Introduction
Hosting a static website on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a foundational exercise for cloud engineers to understand storage, networking, and serverless deployment concepts. Static websites consist of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files without a backend database. Leveraging GCP’s Cloud Storage, Cloud CDN, and Load Balancing allows engineers to deploy highly scalable, cost-efficient, and secure websites.
At Curiosity Tech, hands-on projects like this help engineers apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios, laying the groundwork for advanced cloud architecture projects.
Why Host a Static Website on GCP?
| Benefit | Explanation |
| Scalability | Cloud Storage scales automatically to serve millions of requests. |
| Cost-Efficiency | Pay only for storage and egress; no server maintenance. |
| High Availability | Data is replicated across multiple regions for redundancy. |
| Secure Delivery | HTTPS via Cloud CDN, IAM access control, and firewall rules. |
| Easy Integration | Connect with Cloud Functions, Cloud Run, or APIs later for dynamic features. |
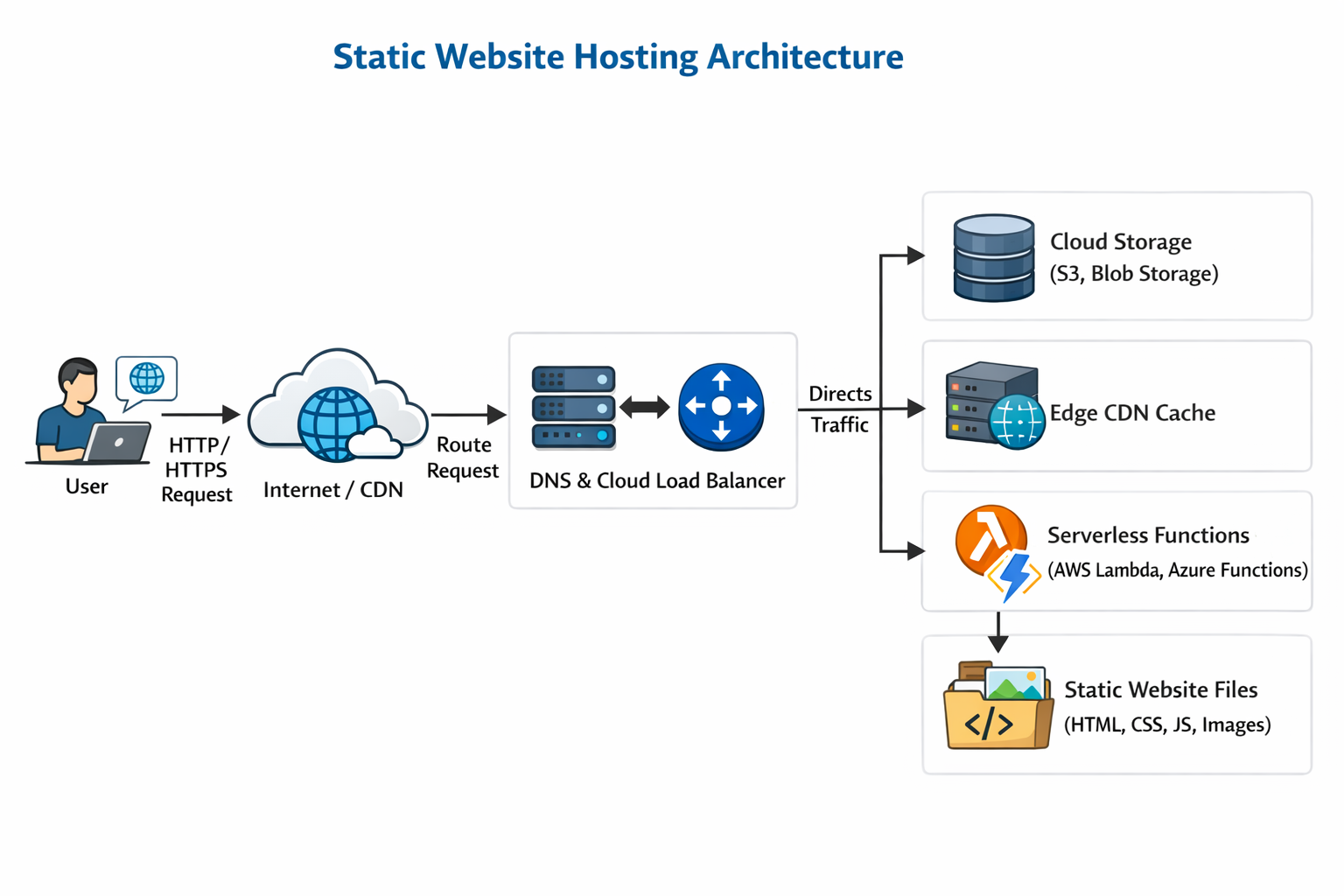
Core GCP Services Used
- Cloud Storage – Object storage for hosting static files.
