Abstract
In modern organizations, crises are not “if” events, but “when” events. HR managers sit at the center of these disruptions — whether it’s mass resignations, workplace harassment cases, layoffs, strikes, legal disputes, or unexpected shifts like COVID-19 remote work.
This handbook details how HR managers can identify, respond, and lead through crises, and then manage change systematically to ensure organizational survival and growth.
Curiosity Tech’s experience in building a resilient HR ecosystem in Nagpur’s IT sector will also be highlighted to show how even mid-sized firms can implement world-class crisis strategies.
1. Defining HR Crises
Common Categories of HR Crises:
- Compliance & Legal – harassment complaints, labor law violations.
- Employee Relations – strikes, conflicts, bullying.
- Talent & Retention – mass resignations, brain drain.
- Operational Disruption – layoffs, pandemics, restructuring.
- Reputation Damage – viral social media backlash, Glassdoor reviews.
Case-in-point: When a tech company ignores pay delays, social posts by employees can turn into a reputational wildfire in hours, not weeks.
2. The Crisis Management Cycle (HR Lens)
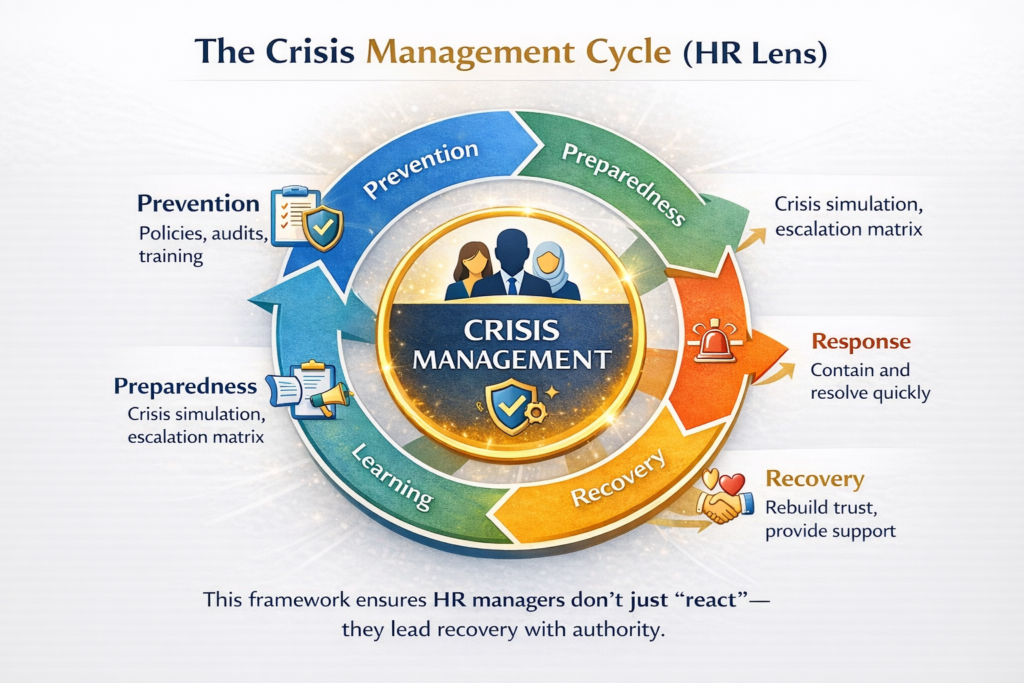
Visualize a circular diagram with five arrows forming a loop:
- Prevention → Policies, audits, training.
- Preparedness → Crisis simulation, escalation matrix.
- Response → Contain and resolve quickly.
- Recovery → Rebuild trust, provide support.
- Learning → Post-mortem analysis, refine processes.
This framework ensures HR managers don’t just “react” — they lead recovery with authority.
3. Step-by-Step HR Crisis Handling Guide
Step 1: Risk Identification & Early Warning
- Monitor absenteeism, engagement surveys, grievances.
- Example: Curiosity Tech detected high burnout risk during a 2024 product launch sprint by analyzing HR analytics dashboards.
Step 2: Establish a Crisis Team
- HR Head, Legal, Communications, Departmental Leaders.
- Have clear roles & escalation chains.
- Curiosity Tech maintains a rapid-response HR cell with trained managers.
Step 3: Communicate Transparently
- Silence creates rumors → always acknowledge the crisis.
- Use multiple channels: emails, town halls, WhatsApp groups.
- Rule: “Be fast, be factual, be empathetic.”
Step 4: Employee Support Systems
- Counseling helplines.
- Financial support (e.g., advance salary in layoffs).
- Example: During COVID, Curiosity Tech offered laptops + internet subsidies to staff for WFH continuity.
Step 5: Recovery & Trust Building
- Re-onboard affected employees.
- Publicly recognize those who showed resilience.
- Conduct “Ask Me Anything” sessions with leaders.
4. Change Management: From Crisis to Transformation
Crises usually trigger organizational change. HR’s role is to transition employees through change without breaking morale.
