Introduction
In 2025, data preprocessing has become one of the most critical skills for a Machine Learning Engineer. Raw data from real-world sources—like customer transactions, sensor logs, or social media—is messy, incomplete, and inconsistent. Without proper preprocessing, even the most advanced ML algorithms fail.
At CuriosityTech.in (Nagpur, Wardha Road, Gajanan Nagar), we emphasize that 70% of a data scientist or ML engineer’s work involves preprocessing. Today, we’ll explore preprocessing in extreme depth: cleaning, scaling, encoding, and making datasets model-ready.
1. Why Preprocessing is Mandatory
- Inconsistent Data → Missing or erroneous values distort model predictions.
- Feature Scaling → Ensures models converge faster and perform better.
- Encoding Categorical Data → Converts non-numeric data into ML-compatible formats.
- Noise Reduction → Improves signal clarity for models.
Industry Perspective: Even when deploying models on AWS Sagemaker or Google Vertex AI, unprocessed datasets lead to failed pipelines. That’s why CuriosityTech students practice preprocessing extensively before deploying ML systems.
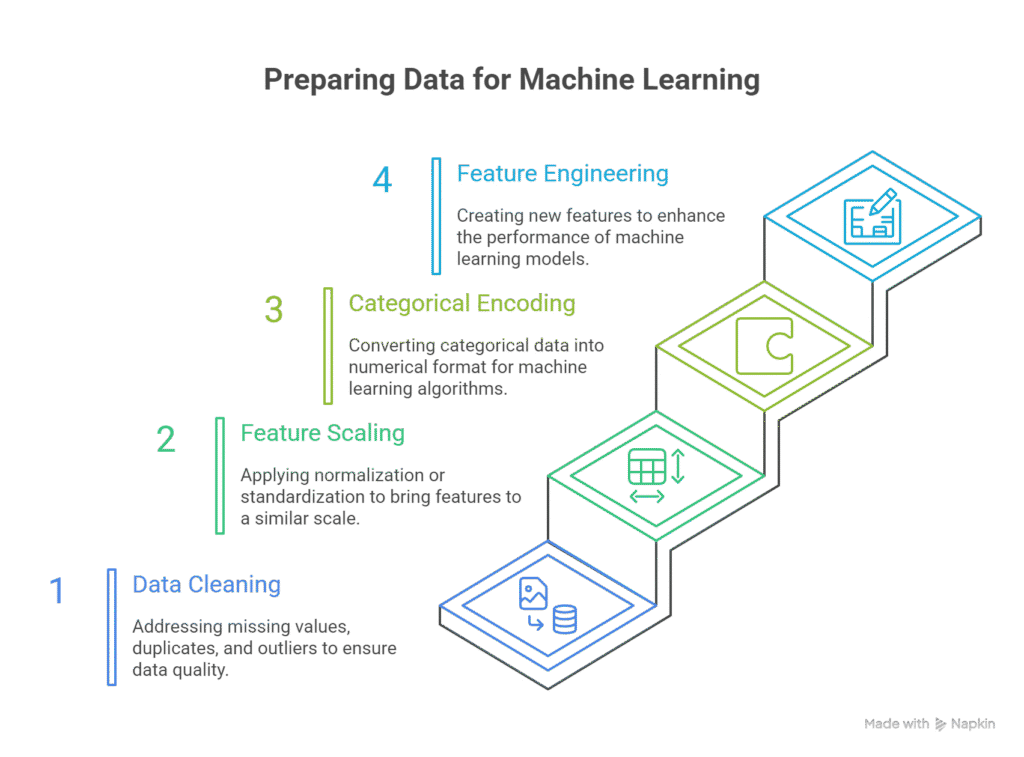
2. Stepwise Preprocessing Guide
Step 1: Data Cleaning
- Handling Missing Values
- Drop missing rows → Simple but may discard valuable data
- Imputation → Fill missing values using mean, median, mode, or predictive imputation
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv(“customer_data.csv”)
df.fillna(df.mean(), inplace=True)
- Removing Duplicates
df.drop_duplicates(inplace=True)
- Outlier Detection & Handling
- Techniques: Z-score, IQR, or domain knowledge
- Example: Capping extreme ages in a customer dataset
At CuriosityTech Park (LinkedIn, Instagram), we often show beginners visualizing outliers using boxplots before deciding on removal.
