Introduction
Azure SQL Database is a fully managed relational database service that allows cloud engineers to deploy, scale, and manage SQL databases without worrying about infrastructure. Unlike on-premises SQL Servers, Azure SQL Database provides automatic backups, high availability, built-in security, and scalability, making it an essential skill for cloud engineers.
At curiositytech.in, learners gain hands-on exposure to Azure SQL Database, from database design and querying to performance optimization and security.
1. What is Azure SQL Database?
Definition:
Azure SQL Database is a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offering that provides:
- Managed database engine
- Automatic updates and patching
- Built-in high availability (99.99% SLA)
- Security features like Transparent Data Encryption (TDE), auditing, and firewall rules
Key Benefits:
- No need to manage underlying infrastructure
- Scale resources dynamically
- Integrated monitoring and alerting
- Supports relational and semi-structured data (JSON, XML)
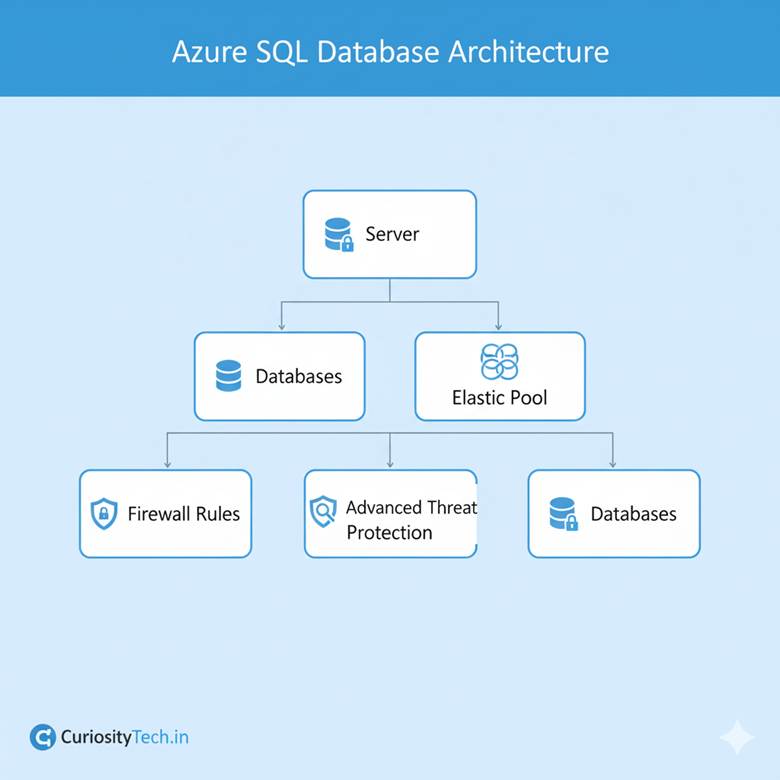
2. Database Architecture
Logical Architecture Components:
| Component | Description |
| Server | Logical container for databases, login accounts, and firewall rules |
| Database | Individual databases with dedicated compute and storage |
| Elastic Pool | Group of databases sharing resources for cost optimization |
| Firewall Rules | Define which IPs can access the database |
| Advanced Threat Protection | Monitors anomalous database activities |
ER Diagram Example: Sample E-commerce Database
3. Deployment Options
- Single Database: Isolated, fully managed database suitable for one application
- Elastic Pool: Multiple databases sharing resources, optimized for variable workloads
- Managed Instance: Near 100% SQL Server compatibility, ideal for migrating on-prem SQL workloads
Practical Scenario:
A startup has multiple microservices, each with its own database. Using an elastic pool, resources are shared across microservices, optimizing cost while maintaining performance.
4. Hands-On: Creating an Azure SQL Database
Step 1: Create SQL Server
- Navigate to Azure Portal → Create Resource → SQL Database → Server
- Provide server name, admin username, password, and region
Step 2: Create SQL Database
- Select Single Database or Elastic Pool
- Configure Compute Tier: General Purpose, Business Critical, or Hyperscale
- Set Storage Size according to expected data volume
Step 3: Configure Security
- Set firewall rules for your IP
- Enable Advanced Data Security and Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
Step 4: Connect to Database
- Use SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or Azure Data Studio
- Connect using server admin credentials
Step 5: Example Query
— Create Products Table
CREATE TABLE Products (
ProductID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name NVARCHAR(100),
Price DECIMAL(10,2),
StockQuantity INT
);
— Insert Sample Data
INSERT INTO Products VALUES (1, ‘Laptop’, 950.00, 10);
— Query Data
SELECT * FROM Products;
5. Performance & Monitoring
- Automatic Indexing: Optimizes queries automatically
- Query Performance Insights: Analyze slow queries
- Metrics & Alerts: CPU, DTU utilization, storage usage
- Geo-Replication: Replicate databases across regions for high availability
6. Security Best Practices
- Use firewall rules and virtual networks to restrict access
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for SQL logins
- Configure Advanced Threat Protection for anomaly detection
- Regularly monitor audit logs
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest using TDE
Infographic Content:

7. Expert Tips to Become an Azure SQL Database Specialist
- Master SQL queries and indexing strategies
- Learn elastic pools and scaling strategies for cost efficiency
- Use Azure CLI and PowerShell for automation
- Understand backup, restore, and disaster recovery processes
- Implement monitoring and alerting for production-grade databases
Conclusion
Azure SQL Database provides a robust, secure, and scalable relational database solution for cloud engineers. By mastering deployment, schema design, performance tuning, and security features, engineers can deliver enterprise-ready cloud applications. Practical labs at curiositytech.in allow learners to bridge the gap between theory and real-world application, ensuring expertise in managed SQL databases.



