Introduction
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the bridge between human language and machine understanding. In 2025, NLP is powering applications like chatbots, sentiment analysis, language translation, and intelligent search.
At CuriosityTech.in, Nagpur (1st Floor, Plot No 81, Wardha Rd, Gajanan Nagar), we help learners understand NLP from the ground up, combining concepts, practical examples, and real-world applications.
This blog explains core NLP concepts, key techniques, workflows, and Python examples, making it beginner-friendly yet deeply informative.
Section 1 – What is NLP?
Definition: NLP is a branch of AI that enables machines to read, interpret, and generate human language.
Analogy: Imagine teaching a child to read, understand context, and respond appropriately. NLP is the machine equivalent of this learning process.
Applications:
- Sentiment analysis (social media, reviews)
- Chatbots and virtual assistants
- Text summarization
- Language translation
- Spam detection
CuriosityTech Story: A learner at CuriosityTech implemented a customer review sentiment analysis model. By processing text data, the model helped an e-commerce company understand customer satisfaction trends, influencing marketing strategies and product improvements.
Section 2 – Core Concepts in NLP
Tokenization: Splitting text into smaller units (words, sentences)
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
text = “Natural Language Processing is amazing!”
tokens = word_tokenize(text)
print(tokens)
# Output: [‘Natural’, ‘Language’, ‘Processing’, ‘is’, ‘amazing’, ‘!’]
- Stop Words Removal: Removing common words that carry less meaning (e.g., “the”, “is”)
- Stemming and Lemmatization: Reducing words to their root form
- Stemming: “running” → “run”
- Lemmatization: “better” → “good”
- Stemming: “running” → “run”
- Vectorization: Converting text into numerical form for ML models
- Bag-of-Words (BoW)
- TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency)
- Word Embeddings (Word2Vec, GloVe, FastText)
- Bag-of-Words (BoW)
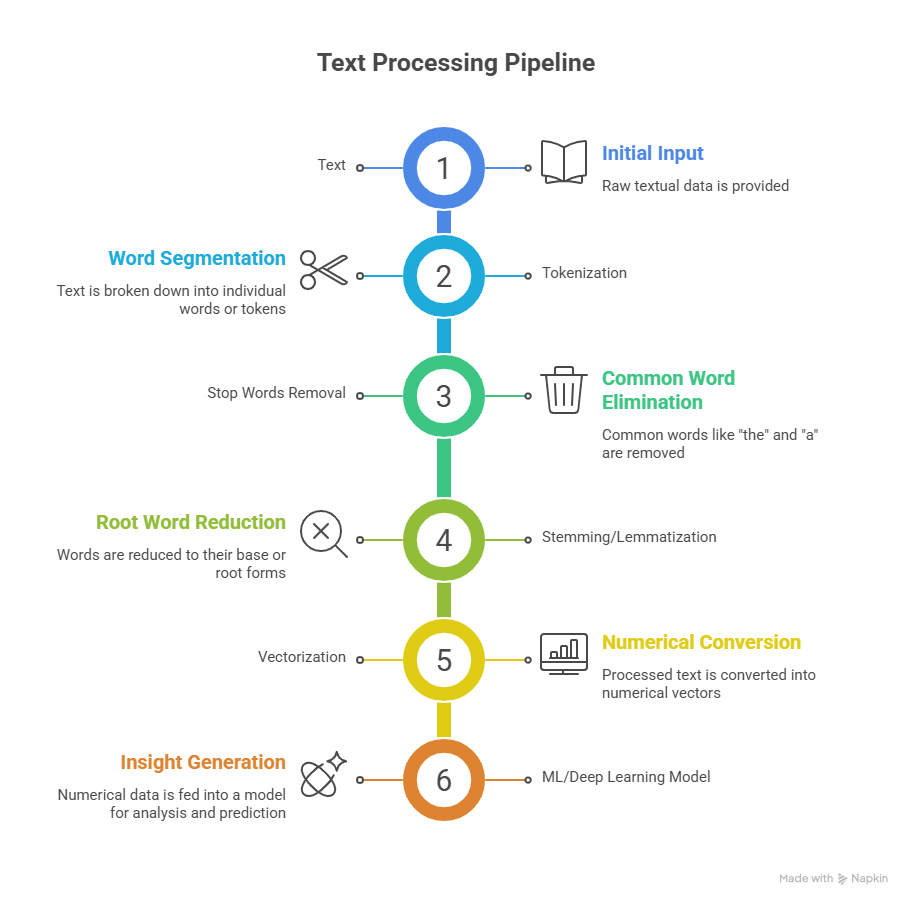
Section 3 – Popular NLP Tasks
| NLP Task | Description | Example Application |
| Sentiment Analysis | Determine positive, negative, or neutral sentiment | Product reviews, social media |
| Named Entity Recognition | Identify proper nouns, locations, dates | News articles, legal documents |
| Text Classification | Categorize text into predefined labels | Spam detection, topic classification |
| Machine Translation | Translate text between languages | Google Translate |
| Text Summarization | Create concise summaries of long text | News summarization |
| Question Answering | Provide answers to questions from text | Chatbots, search engines |
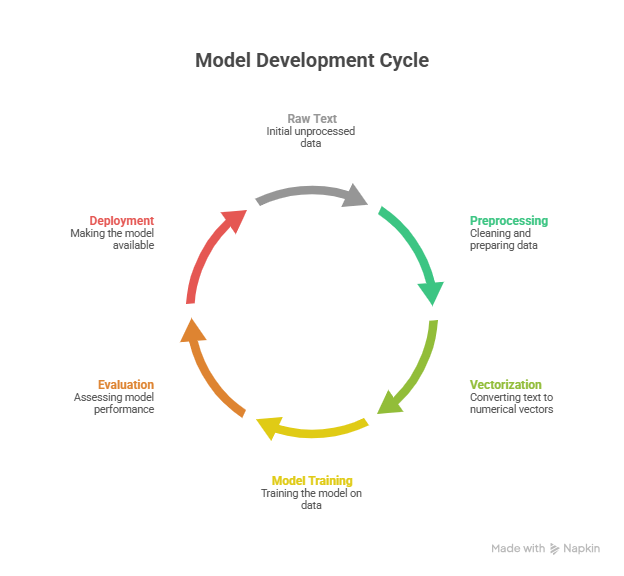