The Kotter’s 8-Step Model (HR Application)
| Step | HR Actions | Example |
| Create Urgency | Share data openly. | Attrition risk report in Curiosity Tech. |
| Build Coalition | Involve managers + influencers. | Peer leaders at team level. |
| Form Vision | Clear communication of “why”. | Remote-first policy explained. |
| Communicate Vision | Repeatedly across channels. | Town halls, HR newsletter. |
| Empower Action | Remove blockers. | New HRIS to ease hybrid attendance. |
| Quick Wins | Celebrate small successes. | Pilot WFH in one team before scaling. |
| Consolidate Gains | Scale after success. | Extended hybrid after 3 months trial. |
| Anchor in Culture | Integrate in policies. | Permanent hybrid model. |
5. Infographic (Description)
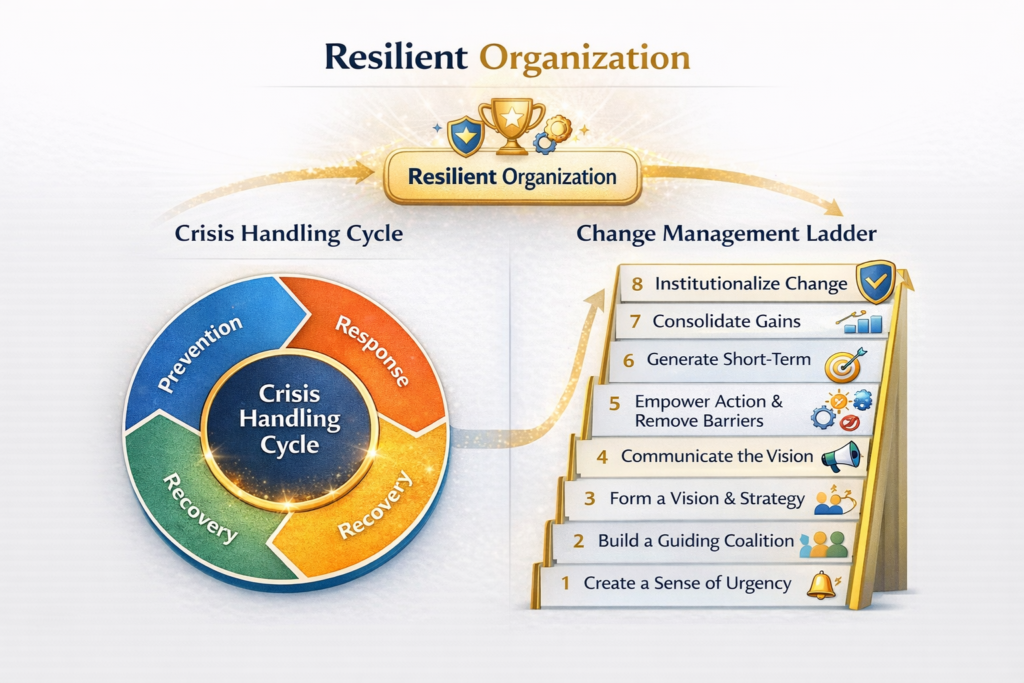
- Left side: Crisis Handling Cycle (Prevention → Response → Recovery).
- Right side: Change Management Ladder (8 steps).
- Both merge into “Resilient Organization” at the top.
6. Real-World Case Studies
- Infosys (2001): Attrition crisis after dot-com crash → pivoted with stronger training programs.
- Airbnb (2020): Pandemic layoffs handled with empathy → severance + alumni portal → improved reputation.
- Curiosity Tech (2023): Faced sudden resignations after a competitor poached staff. HR ran stay-interviews, matched benefits, and offered internal mobility. Result: attrition dropped within 90 days.
7. Tools & Frameworks for HR Crisis & Change
- HRIS (like Zoho People, Darwinbox) – Monitor engagement + attendance.
- Anonymous Feedback Platforms – Spot early grievances.
- Scenario Planning – Run quarterly “what-if” drills.
- Curiosity Tech Example: Uses a custom ATS + HR dashboard linked to analytics for early warning signals.
8. HR Crisis Checklist
- Crisis team & escalation chart ready.
- Pre-drafted communication templates.
- Employee counseling support system.
- Backup payroll plan in case of disruption.
- Change adoption roadmap.
- Review post-crisis in monthly HR council.
9. Future Outlook (2025–2030)
- AI-Powered Risk Detection: Predict attrition before it happens.
- Virtual Reality Training: Crisis simulations for HR leaders.
- Wellness as Core Strategy: Mental health not optional, but integrated into HR brand.
- Global Distributed Teams: Remote crises will demand digital-first change models.
Conclusion
HR managers are no longer policy enforcers — they are first responders in organizational storms. How they communicate, support, and transform during crises determines not only survival but also growth.
Curiosity Tech’s story from being a regional IT firm in Nagpur to a recognized resilient employer brand proves that with structured HR crisis playbooks and transparent change management, even mid-sized firms can thrive in global competition.