Introduction
On Day 17, we focus on AWS cost optimization, an essential skill for cloud engineers. Managing costs efficiently ensures organizations maximize ROI, avoid unnecessary expenses, and maintain scalable and sustainable cloud architectures.
At CuriosityTech.in, learners understand that cost optimization is not just about spending less—it’s about intelligent resource planning, automation, and continuous monitoring.
1. Understanding AWS Billing and Pricing Models
AWS pricing can be complex, with different models across services:
| Service Type | Pricing Model | Description |
|---|---|---|
| EC2 | On-Demand | Pay per hour/second for running instances |
| EC2 | Reserved Instances | Commit 1 or 3 years → lower hourly cost |
| EC2 | Spot Instances | Bid for unused capacity → cheapest but can be interrupted |
| S3 | Storage Classes | Standard, Intelligent-Tiering, Glacier → cost varies by access |
| Lambda | Pay-per-invocation | Charged per 1ms of execution and memory |
| RDS | On-Demand / Reserved | Compute and storage billed separately |
| CloudFront | Pay-per-GB data transfer | Edge caching can reduce costs |
Expert Tip: Understanding each service’s pricing model is the first step toward optimized cloud cost management.
2. Core Cost Optimization Pillars
AWS cost optimization follows 5 pillars:
A. Right Sizing
- Match compute, storage, and network resources to actual usage
- Example: Use
t3.smallEC2 instance instead ofm5.largeif traffic is low
B. Reserved & Spot Instances
- Reserve instances for predictable workloads → up to 75% savings
- Use spot instances for batch jobs or non-critical workloads
C. Storage Optimization
- Use S3 Intelligent-Tiering or Glacier for infrequently accessed data
- Delete unused EBS volumes and snapshots
D. Monitoring & Automation
- CloudWatch and Cost Explorer → track usage and anomalies
- Automate shutdown of non-production environments using Lambda
E. Serverless and Managed Services
- Lambda, Fargate, and managed databases reduce idle resource costs
- Pay only for actual usage
3. AWS Cost Management Tools
| Tool | Purpose | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| AWS Cost Explorer | Visualize and analyze spending | Monthly/Service/Tag breakdowns |
| AWS Budgets | Set custom budgets | Alerts for threshold breaches |
| AWS Trusted Advisor | Recommendations for cost, performance, security | Underutilized resources, idle instances |
| AWS CloudWatch | Monitor resource usage | Detect spikes and underutilization |
| AWS Pricing Calculator | Forecast costs | Compare different architecture scenarios |
CuriosityTech.in Insight: Beginners often ignore tagging resources, which is critical for tracking costs per department, project, or environment. Proper tagging is emphasized in training.
4. Practical Cost Optimization Strategies
a) Compute Optimization
- Auto Scaling: Scale EC2 instances based on demand
- Right-sizing: Analyze CPU/memory metrics → choose smaller instance types
- Spot Instances: Run batch workloads or dev/test environments
b) Storage Optimization
- S3 Lifecycle Policies: Move older data to Glacier or delete automatically
- Delete Unused EBS Volumes: Save money from unattached storage
- Use Compression: Reduce S3 storage and data transfer costs
c) Database Optimization
- RDS Reserved Instances for predictable workloads
- Aurora Serverless for variable workloads → pay only when used
- Use Read Replicas wisely → avoid over-provisioning
d) Networking Optimization
- Use CloudFront to cache content globally → reduce direct S3 GET requests
- Review Data Transfer Out → optimize architecture to reduce cross-region traffic
5. Cost Analysis Example
| Resource | Current Usage | Optimized Usage | Monthly Cost Saving |
|---|---|---|---|
| EC2 m5.large (On-Demand) | 1 instance, 24/7 | t3.medium + Auto Scaling | 60% |
| S3 Standard Storage | 500 GB | Intelligent-Tiering | 30% |
| RDS db.t3.medium | On-Demand | Reserved 1-year | 40% |
| CloudFront | 2 TB data transfer | Enable caching, TTL 1 day | 25% |
Observation: Applying right-sizing, reserved instances, and caching can lead to 50–60% overall savings.
