Introduction
The landscape of mobile app development has transformed dramatically in 2025. Developers now have the choice between native apps and cross-platform frameworks. Among cross-platform solutions, three frameworks have emerged as dominant: Flutter, React Native, and Xamarin.
Choosing the right framework is critical for performance, scalability, UI design, and developer productivity. At CuriosityTech (Website: https://curiositytech.in, Phone: +91-9860555369, Email: contact@curiositytech.in), we help aspiring developers and enterprises understand these frameworks in-depth to make informed decisions.
This blog will analyze each framework’s architecture, performance, UI capabilities, strengths, limitations, and real-world use cases, providing a roadmap for beginners and advanced developers.
1. Flutter – Google’s Cross-Platform Powerhouse
Overview
- Language: Dart
- Launch Year: 2017
- Best For: Highly customizable UIs, near-native performance apps, rapid prototyping.
Flutter enables developers to build single codebase applications for Android, iOS, web, and desktop. Its core philosophy revolves around widgets, where every UI element is customizable and reusable.
Architecture
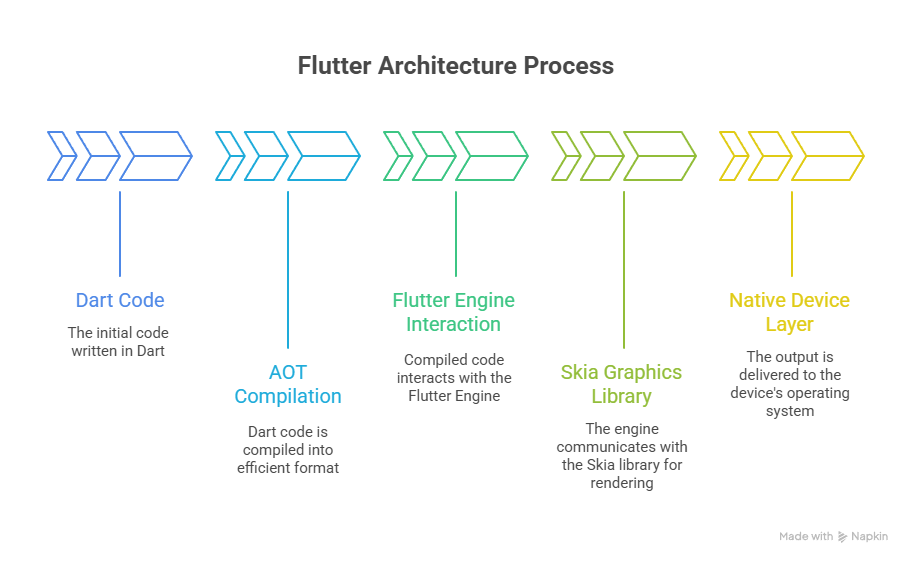
- Dart code is compiled ahead-of-time (AOT) to native machine code, ensuring high performance.
- The Skia graphics engine handles rendering, enabling smooth animations across platforms.
Strengths
- Hot Reload for instant UI updates.
- Rich widget library for creating sophisticated, customizable UIs.
- Large community support and growing plugin ecosystem.
Limitations
- Larger binary size.
- Dart language requires learning if new to developers.
- Some native device features may need third-party plugins.
Example: Flutter Button Widget
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () => print(‘Button Pressed’),
child: Text(‘Click Me’),
)
This single widget works seamlessly on both iOS and Android, showcasing Flutter’s “write once, run anywhere” capability.
2. React Native – JavaScript-Based Framework
Overview
- Language: JavaScript / TypeScript
- Launch Year: 2015
- Best For: Developers familiar with web development, rapid development cycles.
React Native bridges JavaScript code to native components, allowing mobile apps to reuse code across platforms while maintaining a near-native experience.
