Introduction
Becoming a professional robotics engineer requires a structured approach combining education, practical experience, certifications, and continuous learning. This roadmap guides aspiring engineers through milestones, skill development, and real-world experience, helping them transition from a beginner to an industry-ready professional.
At Curiosity Tech., learners access career planning tutorials, hands-on projects, and expert mentorship to navigate this roadmap effectively.
1. Stage 1: Foundational Learning (0–12 months)
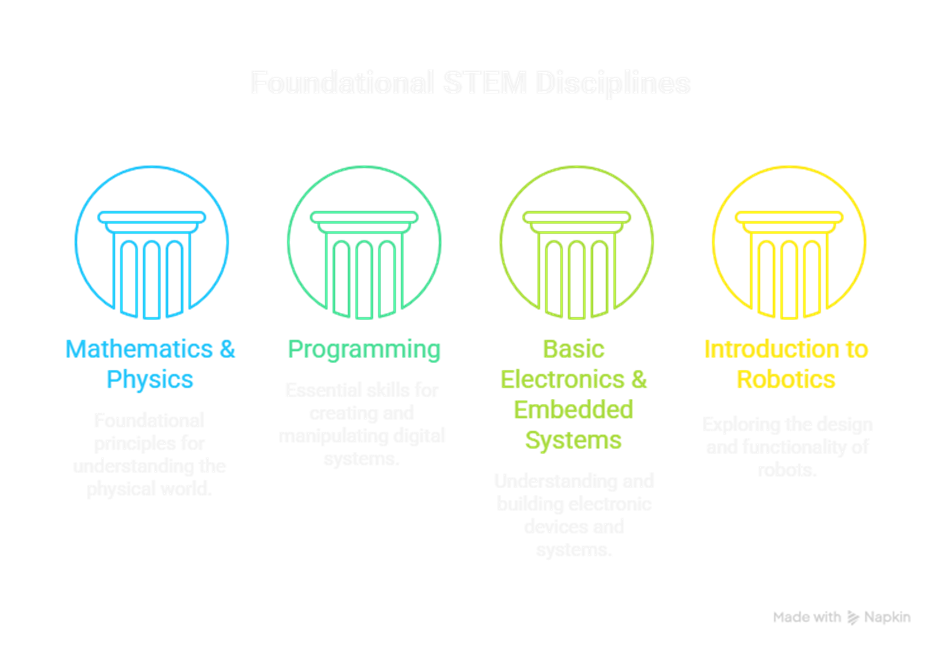
Objective: Build a strong foundation in mathematics, physics, programming, and basic robotics concepts.
Key Focus Areas:
- Mathematics & Physics: Linear algebra, calculus, kinematics, dynamics.
- Programming: Python, C/C++ fundamentals.
- Basic Electronics & Embedded Systems: Arduino, Raspberry Pi, sensors, actuators.
- Introduction to Robotics: Basic robot types, motors, controllers, sensors.
Practical Steps:
- Complete online courses in robotics fundamentals.
- Build small robots, such as line-following or obstacle-avoiding robots.
- Document projects to track learning.
Diagram Idea: Timeline showing months 0–12 with foundational skills and beginner projects.
