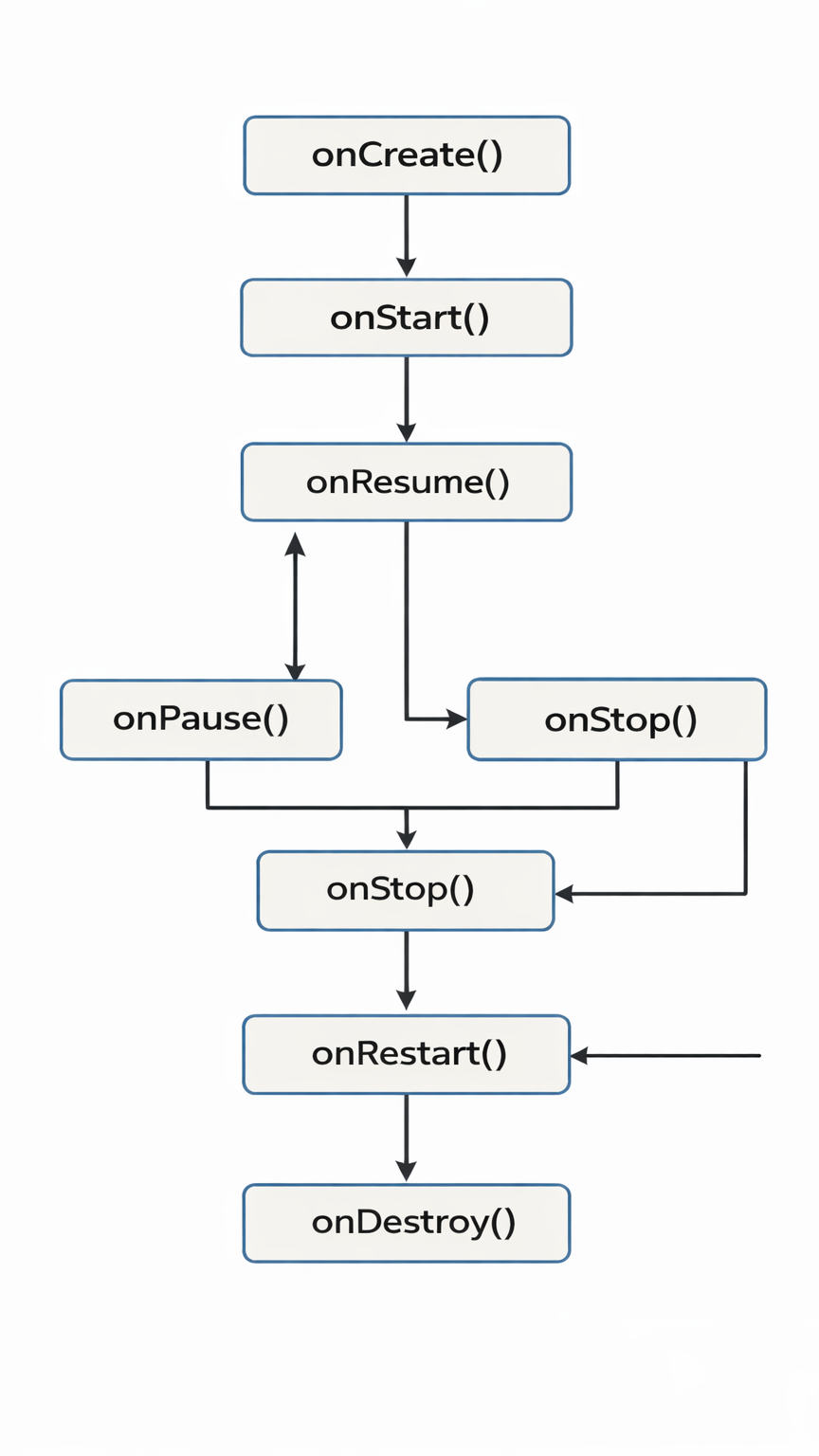
The activity lifecycle consists of callbacks triggered by the Android system to indicate changes in activity state. These states are:
- onCreate() :-
- Called when the activity is first created.
- Initialize UI components, set up bindings, and prepare resources.
Example:
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
}
- onStart() :-
- Activity is becoming visible to the user.
- Ideal for initializing components that refresh the UI.
- onResume() :-
- Activity is at the foreground and the user can interact with it.
- Resume animations, video playback, or sensor updates.
- onPause() :-
- Called when another activity comes in the foreground.
- Save user data, stop animations, or release heavy resources to reduce memory usage.
- onStop() :–
- Activity is no longer visible.
- Release resources or commit unsaved changes.
