Introduction
In 2025, data scientists face massive datasets from sources like IoT devices, e-commerce platforms, social media, and financial transactions. Handling this “big data” requires specialized tools beyond traditional databases.
At CuriosityTech.in, Nagpur (1st Floor, Plot No 81, Wardha Rd, Gajanan Nagar), learners gain practical skills in Hadoop and Spark, understanding distributed storage, processing, and analytics for real-world applications.
This blog provides a complete guide to big data tools, workflows, architecture, and examples, helping learners make informed decisions about Hadoop vs Spark usage.
Section 1 – What is Big Data?
Definition: Big Data refers to datasets that are too large or complex to process with traditional tools.
Characteristics (The 5 V’s):
- Volume: Massive data sizes (TBs, PBs)
- Velocity: High-speed data generation (real-time streaming)
- Variety: Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data
- Veracity: Data quality and reliability challenges
- Value: Extracting insights for business impact
CuriosityTech Story:
A learner analyzed e-commerce clickstream data, applying Spark to process 2 TB of logs daily, uncovering trends that influenced marketing campaigns.
Section 2 – Hadoop: Distributed Storage & Batch Processing
Overview:
Hadoop is an open-source framework for storing and processing large datasets in a distributed environment.
Core Components:
| Component | Function |
| HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) | Distributed storage across multiple nodes |
| MapReduce | Batch processing framework for parallel computation |
| YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator) | Manages cluster resources and job scheduling |
| Hive | SQL-like interface for querying large datasets |
| Pig | Dataflow scripting language for batch processing |
Advantages:
- Handles massive datasets
- Fault-tolerant storage and processing
- Open-source and widely adopted
Limitations:
- Slower for real-time processing
- Complex programming for beginners
Workflow Diagram Description:
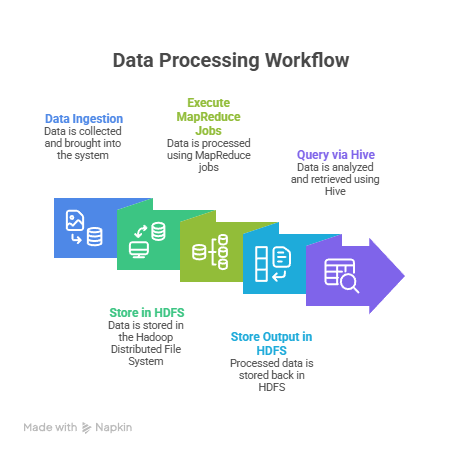
Section 3 – Apache Spark: Distributed Analytics & Real-Time Processing
Overview:
Apache Spark is a fast, in-memory data processing framework designed for both batch and real-time analytics.
Core Components:
| Component | Function |
| Spark Core | Distributed computing engine |
| Spark SQL | SQL queries on structured data |
| Spark Streaming | Real-time data processing |
| MLlib | Machine learning library |
| GraphX | Graph processing library |
Advantages:
- In-memory processing → much faster than Hadoop MapReduce
- Supports batch, streaming, and ML in a single framework
- Compatible with Python, Scala, R, and Java
Limitations:
- Higher memory requirement
- Complexity increases with very large clusters
Workflow Diagram Description:
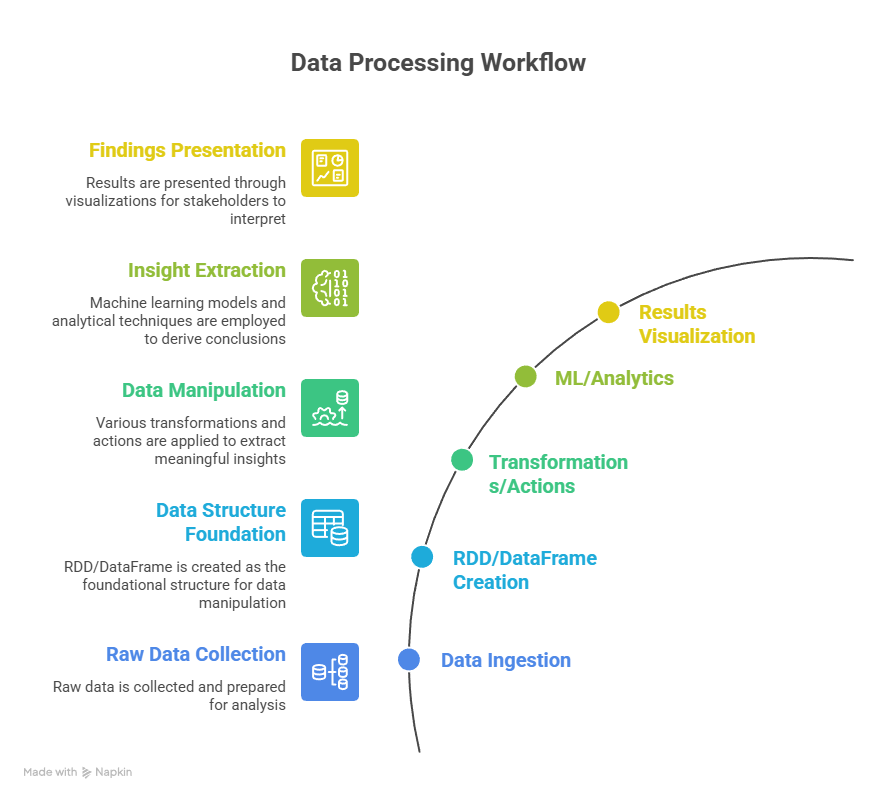
Section 4 – Hadoop vs Spark Comparison
| Feature | Hadoop | Spark |