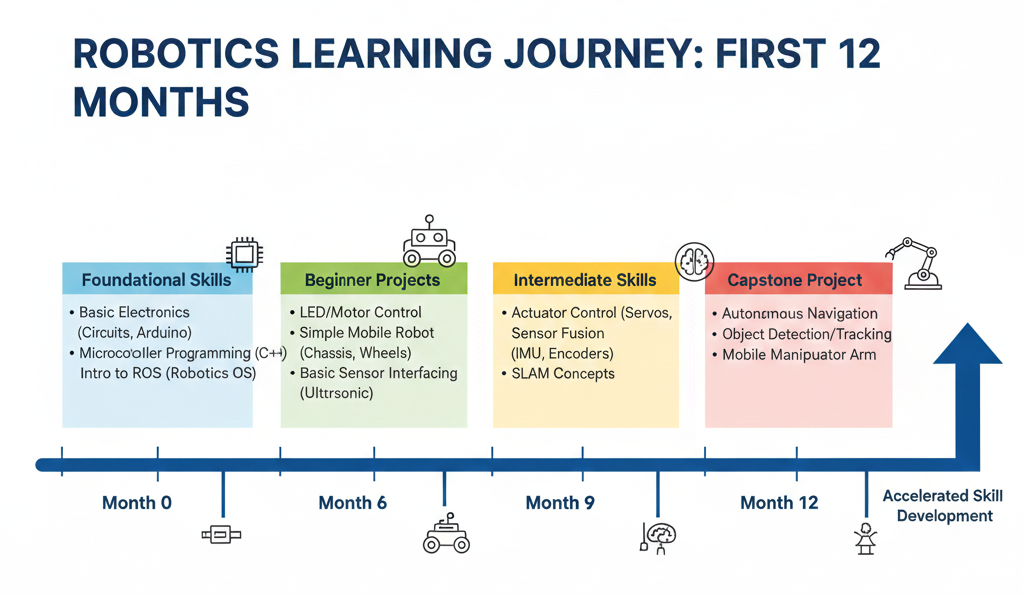
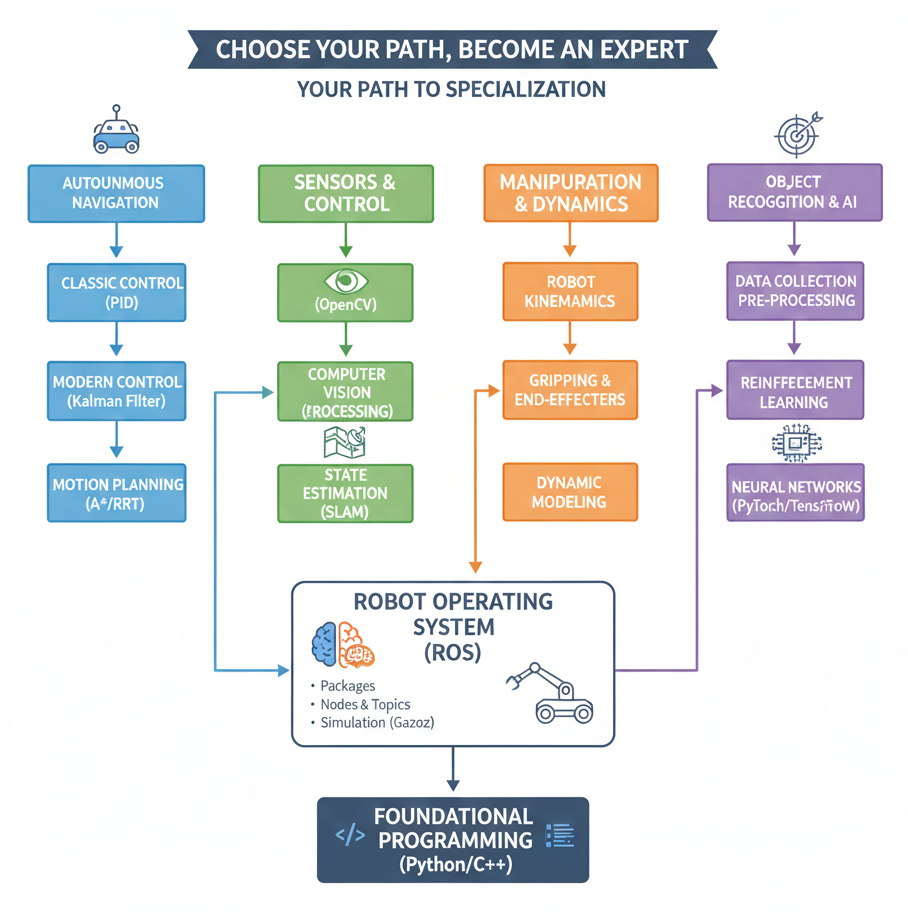
2. Stage 2: Intermediate Skills & Specialization (12–24 months)
Objective: Gain hands-on experience in robot programming, ROS, and simulation tools, and begin specialization in a chosen field.