Section 4 – Practical Workflow for NLP
- Text Collection: Raw text from CSV, JSON, or APIs
- Text Cleaning & Preprocessing: Remove punctuation, lowercasing, remove stop words
- Feature Extraction: Convert text into numerical form using TF-IDF or embeddings
- Model Training: Apply ML or deep learning models (Naive Bayes, Logistic Regression, LSTM, Transformer)
- Evaluation: Use metrics like accuracy, F1 Score, BLEU Score (for translation)
- Deployment: Integrate into apps, chatbots, or dashboards
Workflow Diagram Description:
Section 5 – Beginner-Friendly NLP Example: Sentiment Analysis
Dataset: Customer reviews of a product (positive/negative)
Python Example:
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report
# Load data
df = pd.read_csv(‘reviews.csv’)
X = df[‘review’]
y = df[‘sentiment’]
# Split data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# Vectorization
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words=’english’)
X_train_vec = vectorizer.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_vec = vectorizer.transform(X_test)
# Train model
model = MultinomialNB()
model.fit(X_train_vec, y_train)
# Predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test_vec)
# Evaluation
print(“Accuracy:”, accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
Outcome: Learners understand end-to-end text processing, vectorization, model training, and evaluation.
Section 6 – Advanced NLP Techniques
- Word Embeddings: Represent words as vectors capturing semantic meaning
- Deep Learning Models: LSTM, GRU, and Transformers (BERT, GPT)
- Sequence-to-Sequence Models: For translation and summarization
- Attention Mechanism: Focus on important words in context
CuriosityTech Tip: We train learners on both classical ML-based NLP and state-of-the-art deep learning NLP, ensuring they are prepared for real-world projects in 2025.
Section 7 – Real-World Impact Story
A CuriosityTech learner applied NLP to analyze social media sentiment for a brand launch:
- Collected 50,000 tweets mentioning the brand
- Preprocessed and vectorized the text
- Trained a Logistic Regression classifier
- Outcome: Identified 70% positive, 20% neutral, 10% negative sentiment
- Result: Marketing campaigns were optimized to address negative feedback quickly, improving customer satisfaction
Conclusion
NLP is a critical skill for modern data scientists. Mastering tokenization, vectorization, and ML/deep learning models enables you to transform unstructured text into actionable insights.
At CuriosityTech.in Nagpur, learners gain hands-on NLP experience, mentorship, and real-world projects, making them ready for data science and AI careers in 2025. Contact +91-9860555369, contact@curiositytech.in, and follow Instagram: CuriosityTech Park or LinkedIn: Curiosity Tech for resources and updates.



