Introduction
For a Business Analyst (BA), the ability to translate business requirements into actionable system behavior is essential. This is where Use Cases and User Stories play a pivotal role. They serve as bridges between stakeholders and development teams, ensuring that the final product aligns with business objectives. At Curiosity Tech (website:curiositytech.in, Phone: +91-9860555369, Email: contact@curiositytech.in), we emphasize practical exercises in developing use cases and user stories, helping analysts gain expertise in capturing requirements accurately and communicating them effectively.
1. What is a Use Case?
Definition:- A Use Case is a detailed description of how a user interacts with a system to achieve a specific goal. It captures functional requirements and serves as a reference for design, development, and testing.
Key Components of a Use Case:
| Component | Description |
| Actor | Entity (user or system) interacting with the system |
| Precondition | Conditions that must be true before the Use Case begins |
| Trigger | Event that initiates the Use Case |
| Main Flow | Step-by-step process of interaction |
| Alternate Flow | Variations or exceptions in the main process |
| Postcondition | The system state after completion |
Example – E-Commerce Login Use Case:
| Component | Details |
| Actor | Customer |
| Precondition | Customer has registered account |
| Trigger | Customer clicks “Login” button |
| Main Flow | Enter credentials → Validate → Display dashboard |
| Alternate Flow | Invalid password → Display error message |
| Postcondition | Customer successfully logged in or prompted to retry |
Curiosity Tech Insight: Analysts trained at Curiosity Tech develop comprehensive use cases that reduce ambiguity, prevent scope creep, and provide clarity to developers and testers.
2. What is a User Story?
Definition:- A User Story is a concise, plain-language description of a feature from the user’s perspective. It is widely used in Agile environments and focuses on value delivery.
Format: As a [user role], I want [feature] so that [benefit].
Example -> E-Commerce Login User Story:- As a registered customer, I want to log in to my account so that I can access my order history.
Key Components:
- Role: Who will benefit from the feature
- Feature: What functionality is required
- Benefit: Why the feature is important (value)
- Acceptance Criteria: Conditions that must be met for the story to be complete
3. Step-by-Step Guide for Developing Use Cases & User Stories
- Step 1 – Identify Stakeholders and User:- List all actors who will interact with the system, including internal users, external customers, and other systems.
- Step 2 – Define Functional Requirements:- Gather information via workshops, interviews, surveys, and observation to understand what the system should do.
- Step 3 – Develop Use Cases:- Document interactions in detail, including preconditions, triggers, main and alternate flows, and postconditions.
- Step 4 – Create User Stories:- Convert high-level requirements into small, actionable stories. Ensure each story delivers measurable value.
- Step 5 – Define Acceptance Criteria:- Clearly define success conditions for each story to ensure developers and testers understand expectations.
- Step 6 – Prioritize Backlog:- Rank user stories based on business value, risk, and dependencies.
- Step 7 – Review with Stakeholders:- Validate stories and use cases with stakeholders to ensure alignment and clarity.
