Introduction
Every serious website on the internet runs on one hidden engine: data.
Users, passwords, products, payments, posts, messages — nothing exists without a database. PHP without MySQL is like a car without fuel. It might look good, but it won’t go anywhere.
In real-world development, what separates a hobby PHP developer from a professional PHP engineer is the ability to design, connect, secure, and optimize databases. At CuriosityTech, where students train inside a real learning ecosystem on Wardha Road, Nagpur, database mastery is taught from the very beginning because this is exactly what companies look for when hiring PHP developers.
Today, on Day 8, we go deep into how PHP and MySQL work together to power modern web applications.
1. Why MySQL Is the Backbone of PHP Applications
PHP is responsible for logic and control.
MySQL is responsible for memory and persistence.
Together they form a dynamic system:
| PHP Handles | MySQL Handles |
| User requests | User data |
| Form validation | Stored information |
| Business logic | Tables and records |
| Page rendering | Long-term storage |
When someone logs into a website, PHP checks credentials, but the username and password live inside MySQL. When someone buys a product, PHP processes the order, but MySQL stores the transaction forever.
This relationship is why PHP and MySQL are often called the “power couple” of web development.
2. How PHP Talks to MySQL
In a live server environment, PHP never stores large data in itself. It sends structured queries to MySQL, receives results, and converts them into HTML pages, JSON responses, or admin dashboards.
The Communication Flow
Browser → PHP Script → MySQL Server → PHP Script → Web Page
Every time a visitor clicks a button, this flow is executed behind the scenes.
This is exactly how login systems, eCommerce sites, learning platforms, and company websites work.
3. Database Structure Used in Professional PHP Projects
When CuriosityTech trains students in backend development, they are not just taught to create random tables. They are taught relational thinking.
A real PHP system uses:
| Component | Purpose |
| Tables | Store structured data |
| Rows | Individual records |
| Columns | Data fields |
| Primary Key | Unique identification |
| Foreign Key | Table relationships |
Example: Online Course Platform
| Table | What It Stores |
| users | Student details |
| courses | Course data |
| enrollments | Who bought what |
| payments | Transaction history |
This kind of structure is what companies expect PHP developers to understand.
4. Why Database Design Matters
Poor database design causes:
- Slow websites
- Crashes
- Data loss
- Security vulnerabilities
Professional PHP developers think before they write SQL. They ask:
- How much data will this store?
- How often will it be accessed?
- Will it grow in the future?
At CuriosityTech, students learn this mindset early, so they don’t just “write queries” — they design systems.
Hierarchical View of PHP–MySQL Integration
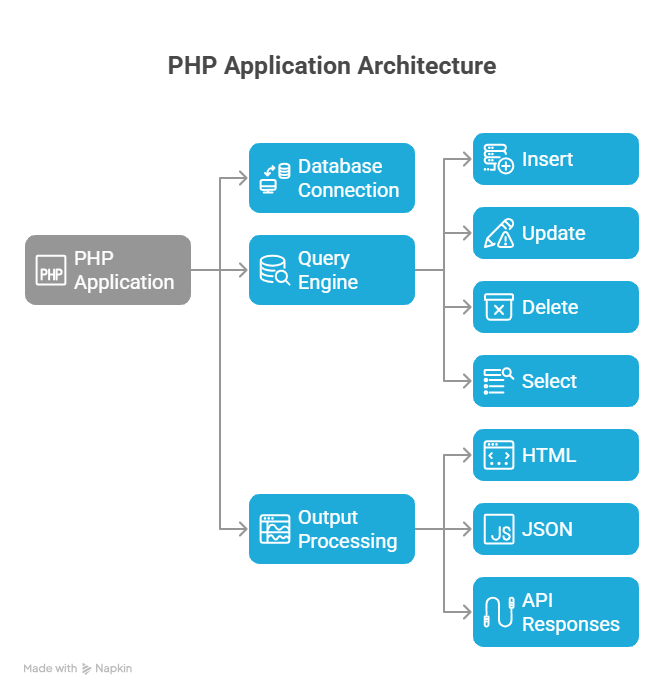
This hierarchy exists inside every professional PHP application.