- onDestroy() :–
- Activity is being destroyed.
- Final cleanup such as removing observers, closing database connections.
- onRestart() :-
- Called when an activity moves from stopped to started state.
- Useful for refreshing UI elements without full recreation.
Lifecycle Diagram
Here’s a hierarchical diagram illustrating transitions between states:
Practical Example
Imagine you are building a music player app. You want music playback to pause when the user navigates to another app and resume when they return:
override fun onPause() {
super.onPause()
mediaPlayer.pause() // Pause music
}
override fun onResume() {
super.onResume()
mediaPlayer.start() // Resume music
}
By managing resources in lifecycle methods, your app conserves battery, prevents crashes, and ensures a smooth user experience.
Advanced Insights :-
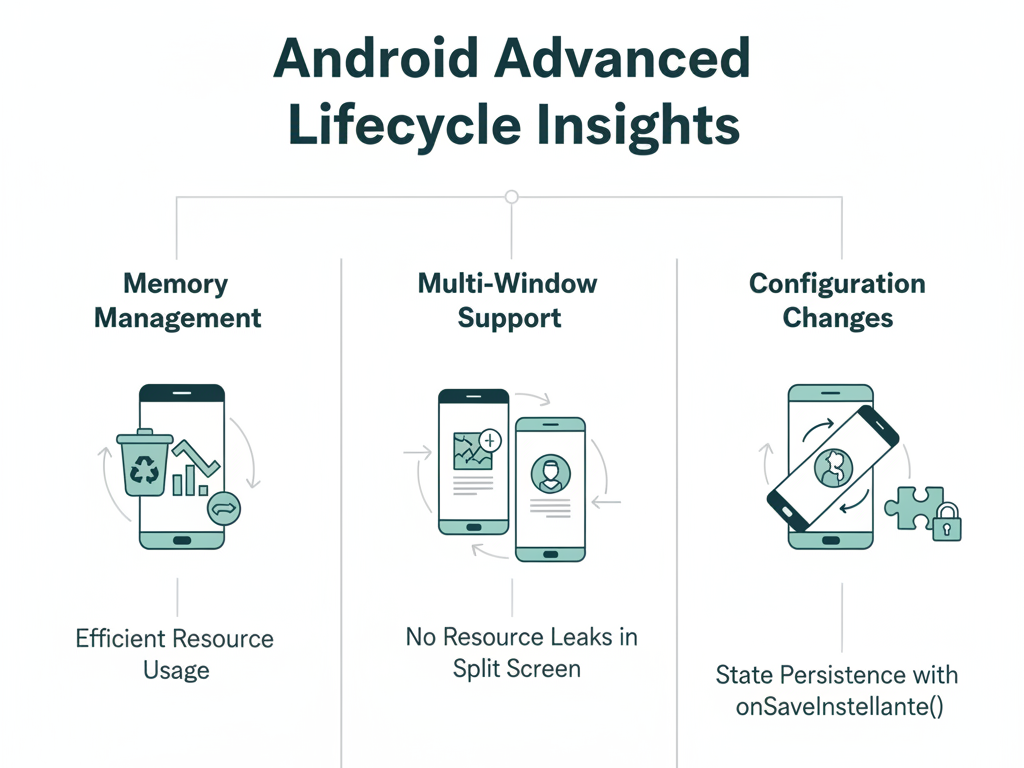
- Memory Management: Proper lifecycle handling ensures efficient memory usage.
- Multi-Window Support: Modern devices allow split screens; understanding lifecycle prevents resource leaks.
- Configuration Changes: Handling rotation or locale changes with onSaveInstanceState() ensures state persistence.
How to Become an Expert in Activity Lifecycle
- Hands-On Practice: Build apps with multiple activities and experiment with lifecycle callbacks.
- Use Logs: Log each lifecycle method to observe transitions in real-time
- Integrate System Events: Handle incoming calls, notifications, and background tasks.
- Explore Jetpack Components: Lifecycle-aware components simplify state management.
CuriosityTech.in Guidance: Our platform offers interactive projects and mentorship for mastering lifecycle management. Students work on real apps, learning how to optimize transitions, handle multi-tasking, and manage resources efficiently.
Conclusion
Understanding the Android Activity Lifecycle is essential for building stable, performant, and user-friendly applications. By mastering the lifecycle, developers can ensure seamless user experiences, efficient resource management, and better app stability. Whether you’re developing simple apps or complex cross-platform solutions, integrating lifecycle management early in your development process is crucial.
At CuriosityTech.in, we provide step-by-step guidance and practical exercises that help learners grasp these concepts intuitively, preparing them for real-world app development.