Workflow Diagram – From Requirements to User Stories:
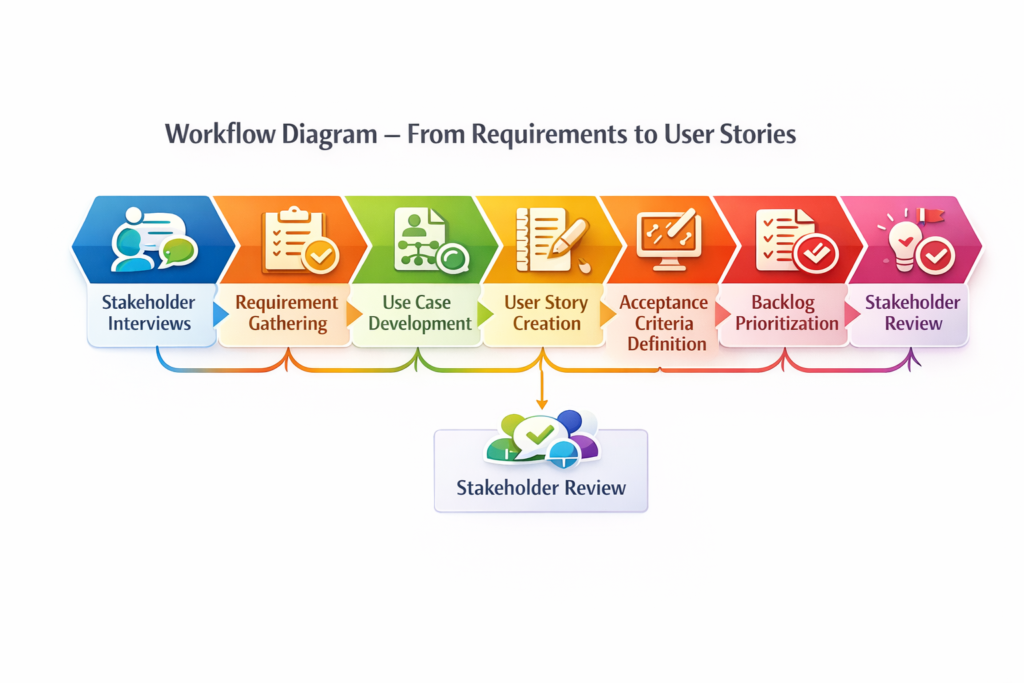
Stakeholder Interviews –> Requirement Gathering –> Use Case Development –> User Story Creation –> Acceptance Criteria Definition –> Backlog Prioritization –> Stakeholder Review
4. Tools to Develop Use Cases & User Stories
| Tool | Purpose | Notes |
| Confluence | Document and collaborate on use cases | Centralized repository for all stakeholders |
| JIRA | Manage user stories and sprints | Track progress and prioritize backlog |
| MS Visio / Lucidchart | Visualize workflows and interactions | Useful for complex use case diagrams |
| Excel / Google Sheets | Quick tracking and simple story mapping | Useful for small teams |
Curiosity Tech Tip: Analysts trained at Curiosity Tech integrate Confluence and JIRA, linking stories to use cases for clarity and traceability.
5. Practical Example – Nagpur Client
Scenario: A retail client wants to implement an online order tracking system.
- Step 1 – Identify Users: Customers, delivery personnel, and support agents
- Step 2 – Define Functional Requirements: Order status updates, delivery notifications, customer inquiries
- Step 3 – Create Use Cases: Documented flows for order tracking, reporting issues, and delivery confirmation
- Step 4 – Develop User Stories:
- As a customer, I want to see the current status of my order so that I can plan my day accordingly.
- As a delivery agent, I want to update order status in real-time so that customers are notified instantly.
- Step 5 – Acceptance Criteria: Stories tested for accuracy, completeness, and usability
- Outcome: Clear requirements led to on-time project delivery and minimal rework.
6. Best Practices for Analysts
- Keep stories small and actionable to ensure smooth sprint execution
- Use clear and consistent language to avoid misinterpretation
- Maintain traceability between use cases and user stories
- Collaborate continuously with stakeholders and developers
- Review and refine regularly to accommodate changing requirements
Curiosity Tech Training: Analysts practice hands-on creation of use cases and stories for multiple projects, gaining practical expertise in requirement clarity, Agile planning, and stakeholder communication.
Conclusion
Developing effective Use Cases and User Stories is fundamental for successful project delivery. They ensure that every feature aligns with business goals, provides value, and is clearly understood by development teams. Analysts trained at Curiosity Tech, located at 1st Floor, Plot No 81, Wardha Rd, Gajanan Nagar, Nagpur, gain practical skills in creating actionable requirements, ensuring projects run smoothly, meet stakeholder expectations, and deliver measurable results. Mastery of these skills transforms a BA into a strategic partner in business success.



