Deploying applications on the cloud can be complex. On Day 14, we explore AWS Elastic Beanstalk (EB), a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) that simplifies application deployment, scaling, and management.
At Curiosity Tech, we teach learners that Elastic Beanstalk is more than a deployment tool—it’s about automating infrastructure, monitoring, and scaling while focusing on application development.
1. What is AWS Elastic Beanstalk?
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a fully managed service that handles:
- Application deployment
- Resource provisioning (EC2, Load Balancers, Auto Scaling)
- Monitoring and logging
- Application scaling
Key Benefits:
- Simplifies deployment: Developers upload code; EB handles infrastructure
- Automatic scaling: Adjusts capacity based on traffic
- Supports multiple languages: Java, Python, Node.js, PHP, Ruby, .NET, Go
- Integration with other AWS services: RDS, S3, CloudWatch
Analogy: Think of Elastic Beanstalk as a full-service restaurant: you bring the recipe (code), and it handles cooking, serving, and cleaning (infrastructure, scaling, monitoring).
2. Elastic Beanstalk Architecture
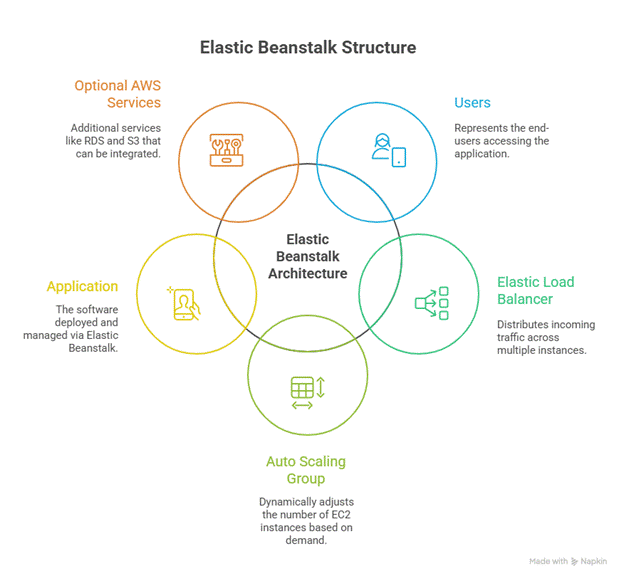
Explanation:
- EB provisions EC2 instances in Auto Scaling groups
- Requests go through Elastic Load Balancer (ALB)
- Optional RDS integration for database
- EB automatically handles health monitoring, patching, and scaling
3. Supported Platforms
| Platform | Description | Use Case |
| Java | Run Java web apps | Spring Boot, Tomcat apps |
| Python | Run Python apps | Flask, Django apps |
| Node.js | Run Node apps | Express.js APIs |
| PHP | Run PHP apps | Laravel, WordPress |
| .NET | Run Windows apps | ASP.NET Core apps |
| Go | Run Go apps | Microservices |
Expert Tip: Choose the platform that matches your code stack. EB automatically installs runtime and dependencies.
4. Deployment Workflow
- Package Application Code: ZIP or WAR file
- Create Elastic Beanstalk Environment: Web Server or Worker Environment
- Upload Application: EB deploys code to EC2 instances
- Automatic Provisioning: EC2, Load Balancer, Auto Scaling, Security Groups
- Monitor Application: Health dashboard and CloudWatch metrics
- Scale Automatically: Adjust number of instances based on traffic
5. Step-by-Step Lab: Deploy a Python Flask App
Step 1 – Prepare Application
- Example app.py:
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route(‘/’)
def hello():
return “Hello from CuriosityTech Elastic Beanstalk!”
- Create requirements.txt:
Flask==2.3.2
- ZIP the application files
Step 2 – Create Elastic Beanstalk Environment
- Navigate to AWS Console → Elastic Beanstalk → Create Application
- Name: CuriosityTech-Flask-App
- Platform: Python 3.x
- Environment Type: Web Server
3 – Upload and Deploy
- Upload ZIP package
- Click Create Environment
- EB provisions resources automatically (EC2, Load Balancer, Security Group, Auto Scaling)
4 – Verify Deployment
- EB provides URL endpoint
- Access in browser → “Hello from CuriosityTech Elastic Beanstalk!”
6. Health Monitoring & Logs
Elastic Beanstalk provides:
- Health Dashboard: Green, Yellow, Red status
- Environment Metrics: CPU, memory, request count, latency
- Logs: Download logs from EC2 instances
- CloudWatch Integration: Custom alarms for performance issues
CuriosityTech.in Insight: Beginners learn how to monitor deployments, troubleshoot issues, and optimize performance using EB dashboards and CloudWatch integration.
7. Best Practices
| Practice | Reason |
| Use versioning for applications | Roll back to previous stable version easily |
| Configure environment variables | Avoid hardcoding sensitive info |
| Enable Auto Scaling | Handle traffic spikes efficiently |
| Integrate RDS using separate instances | Decouple application and database for flexibility |
| Monitor application logs and health | Detect issues early and optimize performance |
8. Common Beginner Mistakes
- Uploading incorrect ZIP structure → deployment fails
- Ignoring security groups and IAM roles → unauthorized access
- Not enabling health monitoring → missed errors and warnings
- Using single instance environment for production → low availability
- Ignoring environment updates → outdated dependencies or security patches
9. Path to Expertise
- Start by deploying simple web apps (Flask, Node.js, or Java)
- Explore multi-instance, Auto Scaling environments
- Integrate RDS, S3, and SQS for full application stack
- Monitor health metrics and logs for performance optimization
- Learn deployment strategies: rolling updates, blue/green deployments
At Curiosity Tech, learners progress from basic deployments to full production-ready applications, mastering infrastructure automation, scaling, and monitoring.
Conclusion
AWS Elastic Beanstalk simplifies application deployment and management by automating provisioning, scaling, and monitoring. By mastering EB, beginners can focus on writing code while AWS handles infrastructure, reducing operational overhead and improving productivity.
Hands-on labs and guidance at CuriosityTech.in provide learners with real-world deployment experience, preparing them for professional cloud engineering and application deployment scenarios.