In modern DevOps, Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment/Delivery (CD) pipelines are critical for automating application builds, tests, and releases. Automation ensures faster delivery, fewer errors, and reliable deployments. At Curiosity Tech, we train DevOps engineers to design, implement, and optimize CI/CD pipelines, integrating code, testing, deployment, and monitoring in a seamless workflow.
What is a CI/CD Pipeline?
A CI/CD pipeline is a set of automated processes that allow software development teams to:
- Continuously integrate code changes from multiple developers.
- Automatically test and validate builds to detect bugs early.
- Deploy applications reliably to staging or production environments.
- Monitor applications post-deployment for performance and errors.
CI/CD eliminates manual deployments, reduces human errors, and accelerates delivery cycles.
Core Components of a CI/CD Pipeline
| Component | Purpose |
| Source Control | Git, GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket – manage code versions |
| Build Server | Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI – compile, package, and build applications |
| Automated Testing | Unit tests, integration tests, security tests – validate quality |
| Artifact Repository | Nexus, Artifactory – store build artifacts |
| Deployment Tools | Kubernetes, Ansible, Helm – deploy applications to servers or cloud |
| Monitoring & Alerts | Prometheus, Grafana, ELK – track deployments, detect issues |
Stepwise CI/CD Pipeline Workflow Diagram
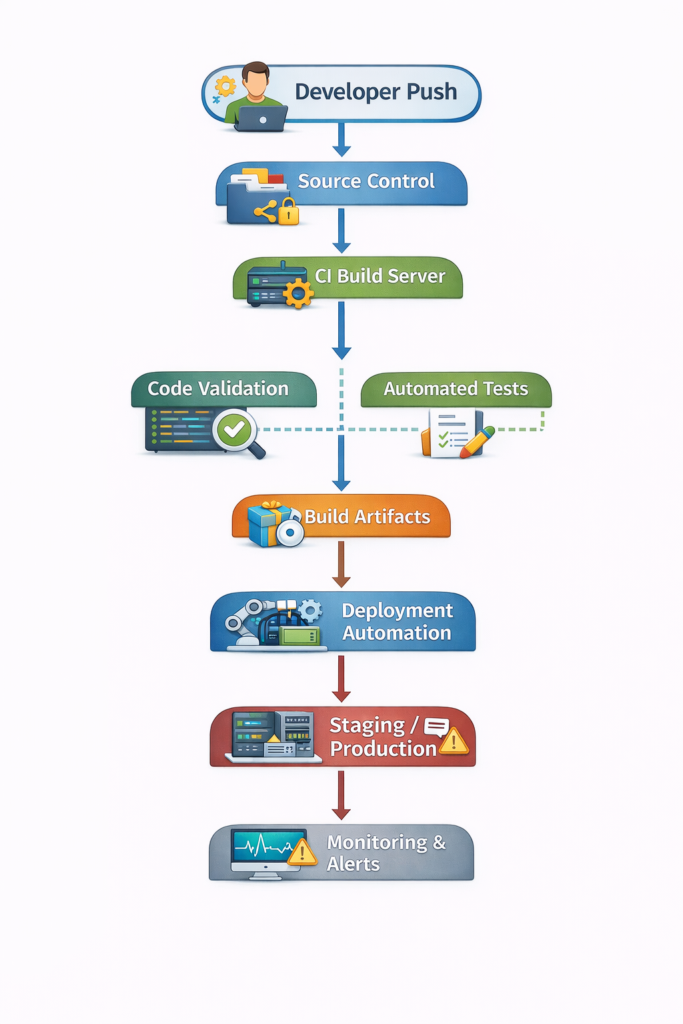
Description: Every code commit triggers automated builds, tests, artifact creation, and deployments, followed by monitoring for reliability and performance.
Step 1: Continuous Integration (CI)
Goal: Automatically integrate code from multiple developers to detect issues early.
Tasks:
- Code pushed to Git repository triggers CI build.
- Run automated unit tests and linting.
- Compile and package code into deployable artifacts.
- Store artifacts in repositories (Nexus, Artifactory).
Best Practices:
- Keep builds fast for immediate feedback.