| Processing | Disk-based batch processing | In-memory batch & streaming |
| Speed | Slower due to disk I/O | Faster, in-memory computation |
| Real-Time Support | Limited | Excellent via Spark Streaming |
| Ease of Use | Complex programming | API simplifies coding (Python, R) |
| ML & Analytics | Limited support | MLlib and GraphX integrated |
| Use Case | Historical batch analytics | Real-time dashboards, predictive analytics |
CuriosityTech Insight:
Learners practice both Hadoop and Spark to understand when to use batch vs real-time processing, a crucial skill for 2025 data science projects.
Section 5 – Practical Example: Using Spark for Big Data ML
Scenario: Predict customer churn using 500 GB e-commerce dataset
Python (PySpark) Workflow:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.ml.feature import VectorAssembler
from pyspark.ml.classification import RandomForestClassifier
from pyspark.ml.evaluation import BinaryClassificationEvaluator
# Initialize Spark
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName(“CustomerChurn”).getOrCreate()
# Load data
df = spark.read.csv(“ecommerce_churn.csv”, header=True, inferSchema=True)
# Feature assembly
assembler = VectorAssembler(inputCols=[‘Age’,’Purchase_Freq’,’Avg_Spend’], outputCol=’features’)
data = assembler.transform(df)
# Split data
train_data, test_data = data.randomSplit([0.8, 0.2], seed=42)
# Train model
rf = RandomForestClassifier(featuresCol=’features’, labelCol=’Churn’)
model = rf.fit(train_data)
# Evaluate
preds = model.transform(test_data)
evaluator = BinaryClassificationEvaluator(labelCol=’Churn’)
print(“ROC-AUC:”, evaluator.evaluate(preds))
Outcome:
- Learners see scalable ML workflows with Spark on large datasets
- Real-time and batch data can both be analyzed efficiently
Section 6 – Tips for Mastering Big Data Tools
- Understand distributed storage and computation concepts
- Start with small datasets before scaling to cluster processing
- Learn PySpark for hands-on ML projects
- Explore HDFS, Hive, and Spark SQL for querying structured data
- At CuriosityTech.in, learners build projects on retail analytics, social media trends, and IoT streams to solidify skills
Section 7 – Real-World Impact Story
A learner applied Spark Streaming to real-time sensor data from a manufacturing plant:
- Detected anomalies and equipment failures early
- Reduced downtime by 25%
- Demonstrated how big data tools transform operational efficiency
Conclusion
Hadoop and Spark are essential tools for modern data scientists, enabling scalable, efficient, and real-time data analytics. Choosing the right tool depends on volume, velocity, and the nature of analysis.
At CuriosityTech.in Nagpur, learners gain hands-on experience with big data workflows, cluster computing, and scalable ML, preparing them for data-intensive projects in 2025. Contact +91-9860555369, contact@curiositytech.in, and follow Instagram: CuriosityTech Park or LinkedIn: Curiosity Tech for resources.



