Introduction
Every project carries risk, whether it’s related to technology, resources, finances, or stakeholders. For business analysts (BAs), identifying, assessing, and managing risks is critical to ensuring that projects are delivered on time, within budget, and meet business objectives. Risk analysis and management provide a proactive approach to mitigate potential threats and seize opportunities. At Curiosity Tech (website:curiositytech.in, Phone: +91-9860555369, Email: contact@curiositytech.in), we train BAs to apply structured risk analysis techniques, real-world simulations, and tools to prepare for uncertainty in projects effectively.
1. What is Risk Analysis in Projects?
Definition :- Risk Analysis is the process of identifying potential threats and evaluating their impact and likelihood, to plan strategies that minimize negative outcomes and maximize opportunities.
Purpose:
- Anticipate and mitigate project risks
- Allocate resources effectively
- Enhance decision-making and stakeholder confidence
Types of Project Risks:
| Risk Type | Description | Example |
| Technical Risks | Related to technology or system implementation | Software bugs, hardware failures |
| Financial Risks | Budget-related or cost overruns | Unexpected increase in software licensing |
| Operational Risks | Inefficiencies in processes or resources | Delays due to insufficient staffing |
| Strategic Risks | Misalignment with business goals | Project does not deliver expected ROI |
| Compliance Risks | Legal or regulatory issues | Non-compliance with data protection laws |
| External Risks | Market, environmental, or geopolitical factors | Supply chain disruption |
Curiosity Tech Insight: Analysts trained at Curiosity Tech learn to classify risks accurately, ensuring that mitigation strategies are focused where they are most needed.
2. Risk Management Process
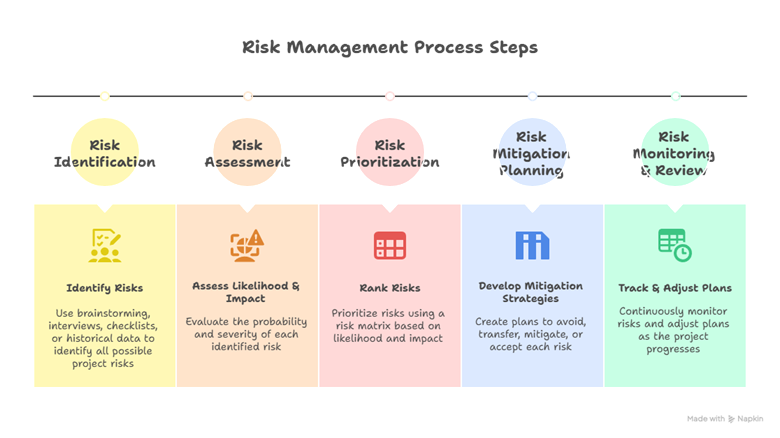
- Step 1 – Risk Identification :- Identify all possible risks using techniques such as brainstorming, interviews, checklists, or historical data review.
- Step 2 – Risk Assessment :- Assess the likelihood and impact of each risk to prioritize them.
- Step 3 – Risk Prioritization :- Rank risks using a risk matrix, considering both probability and severity.
- Step 4 – Risk Mitigation Planning :- Develop strategies to avoid, transfer, mitigate, or accept risks.
- Step 5 – Monitor and Review :- Continuously track risks and adjust plans as the project progresses.
3. Risk Assessment Tools
| Tool | Purpose | Notes |
| Risk Matrix | Visual representation of risk severity vs probability | Helps prioritize critical risks |
| SWOT Analysis | Identify internal and external threats | Simple, effective for early-stage projects |
| FMEA (Failure Mode & Effects Analysis) | Evaluate process or system risks systematically | Assigns risk priority numbers (RPN) |
| Monte Carlo Simulation | Predict probability and impact of uncertain variables | Advanced modeling for complex projects |
| Excel / Google Sheets | Risk tracking and reporting | Widely accessible, easy to customize |
Curiosity Tech Approach: Analysts are trained to create risk registers in Excel or specialized software, linking each risk to mitigation strategies and owners.
4. Risk Matrix Example
| Likelihood \ Impact | Low Impact | Medium Impact | High Impact |
| High Likelihood | Medium Risk | High Risk | Critical Risk |
| Medium Likelihood | Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk |
| Low Likelihood | Low Risk | Low Risk | Medium Risk |
Interpretation:
- Critical Risk: Immediate mitigation required
- High Risk: Plan mitigation, monitor closely
- Medium Risk: Monitor regularly, prepare contingency
- Low Risk: Acceptable, minimal monitoring
Example: For a software project, a critical risk could be a database failure with high likelihood; mitigation may involve backup systems and redundancy.
5. Case Study – Risk Management in Action (Nagpur Client)
- Scenario: An e-commerce client planned to launch a new mobile app. Risks included:
- Technical Risk: Integration with existing ERP system
- Operational Risk: Limited testing resources
- Financial Risk: Budget overrun due to third-party APIs
Risk Analysis Approach:
- Identify Risks: Documented in risk register with owners and mitigation plans
- Assess & Prioritize: Used risk matrix to classify risks
- Mitigation Strategies:
- Technical Risk → Conducted sandbox testing before integration
- Operational Risk → Hired temporary QA staff
- Financial Risk → Negotiated fixed-cost API contracts
- Monitoring: Weekly review meetings with stakeholders
Outcome: Risk mitigation ensured on-time launch, reduced errors, and controlled costs, demonstrating the value of structured risk management.
6. Practical Tips for Business Analysts
- Engage Stakeholders Early: Include stakeholders in risk identification to capture overlooked threats
- Use Visuals: Risk matrices and dashboards simplify communication
- Document Everything: Maintain a risk register with owners, status, and mitigation plans
- Review Continuously: Risks evolve; monitoring is ongoing
- Combine Techniques: Use multiple assessment methods like SWOT, FMEA, and Monte Carlo for robust analysis
Curiosity Tech Training: Analysts practice real-life project simulations, creating risk registers, assessing severity, and designing mitigation strategies to gain hands-on expertise.
Conclusion
Risk Analysis and Management are critical competencies for business analysts. They allow organizations to anticipate challenges, reduce uncertainties, and make informed decisions. At Curiosity Tech, located at 1st Floor, Plot No 81, Wardha Rd, Gajanan Nagar, Nagpur, BAs are trained in structured risk management methodologies, tools, and real-world simulations. By mastering these techniques, analysts ensure projects succeed even in uncertain environments, creating value and trust with stakeholders.



