Introduction
Migrating enterprise applications to the cloud is a complex but critical process for modern businesses. Azure provides tools, best practices, and managed services that simplify migration, minimize downtime, and improve scalability.
At curiosity tech learners gain hands-on experience planning and executing migrations, covering assessment, migration strategies, optimization, and post-migration monitoring.
1. Case Study Overview
Client Scenario: A mid-sized financial services company wants to migrate its on-premises ERP and customer management applications to Azure. Key goals include:
- Minimize downtime and business disruption
- Reduce operational costs and hardware dependency
- Improve scalability and resilience
- Integrate with cloud services like Azure SQL Database, AKS, and App Service
Current On-Premises Architecture:
- Multiple Windows and Linux VMs
- SQL Server databases hosted on local SAN storage
- Monolithic application with web, API and background services
- Load balancer for user traffic
2. Migration Strategy
Phases of Migration:
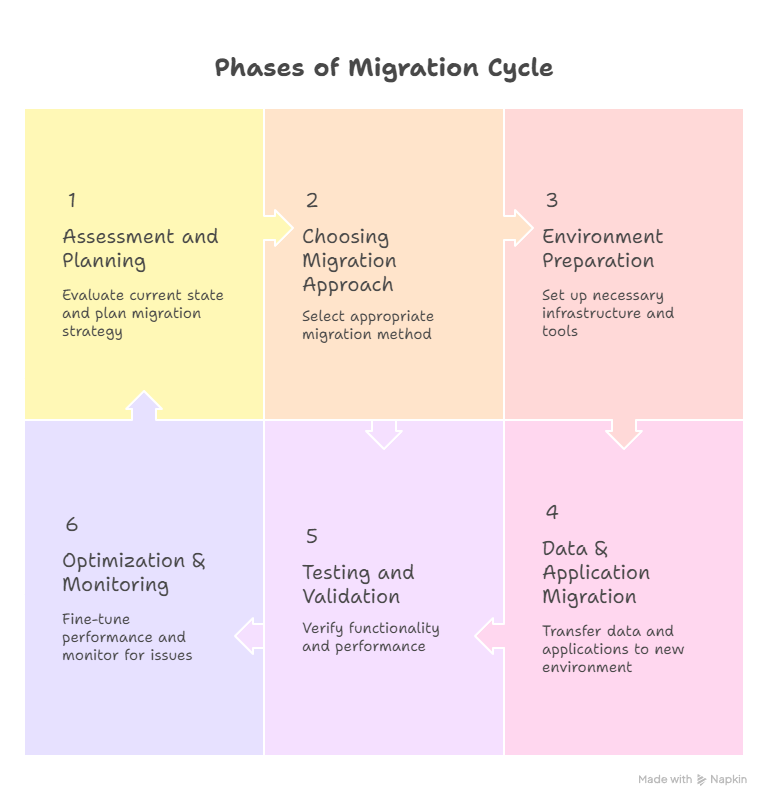
Migration Approach:
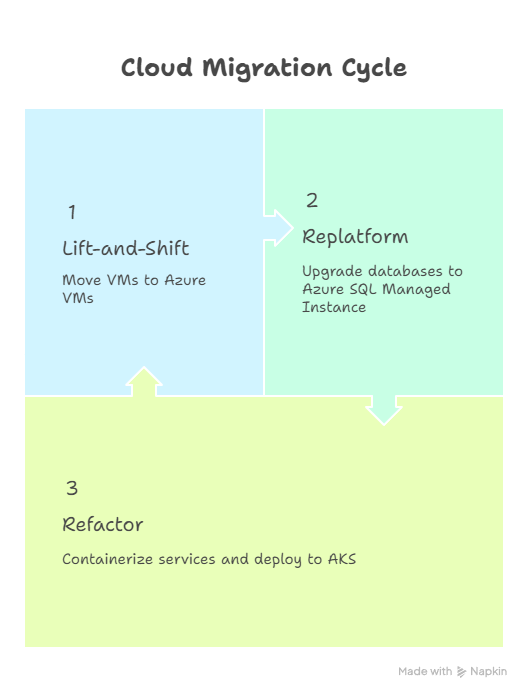
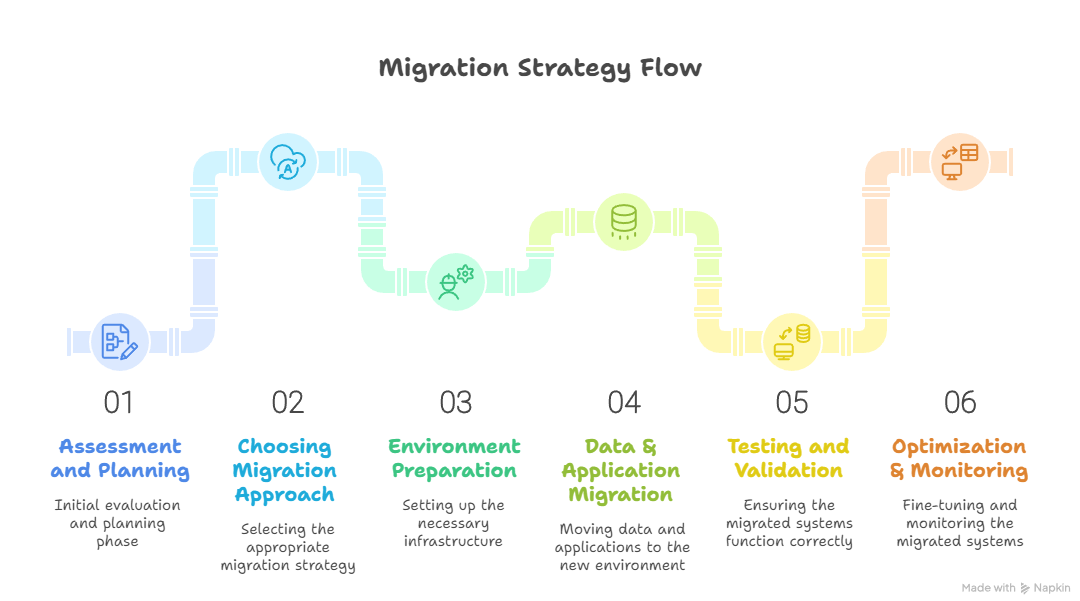
Diagram: Migration Strategy Workflow
3. Step-by-Step Migration Execution
Step 1: Assessment
- Use Azure Migrate to scan on-premises VMs, databases, and storage
- Identify dependencies between applications
- Estimate cost and sizing for Azure resources
Tools: Azure Migrate, Dependency Visualization, Azure Cost Calculator
Step 2: Environment Preparation
- Create Azure Resource Groups and VNETs
- Configure subnets, NSGs, and load balancers
- Set up Azure Site Recovery for replication of critical VMs
Step 3: Data Migration
- Migrate databases using Azure Database Migration Service (DMS)
- Ensure schema compatibility and minimal downtime
- Enable transaction replication for near-real-time sync
az dms project create –name ERP-Migration –resource-group RG-Migration –location eastus
az dms task create –project-name ERP-Migration –name DB-Migration-Task
Step 4: Application Migration
- Lift-and-Shift: Move on-premises VMs to Azure VMs