Key Focus Areas:
- ROS (Robot Operating System): Navigation, motion planning, sensor integration.
- Control Systems: PID controllers, trajectory planning.
- Simulation Tools: Gazebo, V-REP, Webots.
- Intermediate Projects: Mobile robots, robotic arms, and SLAM-enabled robots.
Specialization Paths:
- Industrial Robotics: Automation, PLC, collaborative robots.
- Healthcare Robotics: Surgical, rehabilitation, telepresence robots.
- Autonomous Systems: Drones, AGVs, self-driving platforms.
- Service Robotics: Education, hospitality, and social robots.
Actionable Strategies:
- Join online robotics challenges or hackathons.
- Start contributing to ROS or open-source robotics projects.
- Gain experience with hardware-software integration.
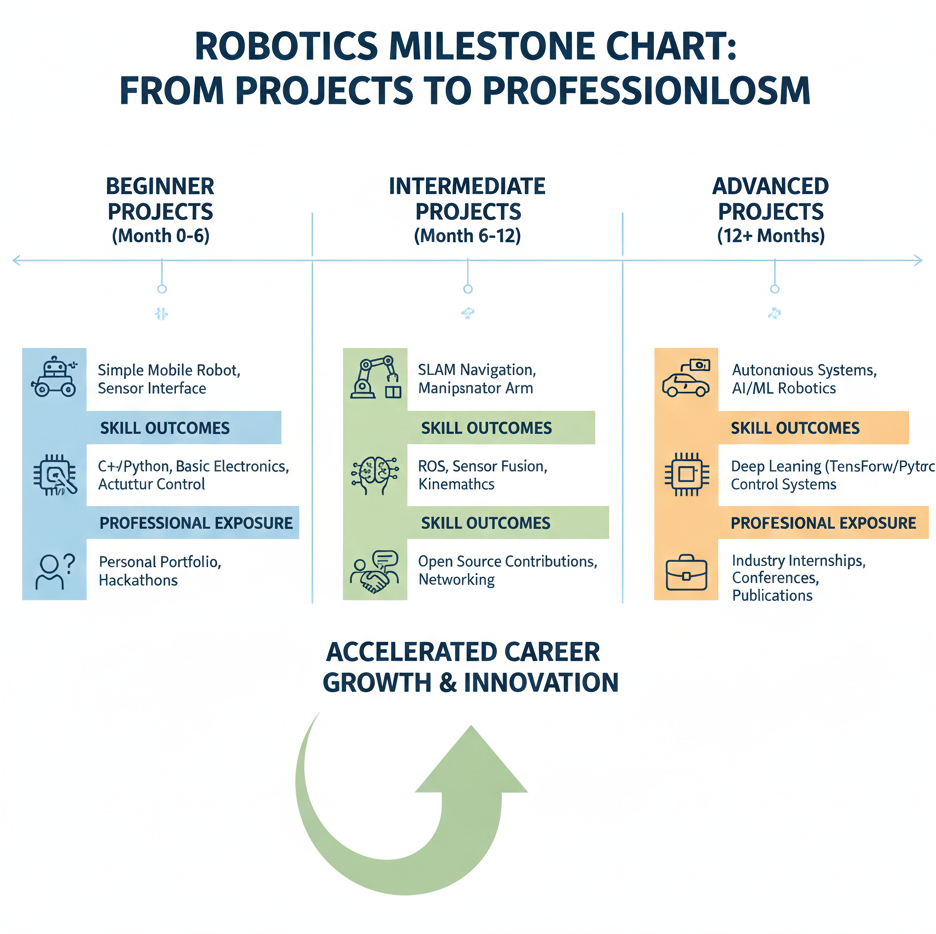
3. Stage 3: Advanced Projects & Professional Experience (24–36 months)
Objective: Apply robotics knowledge in real-world environments, develop expertise, and prepare for certifications.
Key Focus Areas:
- AI & Machine Learning: Computer vision, reinforcement learning, autonomous navigation.
- Cloud & IoT Robotics: Remote monitoring, cloud computation, collaborative systems.
