Introduction
In modern cloud engineering, Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) pipelines are essential for delivering robust, error-free applications quickly and consistently. Google Cloud Platform provides Cloud Build and Artifact Registry to streamline CI/CD for containerized and serverless applications.
At Curiosity Tech , engineers are trained to design, implement, and optimize CI/CD pipelines, enabling rapid development, automated testing, secure artifact management, and reliable deployments across GCP services.
What is CI/CD?
CI/CD is the process of automating code integration, testing, and deployment:
- Continuous Integration (CI): Developers frequently merge code into a central repository; automated builds and tests run to ensure stability.
- Continuous Deployment (CD): Code changes are automatically deployed to production or staging environments after passing tests.
Benefits:
- Faster release cycles
- Improved code quality through automated testing
- Reduced manual deployment error
- Traceability and auditability
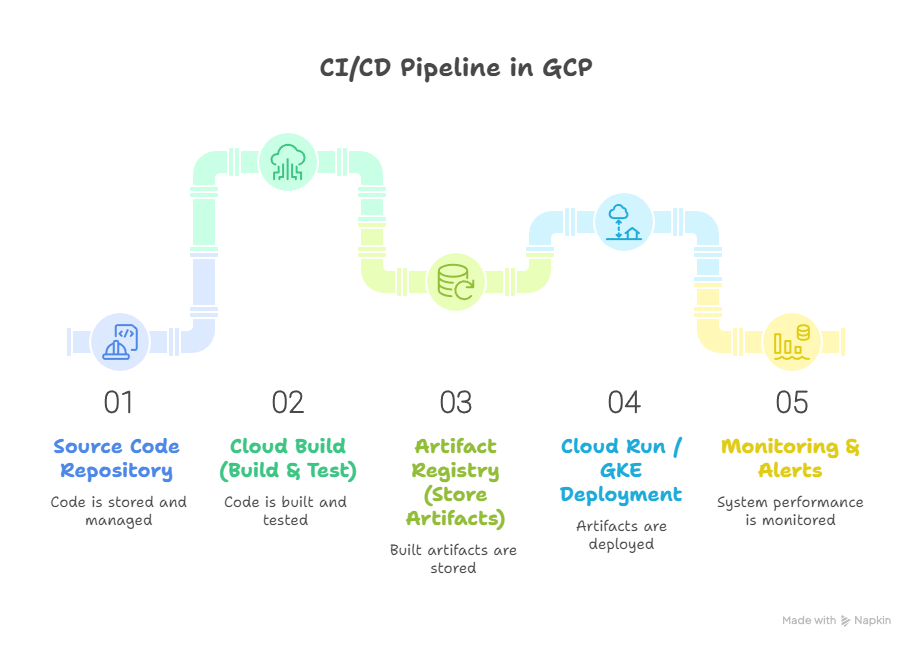
Core GCP Services for CI/CD
| Service / Tool | Purpose |
| Cloud Build | Fully managed CI/CD service that builds, tests, and deploys code. |
| Artifact Registry | Stores and manages container images, language packages, and artifacts. |
| Cloud Source Repositories | Managed Git repositories integrated with CI/CD pipelines. |
| Cloud Deploy | Automates continuous delivery of applications to GKE or Cloud Run. |
| Cloud Monitoring | Monitors pipeline performance and deployment success metrics. |
Diagram Concept: CI/CD Pipeline in GCP
Cloud Build Overview
Cloud Build executes build steps defined in a YAML file (cloudbuild.yaml) in containers, supporting:
- Building Docker images
- Running unit tests and integration tests
- Deploying to Cloud Run, GKE, or App Engine
- Creating artifacts in Artifact Registry
- Parallel execution of build steps for efficiency
Example cloudbuild.yaml for a Node.js App:
steps:
– name: ‘gcr.io/cloud-builders/npm’
args: [‘install’]
– name: ‘gcr.io/cloud-builders/npm’
args: [‘test’]
– name: ‘gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker’
args: [‘build’, ‘-t’, ‘us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/my-project/my-repo/my-app:latest’, ‘.’]
images:
– ‘us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/my-project/my-repo/my-app:latest’
Artifact Registry Overview
Artifact Registry is a centralized repository for storing container images, Maven packages, npm packages, and Python packages.
Benefits:
- Integrated with Cloud Build for CI/CD
- Secure with IAM-based access control
- Supports regional storage for reduced latency and cost
- Version control for artifacts
Example: Store and retrieve container images for multiple deployment stages (staging, production).
Step-by-Step CI/CD Pipeline Setup
Step 1: Configure Source Repository
- Use Cloud Source Repositories or GitHub/GitLab.