Infographic Description
Title: How PHP and MySQL Work Together
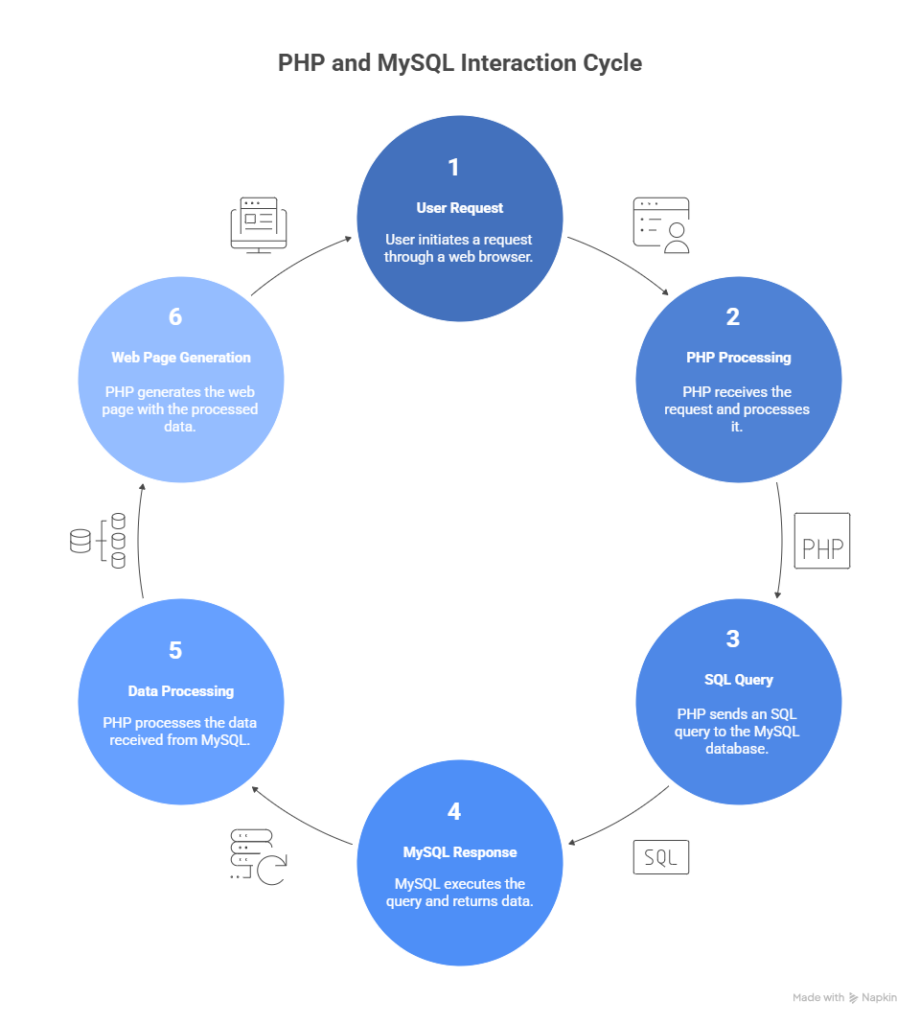
This shows the invisible cycle that happens thousands of times per minute on large websites.
5. Security in PHP-MySQL Systems
One of the biggest dangers in PHP applications is SQL Injection. This happens when attackers send malicious input through forms and PHP blindly passes it to MySQL.
Professional developers prevent this by:
- Sanitizing input
- Using prepared statements
- Validating all user data
This security-first approach is heavily emphasized during training at CuriosityTech, because companies demand developers who can protect real user data.
6. Where This Knowledge Is Used in Real Life
Every system built by PHP developers uses database integration:
| Industry | PHP-MySQL Usage |
| eCommerce | Orders, users, payments |
| Education | Students, courses |
| Healthcare | Records, reports |
| Startups | User platforms |
| Corporates | CRM, ERP |
This is why database knowledge is one of the highest-paid PHP skills in the job market.
Conclusion
PHP without MySQL is incomplete.
MySQL without PHP is unusable.
Together, they form the foundation of modern web systems. When you understand how PHP connects, queries, secures, and processes database data, you move from being a coder to becoming a backend engineer.
That is exactly why institutes like CuriosityTech focus so deeply on PHP-MySQL integration — because this is what real companies actually use.