- Complex Projects: Autonomous drones, smart warehouses, teleoperated robots.
- Internships & Industry Experience: Gain exposure to industrial or research robotics applications.
Actionable Steps:
- Undertake capstone projects integrating AI, sensors, and cloud robotics.
- Document experiments and results.
- Prepare for certifications like ROS Developer, AI Robotics Specialist, or Industrial Automation Expert.
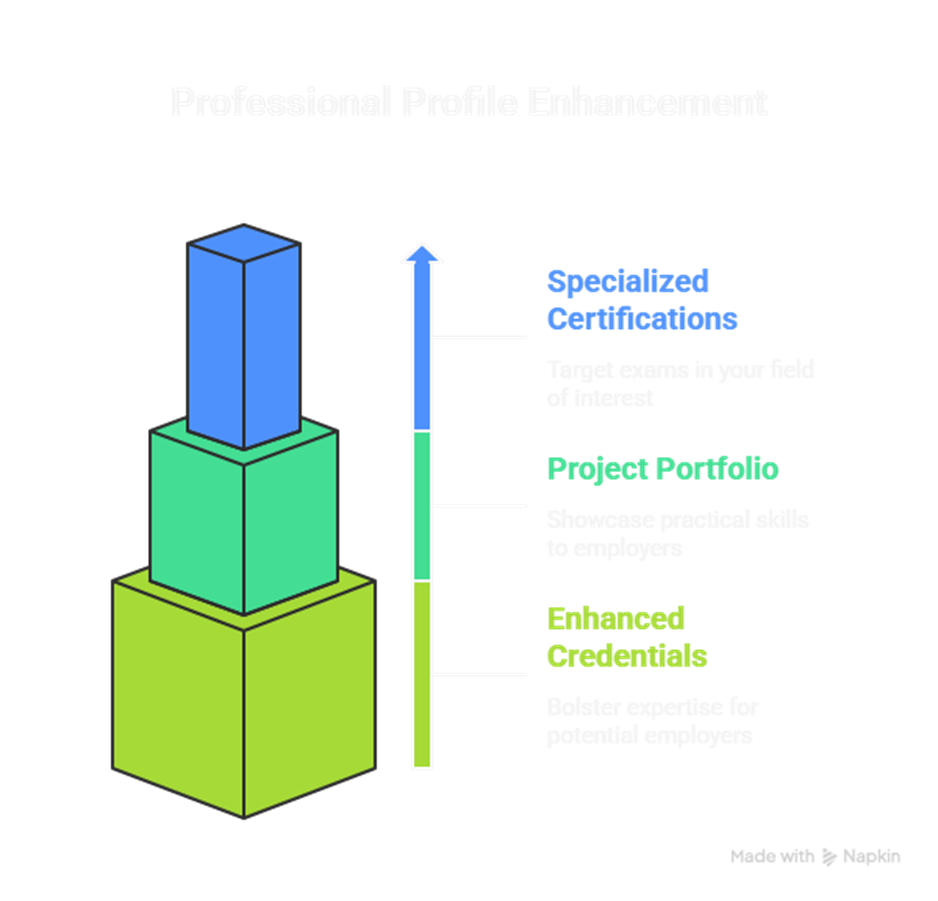
4. Stage 4: Certification & Professional Recognition (36–48 months)
Objective: Validate expertise through industry-recognized certifications and establish professional credibility.
Recommended Certifications:
| Certification | Provider / Focus Area |
| ROS Developer Certification | Open Robotics / ROS programming |
| AI & Machine Learning in Robotics | Coursera / EdX / TensorFlow integration |
| Industrial Robotics & PLC | Siemens / Rockwell |
| Cloud & IoT Robotics | AWS IoT / Azure IoT Hub |
| Professional Robotics Engineer | IEEE / Robotics Certification Board |
Actionable Strategies:
- Target specialized certification exams in your field of interest.
- Build a portfolio of projects showcasing practical skills.
- Network with professionals via conferences, webinars, and LinkedIn.