Architecture
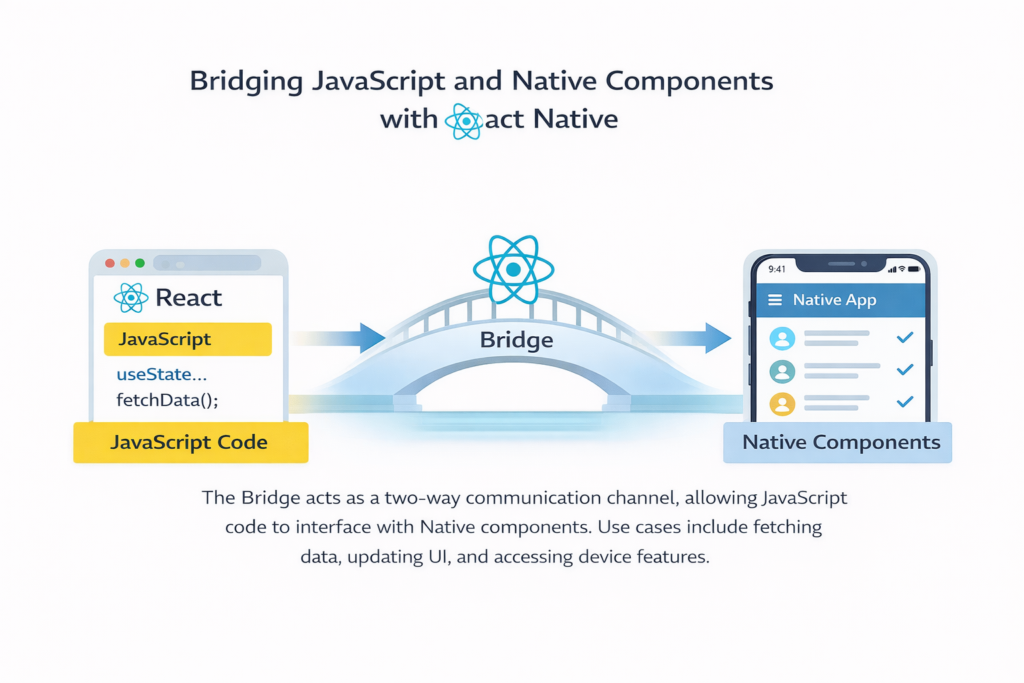
- The JavaScript thread communicates with native modules through a bridge.
- Developers can also write native modules in Swift, Objective-C, or Java/Kotlin when necessary.
Strengths
- Leverages existing web development skills.
- Hot Reload for instant feedback.
- Large ecosystem with numerous open-source libraries.
Limitations
- Performance may be slightly lower for heavy computations.
- Debugging native modules can be challenging.
- Bridge architecture may introduce minor latency in complex apps.
Example: React Native Button
import { Button, View, Text } from ‘react-native’;
export default function App() {
return (
<View>
<Text>Hello React Native</Text>
<Button title=”Click Me” onPress={() => alert(‘Button Pressed’)} />
</View>
);
}
This demonstrates the ease of building cross-platform UI components with minimal platform-specific code.
3. Xamarin – Microsoft’s .NET Solution
Overview
- Language: C#
- Launch Year: 2011
- Best For: Enterprise apps, apps needing integration with .NET backends.
Xamarin allows developers to write C# code that compiles into native assemblies for iOS and Android, offering near-native performance. Xamarin.Forms further allows UI code sharing across platforms.
Architecture
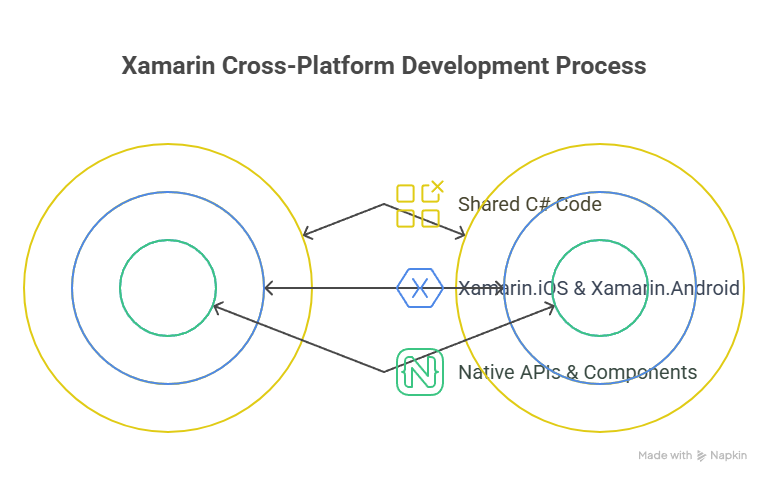
Provides full access to native APIs, while allowing business logic and some UI components to be shared.
Strengths
- Near-native performance.
- Strong support for enterprise solutions.
- Seamless integration with Microsoft ecosystem.
Limitations
- UI customization can be complex.
- App size may be larger.
- Community support is smaller than Flutter or React Native.
Example: Xamarin Button
Button button = new Button { Text = “Click Me” };
button.Clicked += (sender, args) =>
{
DisplayAlert(“Alert”, “Button Pressed”, “OK”);
};
This code demonstrates event handling and cross-platform functionality using C#.
Comparison Table: Flutter vs React Native vs Xamarin
How to Become an Expert in Cross-Platform Frameworks
Conclusion
Choosing the right cross-platform framework in 2025 is critical for performance, scalability, and developer productivity.
- Flutter excels in UI customization and smooth animations.
- React Native is ideal for web developers seeking rapid development cycles.
- Xamarin provides enterprise-grade solutions with seamless .NET integration.
By understanding these frameworks, experimenting with hands-on projects, and leveraging expert guidance from CuriosityTech, developers can confidently deliver robust, high-performance mobile apps across multiple platforms.