- Cloud CDN – Content delivery for low-latency global access.
- Cloud Load Balancer (Optional) – Distribute traffic across multiple regions.
- Cloud DNS – Manage custom domains.
- IAM – Control access to storage buckets.
Diagram Concept: Static Website Hosting Architecture
Step-by-Step Guide to Hosting a Static Website
Step 1: Create a Cloud Storage Bucket
- Navigate to GCP Console → Cloud Storage → Create Bucket.
- Choose a unique globally recognized bucket name.
- Select region or multi-region depending on traffic requirements.
- Choose Standard Storage Class for static website hosting.
- Disable public access initially; we will configure public access next.
Step 2: Upload Website Files
- Upload index.html, style.css, and script.js to the bucket.
- Ensure the file names are lowercase and follow standard URL conventions.
Example:
index.html
about.html
assets/css/style.css
assets/js/script.js
Step 3: Configure Bucket for Website Hosting
- Go to Bucket Settings → Edit Website Configuration.
- Set Index Page: index.htmL
- Set 404 Page (Optional): 404.html
- Make files publicly accessible via IAM or ACLs for global access.
Step 4: Enable HTTPS and CDN (Optional but Recommended)
- Configure Cloud CDN for low-latency delivery across regions.
- Use HTTPS via Load Balancer:
- Create HTTP(s) Load Balancer
- Add backend bucket as origin
- Enable SSL certificate (managed by GCP)
This ensures secure, fast delivery of static content globally.
Practical Tips for Hosting Static Websites
| Tip | Explanation |
| Use Versioned URLs | Cache-busting for CSS/JS to prevent stale content. |
| Enable Logging | Monitor access via Cloud Storage logs. |
| Use Object Lifecycle Policies | Automatically delete old files or move to cheaper storage classes. |
| Custom Domain | Configure Cloud DNS for branding and SEO benefits. |
| Optimize Assets | Minify CSS/JS and compress images to reduce load time. |
Real-World Scenario: Portfolio Website
Objective: Host a personal portfolio website showcasing projects.
- Bucket Creation: portfolio-bucket-2025
- Upload Files: HTML pages, images, CSS, JS
- Enable Website Hosting: Set index.html as entry point
- Enable HTTPS & CDN: Use Cloud Load Balancer and SSL for security
- Connect Domain: www.myportfolio.com via Cloud DNS
The website is now globally accessible, secure, and scalable, ready for further enhancements like integrating serverless APIs or analytics.
Advanced Practices
- Integrate with Cloud Functions or Cloud Run – Add dynamic behavior or API endpoints.
- Monitoring & Alerts – Track website traffic and error rates using Cloud Monitoring and Logging.
- Automate Deployments – Use CI/CD pipelines to automatically update website files on push.
- SEO & Analytics – Integrate Google Analytics for insights and tracking.
- Security Enhancements – Restrict bucket access to only the load balancer using Signed URLs.
At Curiosity Tech, engineers practice building full-stack serverless websites starting from static hosting, gradually adding dynamic features.
Conclusion
Hosting a static website on GCP demonstrates how cloud storage, CDN, load balancing, and DNS come together to provide secure, scalable, and cost-efficient deployments. Engineers who master this process gain a solid foundation in cloud architecture, security, and operational best practices.
Curiosity Tech provides hands-on labs and projects to guide engineers through real-world cloud deployments, preparing them for advanced GCP applications and certification readiness.