Introduction
High Availability (HA) and Disaster Recovery (DR) are critical components of cloud architecture. They ensure that applications remain accessible, resilient, and recoverable even during failures. Azure provides multiple services and strategies to design, implement, and test HA/DR solutions, ensuring business continuity.
At curiositytech.in, learners gain hands-on experience building resilient cloud architectures, simulating failovers, and implementing recovery strategies for enterprise-grade applications.
1. Understanding High Availability (HA) and Disaster Recovery (DR)
| Concept | Definition |
| High Availability (HA) | Ensures minimal downtime and continuous operation of services. Achieved using redundancy and fault-tolerant architecture. |
| Disaster Recovery (DR) | Ensures data and service recovery in case of catastrophic failures (region outages, natural disasters, cyberattacks). |
Azure’s HA & DR Approach:
- Availability Zones: Physically separate datacenters within a region.
- Availability Sets: Groups of VMs with redundant resources
- Geo-Redundant Storage (GRS): Replicates data across regions
- Azure Site Recovery (ASR): Automates failover and recovery
2. High Availability Architecture
Scenario :- A financial services company wants 24/7 availability for its web application.
Key Components:
- Azure App Service with multiple instances
- Load Balancer / Traffic Manager to distribute requests
- Availability Sets for VMs
- SQL Database with Geo-Replication
Diagram :- High Availability Setup
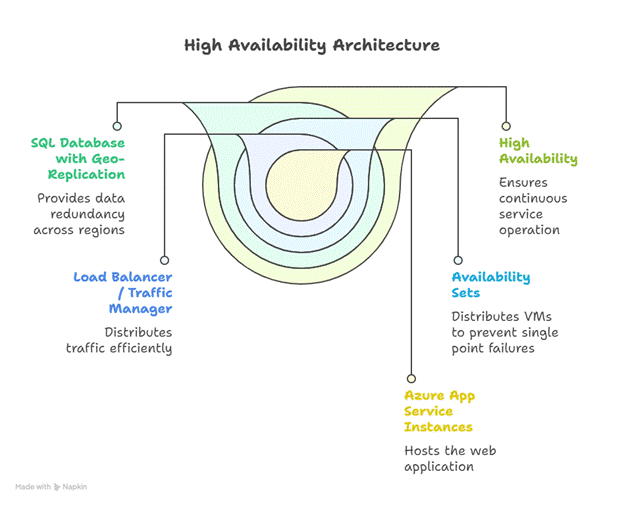
Insights:
- Multi-region deployment ensures zero downtime during regional failures
- Load balancing distributes traffic evenly, avoiding resource overload
3. Disaster Recovery Strategy
Scenario :- A SaaS startup wants to ensure business continuity if Region 1 fails.
Key Steps:
- Replicate VMs: Use Azure Site Recovery to replicate production VMs to secondary region
- Replicate Database: Use SQL Database Geo-Replication to replicate to another region
- Storage Backup: Use Geo-Redundant Storage (GRS) for blobs and files
- Failover Plan: Automate or manually trigger failover
- Testing: Conduct failover drills to validate DR strategy
Diagram: Disaster Recovery Workflow
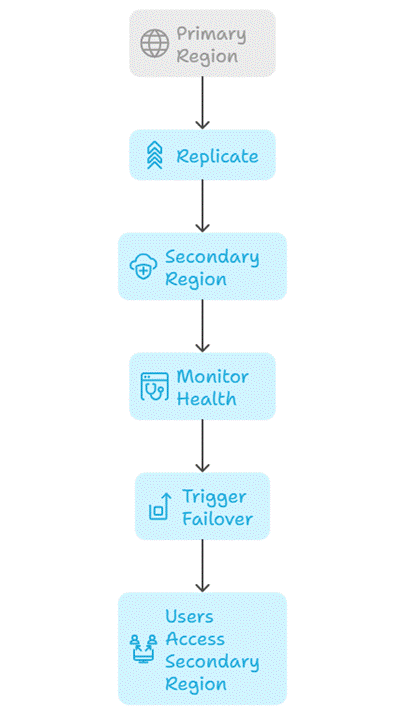
4. Step-by-Step Implementation
Step 1: Configure Availability Sets
az vm availability-set create \
–resource-group RG-HA-DR \
–name AS-HA \
–platform-fault-domain-count 2 \
–platform-update-domain-count 5
- Ensures VMs are spread across fault and update domains
Step 2: Deploy Geo-Redundant Storage
- Enable GRS for storage accounts to replicate across regions
Step 3: Configure Azure SQL Geo-Replication
az sql db replica create \
–name MyDatabase \
–resource-group RG-HA-DR \
–server PrimaryServer \
–partner-server SecondaryServer
- Enables readable secondary database for HA and DR
Step 4: Enable Azure Site Recovery
- Replicate VMs and workloads to secondary region
- Configure Recovery Plan with failover priorities
Step 5: Testing & Monitoring
- Use test failover to validate recovery time objective (RTO)
- Monitor replication health and metrics
5. Best Practices for HA & DR
| Area | Best Practices |
| Compute & App Services | Use multiple instances, auto-scaling, Availability Zones |
| Database | Enable Geo-Replication, backups, and failover groups |
| Storage | Use GRS or RA-GRS for critical data |
| Networking | Use Traffic Manager or Azure Front Door for geo-load balancing |
| Recovery Planning | Regular DR drills, define RTO & RPO, and maintain documentation |
Scenario :- A healthcare platform conducts quarterly DR drills, simulating a region outage. Failover to secondary region completes in less than 5 minutes, ensuring zero disruption for patients and clinicians.
6. Expert Tips for Cloud Engineers
- Understand RTO & RPO: Recovery Time Objective & Recovery Point Objective are critical metrics for HA/DR planning
- Test Regularly: Conduct simulated failovers to verify effectiveness
- Automate Recovery: Use Azure Site Recovery and Runbooks
- Monitor Continuously: Azure Monitor and Log Analytics provide replication health insights
- Cost-Effective Design: Use auto-scaling and spot VMs for non-critical workloads
At curiositytech.in, learners practice building HA/DR architectures, simulate region failovers, and analyze metrics to optimize resilience in real-world scenarios.
Conclusion
High Availability and Disaster Recovery are non-negotiable for enterprise cloud applications. Azure provides the tools and strategies to maintain uptime, protect data, and recover quickly. By implementing multi-region architectures, replication, failover plans, and monitoring, engineers can ensure robust business continuity. Hands-on labs at curiositytech.in provide practical experience in designing resilient, production-ready cloud environments.