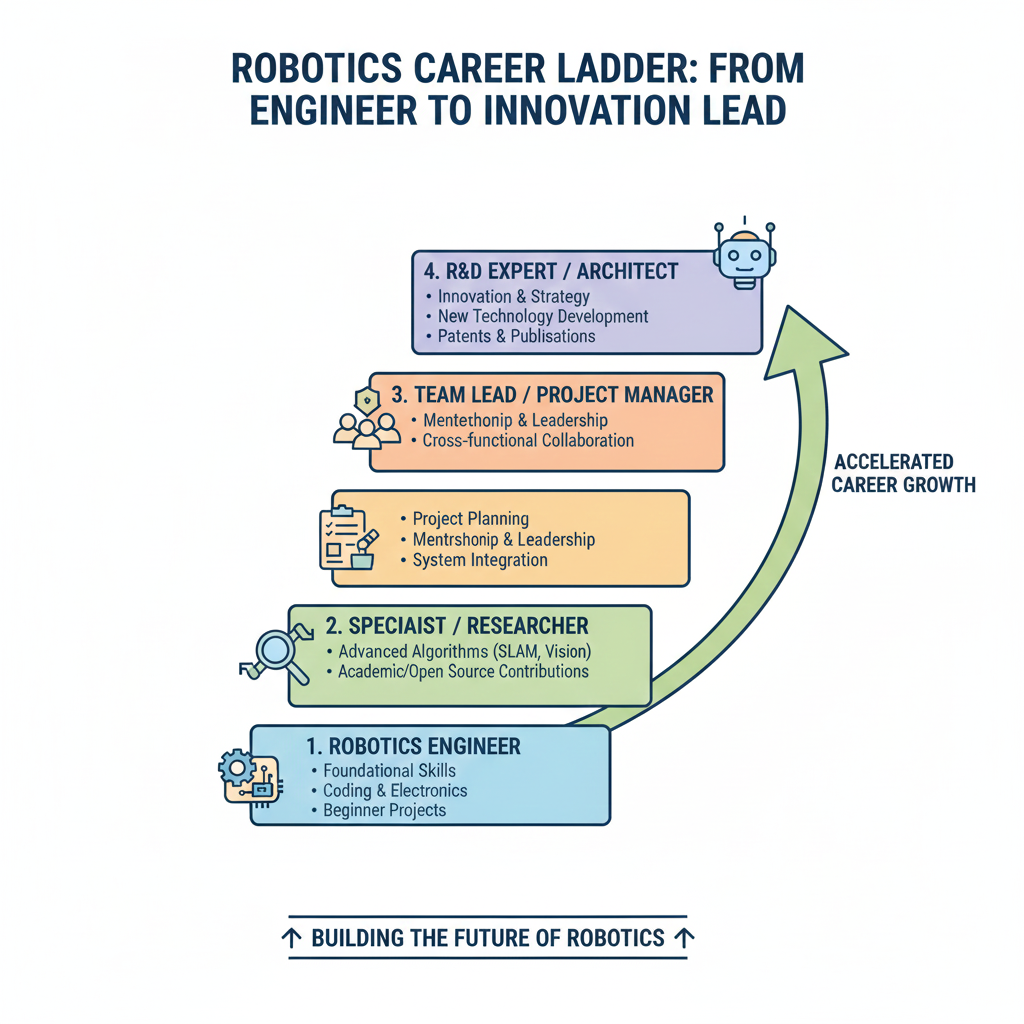
5. Stage 5: Expert-Level & Leadership Roles (48+ months)
Objective: Transition into R&D, system architecture, or team leadership roles in robotics.
Key Focus Areas:
- Advanced R&D: AI-driven robotics, swarm robotics, human-robot interaction.
- System Architecture: Designing multi-robot systems and integrated solutions.
- Mentorship & Leadership: Lead teams, train junior engineers, manage robotics projects.
Actionable Steps:
- Take on complex, multi-disciplinary projects in industry or academia.
- Publish research papers or case studies in robotics journals.
- Develop innovative solutions and pursue patents or awards.
