Introduction
In the world of business analysis, Gap Analysis and Feasibility Studies are essential tools for understanding where an organization currently stands versus where it needs to be, and determining whether a proposed project or solution is viable. Mastery of these concepts allows business analysts (BAs) to identify opportunities, reduce risks, and ensure strategic alignment. At Curiosity Tech (website:curiosity tech, Phone: +91-9860555369, Email: contact@curiositytech.in), we guide professionals through real-world gap analysis and feasibility exercises, enabling them to bridge business needs and actionable solutions.
1. What is Gap Analysis?
Definition: Gap Analysis is the process of comparing current performance with desired performance to identify gaps and recommend improvements. It helps organizations understand what steps are needed to achieve business objectives.
Key Objectives of Gap Analysis:
- Identify performance gaps
- Highlight inefficiencies or redundancies
- Set realistic improvement goals
- Align operations with strategic objectives
Example Table – Gap Analysis Template
| Area | Current State | Desired State | Gap Identified | Recommended Action |
| Customer Support | Average response 48 hours | Response within 24 hours | Slow response times | Implement ticketing system & training |
| Sales Process | Manual lead tracking | Automated CRM system | Inefficient manual tracking | Deploy CRM & automate follow-ups |
| Inventory Management | Stock discrepancies 15% | <3% discrepancy | Lack of accurate tracking | Introduce barcode scanning & regular audits |
Curiosity Tech Insight: In practice, our analysts at the Nagpur office used Gap Analysis to reduce operational inefficiencies by 30% for a client in the logistics sector, demonstrating its real-world impact.
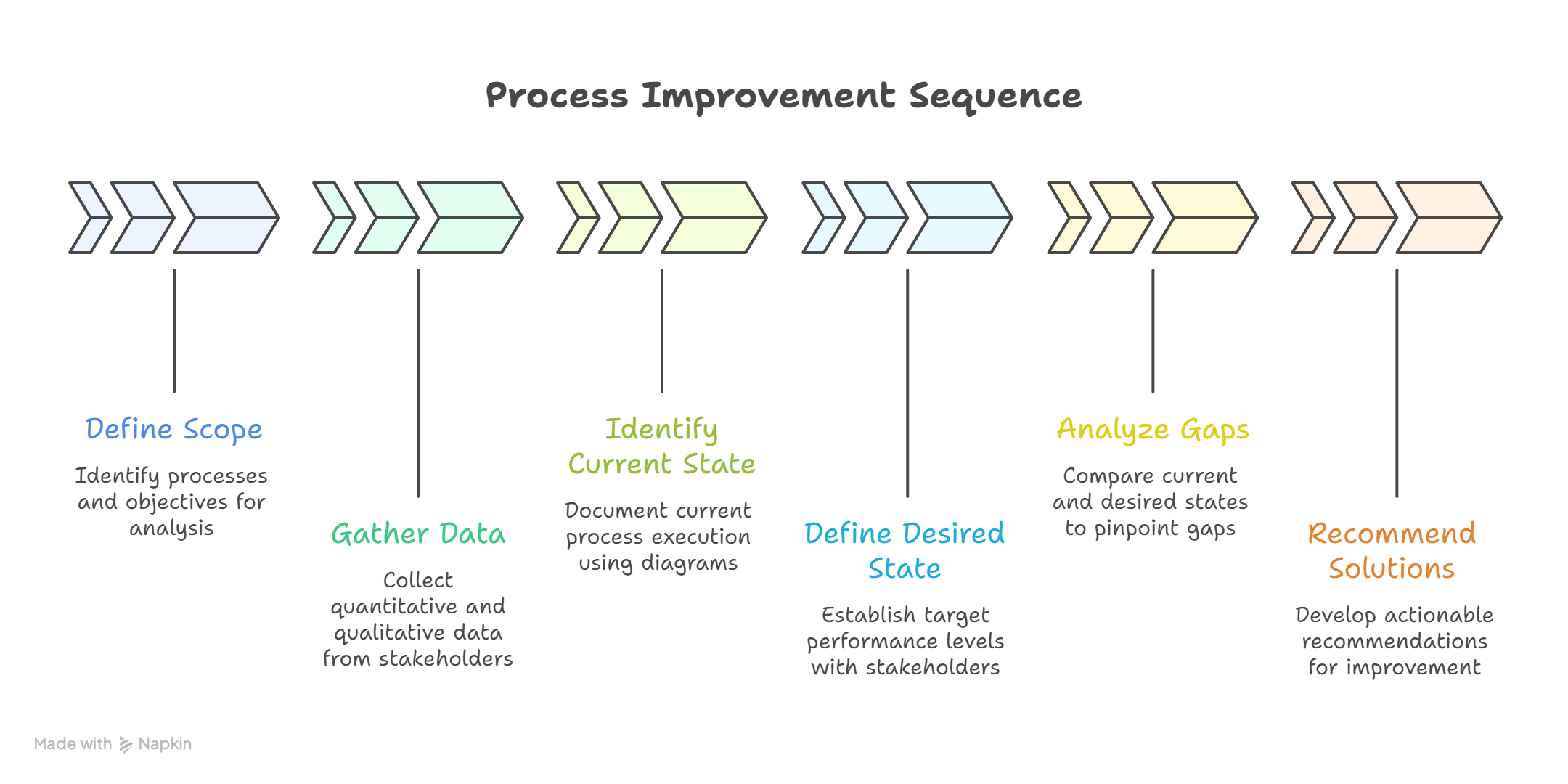
2. Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting Gap Analysis
Step 1 – Define the Scope:-Identify the processes, systems, or areas to analyze. Clearly define objectives to avoid ambiguity.