- Branch strategy: main for production, develop for staging.
Step 2: Configure Cloud Build
- Create cloudbuild.yaml with build, test, and deploy steps.
- Define triggers to automatically build on commits or PR merges.
Step 3: Build and Store Artifacts
- Build Docker images or packages.
- Push to Artifact Registry with version tags for traceability.
Step 4: Deploy to Cloud Run or GKE
gcloud run deploy my-app \
–image us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/my-project/my-repo/my-app:latest \
–platform managed \
–region us-central1 \
–allow-unauthenticated
- Cloud Build can automate this step with deployment triggers.
Step 5: Monitor Pipeline
- Use Cloud Monitoring and Cloud Logging to track build failures, deployment success, and latency metrics.
- Set alerts for failed builds or failed deployments.
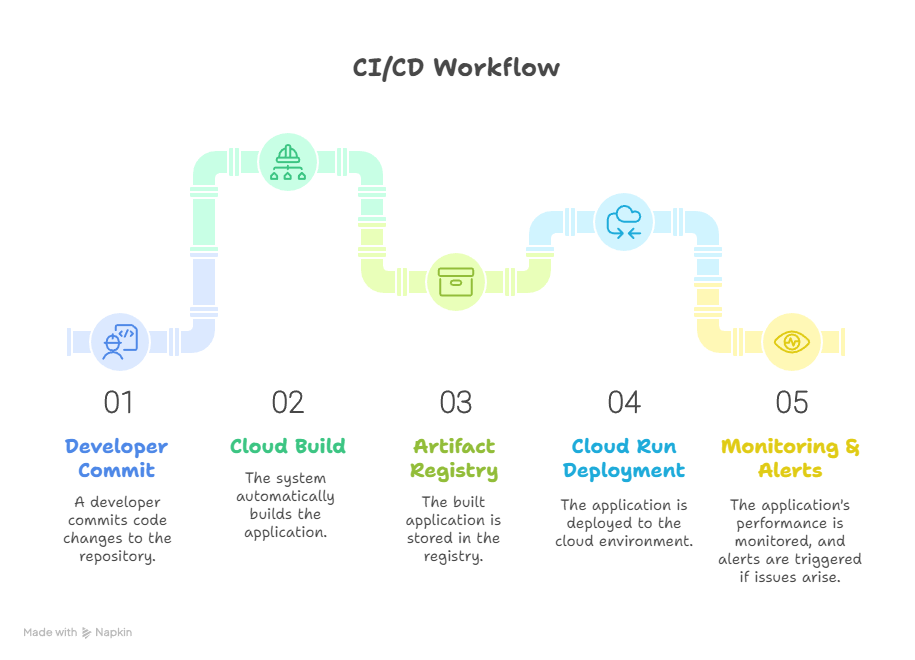
Practical Example: Deploying a REST API via CI/CD
Scenario: Automate deployment of a Node.js REST API to Cloud Run.
- Code Repository: Store API in Cloud Source Repositories.
- Cloud Build Pipeline: Install dependencies, run tests, build Docker image, push to Artifact Registry.
- Deployment: Deploy to Cloud Run automatically using Cloud Build trigger.
- Monitoring: Alert DevOps if deployment fails or latency exceeds threshold.
Diagram:- CI/CD Workflow
Best Practices for CI/CD in GCP
- Use Versioning: Tag artifacts for traceability and rollback.
- Automate Testing: Include unit, integration, and end-to-end tests in Cloud Build.
- Separate Environments: Use staging and production pipelines.
- Security: Store secrets in Secret Manager, restrict Artifact Registry access via IAM.
- Parallel Builds: Use Cloud Build parallel steps to reduce pipeline time.
- Audit & Logging: Track all build, push, and deploy events for accountability.
At Curiosity Tech, engineers learn to build CI/CD pipelines from scratch, integrate with GCP services, and optimize cost, speed, and reliability.
Advanced Practices
- Canary Deployments: Split traffic between old and new versions for safe rollouts.
- Blue-Green Deployments: Maintain two production environments and switch traffic after validation.
- Automated Rollbacks: Roll back to previous version if deployment metrics fail.
- Multi-Region Deployments: Ensure high availability across regions.
Conclusion
Mastering CI/CD with Cloud Build and Artifact Registry is critical for cloud engineers to deliver fast, reliable, and secure applications. By automating builds, tests, artifact management, and deployments, engineers can focus on developing features while minimizing errors and downtime.
At Curiosity Tech , hands-on CI/CD projects prepare engineers to design enterprise-grade pipelines, integrate with serverless and containerized applications, and optimize cloud operations.