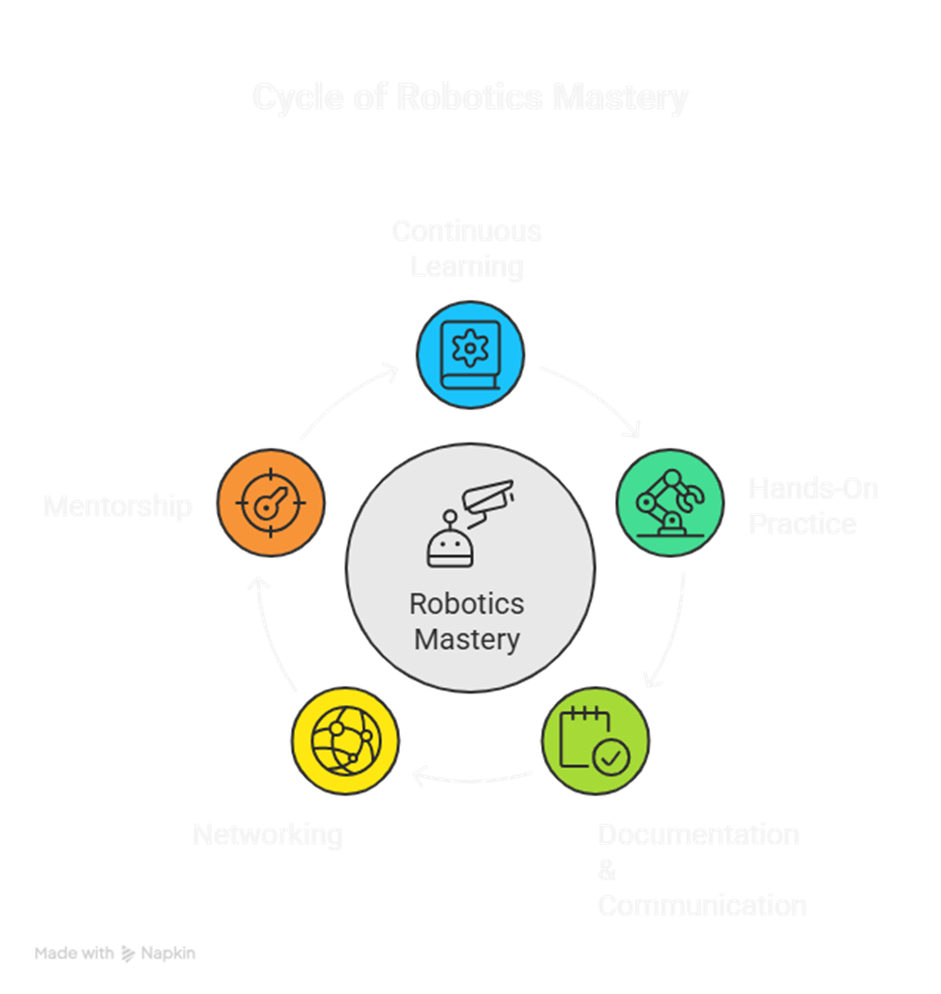
6. Additional Tips for Success
- Continuous Learning: Robotics is evolving; always learn new tools and AI techniques.
- Hands-On Practice: Projects and simulations are essential for mastering real-world robotics.
- Documentation & Communication: Maintain detailed logs and share insights with the community.
- Networking: Join robotics forums, professional groups, and competitions.
- Mentorship: Seek guidance from experienced engineers and platforms like CuriosityTech.in.
Curiosity Tech provides a complete roadmap, hands-on projects, and mentorship programs that align with industry requirements, enabling learners to transition seamlessly from beginners to professional robotics engineers.
Conclusion
Becoming a professional robotics engineer requires a structured roadmap combining education, practical projects, specialization, certification, and continuous learning. By following the stages outlined—from foundational skills to expert-level R&D—you can develop the expertise, credibility, and industry readiness necessary to thrive in the robotics field. Platforms like Curiosity Tech provide practical tutorials, project guidance, and career mentorship, helping learners achieve their goals efficiently and confidently.