6. Cost Optimization Framework
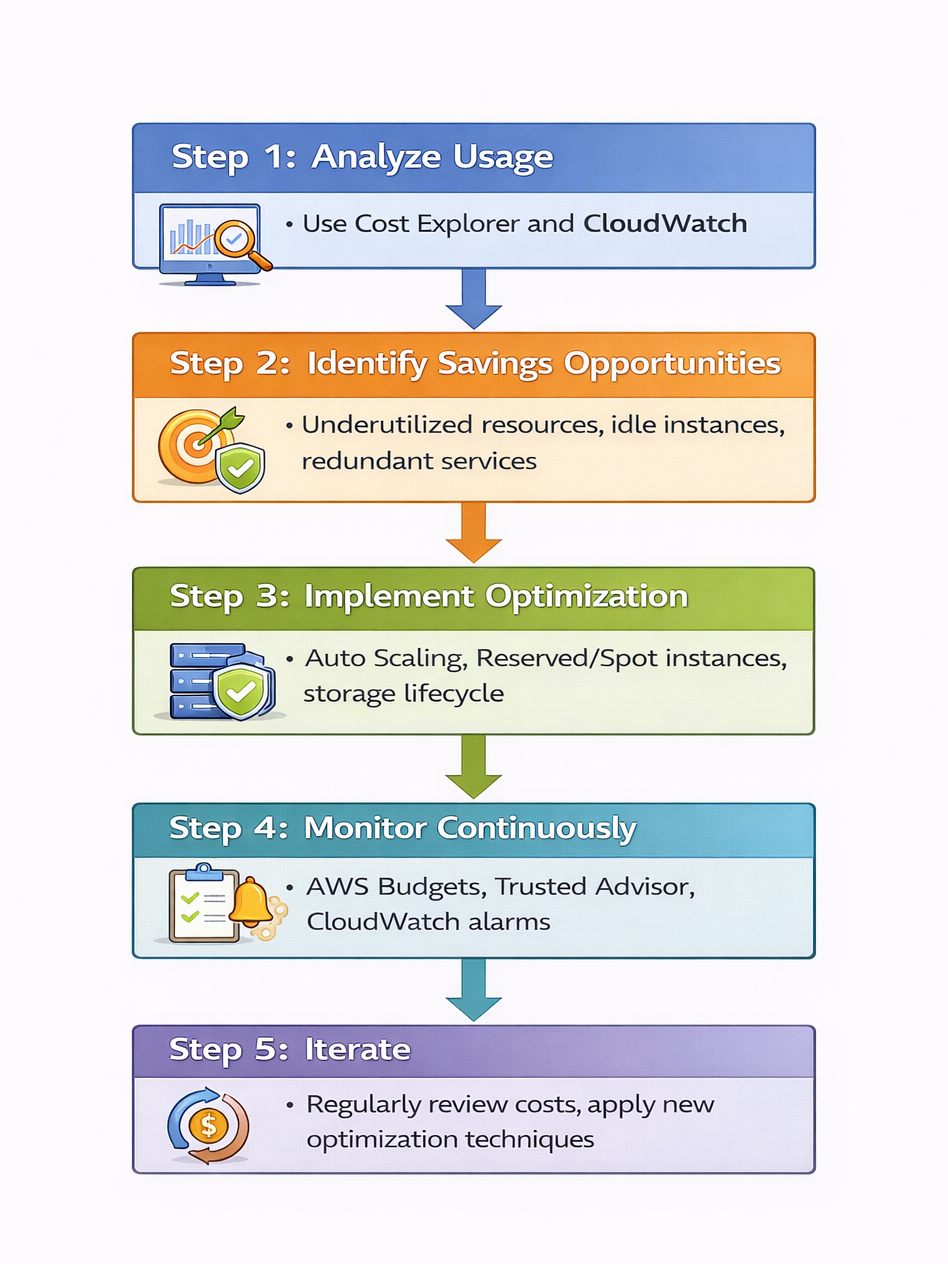
- Step 1: Analyze Usage :- Use Cost Explorer and CloudWatch
- Step 2: Identify Savings Opportunities :- Underutilized resources, idle instances, redundant services
- Step 3: Implement Optimization :- Auto Scaling, Reserved/Spot instances, storage lifecycle
- Step 4: Monitor Continuously :- AWS Budgets, Trusted Advisor, CloudWatch alarms
- Step 5: Iterate :- Regularly review costs, apply new optimization techniques
7. Common Beginner Mistakes
- Leaving non-production instances running overnight → high costs
- Using default storage classes for infrequently accessed data → overspending
- Ignoring data transfer costs → hidden expenses
- Not leveraging Reserved or Spot instances → higher compute costs
- Failing to tag resources → difficult to attribute costs
CuriosityTech.in Insight: Cost optimization labs teach learners real-world scenarios, where they analyze bills, adjust resources, and implement savings strategies without affecting performance.
8. Advanced Techniques
- Serverless Architectures: AWS Lambda + API Gateway reduces idle compute costs
- Containerization: ECS/Fargate charges only for active container runtime
- Predictive Scaling: Forecast usage with CloudWatch metrics → optimize costs proactively
- Cost Anomaly Detection: Use AI/ML in Cost Explorer to detect unusual spending
9. Path to Expertise
- Start by analyzing monthly AWS bills using Cost Explorer
- Implement resource right-sizing and delete idle resources
- Leverage Reserved and Spot instances for compute optimization
- Automate cost monitoring with AWS Budgets and CloudWatch alarms
- Continuously refine architecture using serverless and managed services
At CuriosityTech.in, learners combine theory with hands-on labs, building practical cost optimization skills, essential for real-world cloud engineering roles.
Conclusion
Cost optimization is a critical skill for AWS cloud engineers. Efficient resource management, automated monitoring, and strategic use of services can reduce expenses significantly while maintaining performance.
Through CuriosityTech.in practical labs, learners gain hands-on experience analyzing costs, implementing optimizations, and monitoring spending, becoming proficient in balancing performance and efficiency in AWS cloud environments.