- Replatform: Upgrade SQL databases to Managed Instances
- Refactor: Containerize APIs and deploy to AKS clusters for scalability
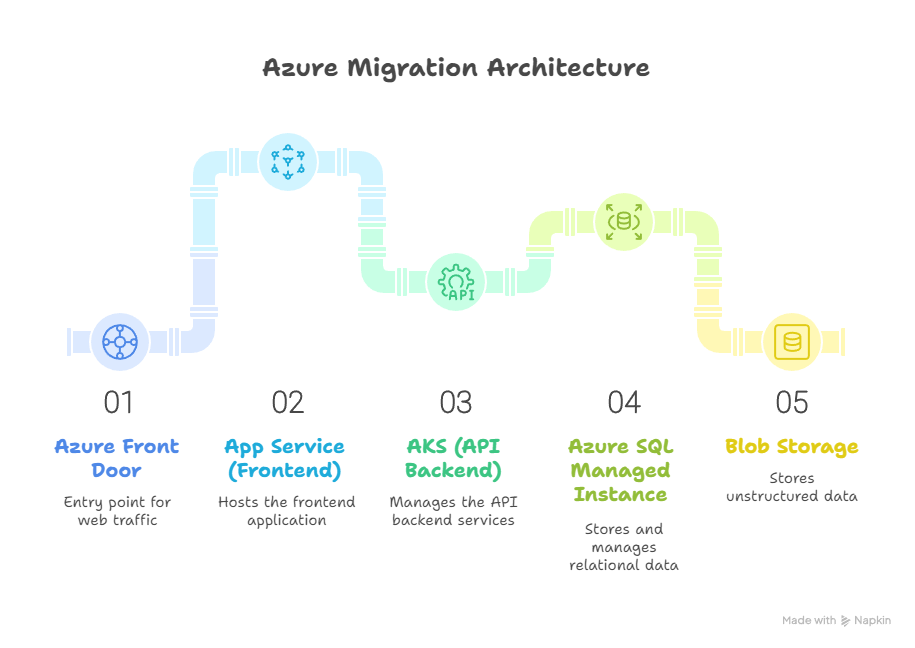
Diagram: Migrated Architecture
Azure Front Door → App Service (Frontend) → AKS (API Backend) → Azure SQL Managed Instance → Blob Storage
Step 5: Testing & Validation
- Functional Testing: Ensure apps work as expected
- Performance Testing: Validate response times and scalability
- Failover Testing: Test HA & DR configuration
Scenario: During testing, the e-commerce backend scaled automatically under simulated traffic spikes, validating autoscaling policies in AKS and App Service.
Step 6: Production Cutover
- Switch traffic to Azure environment using DNS updates or Azure Front Door routing
- Monitor application health using Azure Monitor and Application Insights
- Decommission on-premises resources gradually
4. Optimization After Migration
- Enable auto-scaling for compute resources
- Move archived files to cool or archive Blob storage tiers
- Implement cost monitoring and optimization using Azure Cost Management
- Leverage Azure Policy for compliance and governance
5. Lessons Learned from the Case Study
- Comprehensive Assessment is Critical: Identifying dependencies avoids downtime
- Use Managed Services: Reduces maintenance overhead and improves scalability
- Test Everything: Functional, performance, and DR testing ensures smooth cutover
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuous monitoring post-migration avoids cost overruns
- Document Migration Process: Ensures repeatability for future workloads
At curiositytech.in, learners simulate end-to-end enterprise migration projects, gaining practical experience in planning, executing, and optimizing cloud adoption strategies.
Conclusion
Migrating enterprise applications to Azure Cloud requires careful planning, strategy selection, and execution. By following a structured approach—assessment, migration, testing, cutover, and optimization—cloud engineers can deliver high-performing, scalable, and cost-efficient solutions. Hands-on projects at curiosity tech prepare learners to manage real-world migrations with confidence and expertise.