2 – Gather Data:- Collect quantitative and qualitative data from stakeholders, process logs, surveys, or reports.
3 – Identify Current State:- Document how processes are currently executed, using flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, or process maps.
4 – Define Desired State:- Collaborate with management and stakeholders to establish target performance levels.
5 – Analyze Gaps:- Compare current and desired states to pinpoint gaps and root causes.
6 – Recommend Solutions:– Develop actionable recommendations, including resource requirements, timelines, and responsible teams.
Workflow Example – Gap Analysis Process
3. Feasibility Studies for Business Analysts
Definition: A Feasibility Study assesses whether a proposed project or solution is practical, viable, and profitable. It ensures that organizations invest in initiatives that deliver value without excessive risk.
Types of Feasibility Studies:
| Type | Purpose | Example |
| Technical Feasibility | Can the solution be built with available technology? | Implementing an ERP system |
| Economic Feasibility | Is the project financially viable? | ROI analysis for a new product launch |
| Operational Feasibility | Will it integrate smoothly into current operations? | Workflow adjustments for new CRM system |
| Legal/Regulatory Feasibility | Does it comply with laws & regulations? | GDPR compliance for data management |
| Schedule Feasibility | Can it be completed within time constraints? | Launching a mobile app within 6 months |
Curiosity Tech Approach: We teach BAs to combine Gap Analysis and Feasibility Studies to prioritize projects, ensuring that organizations invest in initiatives that are both needed and achievable.
4. Combining Gap Analysis & Feasibility Studies
Why Combine?
- Gap Analysis identifies what needs to change
- Feasibility Study evaluates whether the change is practical
Example Scenario – Nagpur Client Case Study:
A manufacturing client wanted to implement an automated inventory system:
- Gap Analysis: Highlighted discrepancies, inefficiencies, and manual errors in the current process
- Feasibility Study: Determined the technical, economic, and operational viability of automation
- Outcome: Project approved and implemented successfully, improving inventory accuracy by 40%
5. Tools for Conducting Gap Analysis & Feasibility Studies
| Tool | Purpose | Notes |
| MS Excel / Google Sheets | Data collection, gap computation | Simple, widely used |
| MS Visio | Process mapping and visual representation | Visualize current vs desired workflows |
| JIRA | Track corrective actions and implementation | Ensure recommendations are executed |
| Confluence | Documentation of findings and recommendations | Maintain a single source of truth |
Pro Tip (Curiosity Tech): Combining visual diagrams from Visio with documented findings in Confluence ensures that stakeholders can understand gaps and approve actionable solutions.
6. Expert Tips for Mastering Gap Analysis & Feasibility Studies
- Engage Stakeholders Early: Collect input from all relevant stakeholders to ensure accuracy.
- Use Visuals: Diagrams, flowcharts, and tables make gaps easy to understand.
- Focus on Impact: Prioritize gaps that affect ROI, customer satisfaction, or operational efficiency.
- Document Assumptions: Clearly state assumptions to avoid misunderstandings.
- Continuous Monitoring: Track implemented changes and assess if gaps are closing.
Conclusion
Gap Analysis and Feasibility Studies are cornerstones of effective business analysis. They allow BAs to identify opportunities, mitigate risks, and guide organizations toward achievable, high-impact solutions. Analysts trained at Curiosity Tech, located at 1st Floor, Plot No 81, Wardha Rd, Gajanan Nagar, Nagpur, develop hands-on expertise in these methodologies, combining practical exercises with real-world case studies. By mastering these tools, a business analyst ensures that projects are not only necessary but also viable and profitable, leading to successful business outcomes.