- Integrate static code analysis (e.g., SonarQube) for quality checks.
- Use branching strategies (Gitflow or trunk-based) for smooth integration.
Step 2: Continuous Delivery / Deployment (CD)
Goal: Automatically deploy builds to staging or production environments.
Tasks:
- Deploy build artifacts to staging environment.
- Run integration tests, security scans, and performance tests.
- Promote successful builds to production automatically (CD) or manually (Continuous Delivery).
- Rollback failed deployments using versioned artifacts.
Best Practices:
- Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to provision environments consistently.
- Implement blue-green or canary deployments to minimize downtime.
- Integrate monitoring tools to detect issues early.
Step 3: Monitoring & Feedback Loop
After deployment, continuous monitoring ensures reliability, performance, and observability.
| Tool | Purpose |
| Prometheus | Collect metrics (CPU, memory, application response) |
| Grafana | Visual dashboards for metrics and alerts |
| ELK Stack | Centralized logging and anomaly detection |
| Alertmanager | Automated notifications for failures or threshold breaches |
At Curiosity Tech., learners practice end-to-end CI/CD automation integrating Jenkins, GitLab CI, Terraform, Kubernetes, Prometheus, and Grafana.
Sample Jenkins Pipeline Script (Declarative)
steps { git ‘https://github.com/user/repo.git’ }
steps { sh ‘./gradlew build’ }
steps { sh ‘./gradlew assemble’ }
echo ‘Pipeline execution complete’
Description: This pipeline automates checkout, build, test, package, and deployment, providing end-to-end CI/CD automation.
Challenges & Solutions in CI/CD Automation
| Challenge | Solution |
| Slow Builds | Use parallel builds, caching, and optimized scripts |
| Test Failures | Run automated tests in isolated environments and mock dependencies |
| Deployment Failures | Implement rollback strategies and blue-green deployments |
| Monitoring Gaps | Integrate unified monitoring dashboards for metrics and logs |
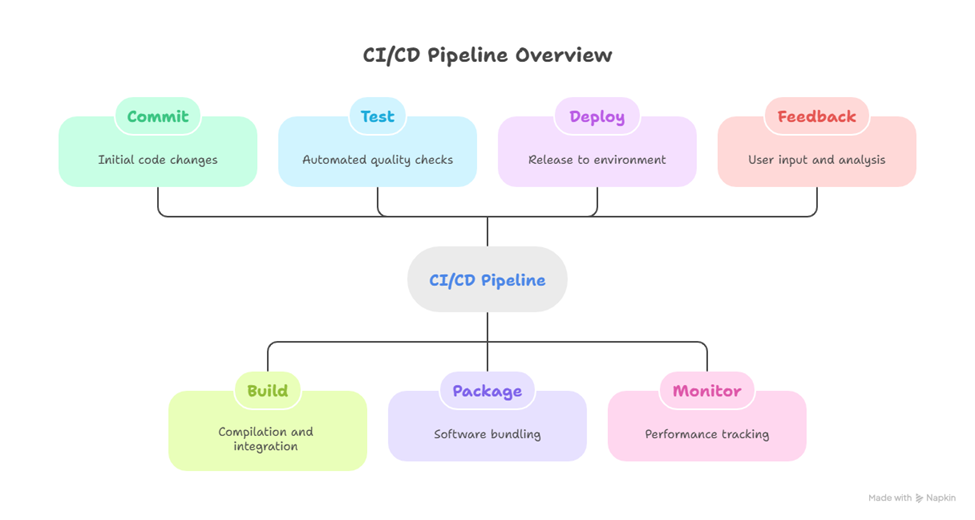
Infographic: CI/CD Pipeline Lifecycle
Conclusion
Automating CI/CD pipelines is the heart of modern DevOps, ensuring faster, reliable, and secure delivery of applications. Mastery involves combining version control, automated testing, deployment automation, and monitoring into a seamless workflow.
At Curiosity Tech, learners practice building fully automated CI/CD pipelines with real-world scenarios, integrating Jenkins, Terraform, Kubernetes, and monitoring tools to deliver production-ready applications confidently.