Step 2: Feature Scaling
ML models like Gradient Descent-based algorithms are sensitive to feature magnitudes.
- Normalization → Scale features to [0,1] range
- Standardization → Center features around mean=0, std=1
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaled_features = scaler.fit_transform(df[[‘age’, ‘income’]])
Lab Note: Scaling is crucial for algorithms like SVM, KNN, Neural Networks, while tree-based models like Random Forest are less sensitive.
Step 3: Encoding Categorical Features
Most ML algorithms require numeric input. Encoding techniques include:
- Label Encoding → Convert categories into integer labels
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
le = LabelEncoder()
df[‘gender’] = le.fit_transform(df[‘gender’])
- One-Hot Encoding → Create binary columns for categories
df = pd.get_dummies(df, columns=[‘city’])
Pro Tip: At CuriosityTech.in, students practice encoding hundreds of categorical features efficiently, which is essential for large-scale real-world datasets.
Step 4: Feature Engineering (Optional but Critical)
- Create new features from existing ones
- Example: Convert date_of_birth → age
- Example: Combine length and width → area
CuriosityTech mentors guide learners to think like engineers, not just coders, ensuring features capture real-world signals.
3. Preprocessing Flowchart (Description for Blog Visual)
Infographic Tip:
4. Hands-On Example: Customer Churn Dataset
- Load Data
df = pd.read_csv(“customer_churn.csv”)
- Clean Missing Values
df[‘tenure’].fillna(df[‘tenure’].median(), inplace=True)
- Scale Numeric Features
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
df[[‘monthly_charges’,’tenure’]] = scaler.fit_transform(df[[‘monthly_charges’,’tenure’]])
4. Encode Categorical Features
df = pd.get_dummies(df, columns=[‘contract_type’, ‘payment_method’])
- Ready for ML Model → Next step is model building (covered in Day 4 & 6).
5. Common Mistakes in Preprocessing
| Mistake | Consequence | How CuriosityTech Guides Students |
| Dropping too many rows | Loss of valuable data | Introduce imputation strategies |
| Not scaling features | Slow convergence, poor performance | Teach when to scale & which method |
| Incorrect encoding | Wrong model predictions | Hands-on encoding labs with multiple datasets |
| Ignoring outliers | Skewed model results | Visual detection & domain-informed handling |
6. Industry Relevance
Preprocessing is mandatory in 2025 ML pipelines, whether deploying on:
- AWS Sagemaker
- Azure ML
- Google Vertex AI
At CuriosityTech.in, students learn to clean, scale, and encode data efficiently, ensuring smooth deployment in production systems.
7. Key Takeaways
- Cleaning, scaling, encoding form the backbone of any ML workflow.
- Proper preprocessing prevents wasted time on failed models.
- Hands-on practice with multiple datasets is crucial to expertise.
- Think like an engineer, not just a coder—understand the why behind every step.
As we tell our learners: “Preprocessing is the bridge between raw data and impactful machine learning.”
Conclusion
Data preprocessing transforms messy, inconsistent, and raw datasets into ML-ready goldmines. By mastering cleaning, scaling, and encoding:
- Models become faster and more accurate.
- Deployment pipelines run smoothly.
- Real-world problems, like customer churn, sales prediction, or fraud detection, become solvable.
At CuriosityTech Nagpur, our approach combines hands-on labs, real-world datasets, and mentorship, ensuring learners excel in both interviews and production-level ML projects. Contact us at contact@curiositytech.in or +91-9860555369 to start your 2025 ML journey.