Introduction
In today’s data-driven business environment, organizations cannot succeed without measuring performance accurately. KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) and metrics allow businesses to monitor progress toward objectives, identify gaps, and make informed decisions. For business analysts (BAs), defining the right KPIs and metrics is a critical skill, as these indicators guide stakeholders, align teams, and influence strategic decisions. At Curiosity Tech (website:curiosity tech, Phone: +91-9860555369, Email: contact@curiositytech.in), we train analysts to define KPIs and metrics that are actionable, measurable, and aligned with business goals, preparing them to drive tangible business outcomes.
1. Understanding KPIs and Metrics
Key Definitions:
- KPI (Key Performance Indicator): A measurable value that demonstrates how effectively a business is achieving a strategic objective.
- Metric: A quantifiable measure used to track the performance of specific processes or activities.
Difference Between KPIs and Metrics:
| Aspect | KPI | Metric |
| Purpose | Measure progress toward strategic goals | Monitor specific operational processes |
| Focus | Strategic impact | Tactical or operational details |
| Example | Customer Satisfaction Score | Average response time of support tickets |
| Decision Impact | Drives business decisions | Supports monitoring and continuous improvement |
Curiosity Tech Insight: Analysts learn to differentiate between KPIs and supporting metrics, ensuring that measurements are meaningful and actionable.
2. Characteristics of Effective KPIs
- Aligned: Linked directly to business goals
- Measurable: Quantifiable with clear units or indicators
- Achievable: Realistic and attainable
- Relevant: Focused on aspects that impact business success
- Time-bound: Measured within a specific time frame
- Example:– KPI: Increase monthly online sales by 15% in Q4
Metric: Average cart value, website traffic, conversion rate
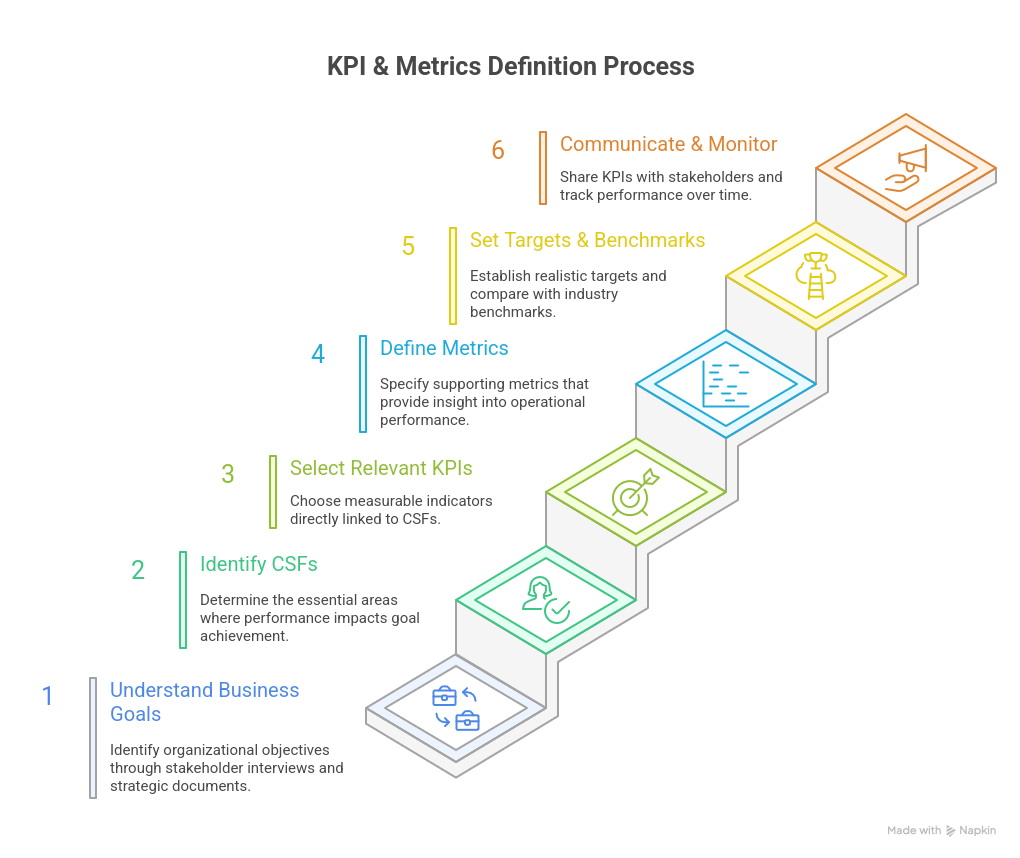
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Defining KPIs and Metrics
1 – Understand Business Goals
Identify organizational objectives through stakeholder interviews, strategic documents, and business plans.
2 – Identify Critical Success Factors (CSFs)
Determine the essential areas where performance impacts goal achievement.
3 – Select Relevant KPIs
Choose measurable indicators directly linked to CSFs.
4 – Define Metrics
Specify supporting metrics that provide insight into operational performance.
5 – Set Targets and Benchmarks
Establish realistic targets, compare with industry benchmarks, and define thresholds for success.
6 – Communicate and Monitor
Share KPIs with stakeholders, track performance over time, and adjust metrics as needed.
Workflow Diagram – KPI & Metrics Definition Process:
Business Goals –> Identify CSFs –> Define KPIs –> Specify Supporting Metrics –> Set Targets & Benchmarks –> Monitor & Review
4. Categories of KPIs and Metrics
| Category | Description | Example KPIs | Example Metrics |
| Financial | Measures revenue, cost efficiency, profitability | Net Profit Margin, ROI | Average order value, cost per transaction |
| Customer | Evaluates customer satisfaction and retention | Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), NPS | Customer support response time, churn rate |
| Operational | Assesses internal efficiency | Order Fulfillment Time, Production Yield | Inventory accuracy, defect rate |
| Employee | Measures staff performance and engagement | Employee Productivity, Retention Rate | Training hours completed, absenteeism rate |
| Project/Process | Tracks project or process success | On-time Delivery, Milestone Completion | Task completion rate, error rates |
Curiosity Tech Training: Analysts practice defining KPIs across multiple domains, ensuring they can monitor both strategic and operational performance effectively.
5. Practical Example – Nagpur Retail Client
Scenario: A retail chain wanted to improve online sales and customer satisfaction.
1 – Define Business Goals:
- Increase sales revenue by 20%
- Improve customer satisfaction ratings
2 – Identify CSFs:
- Website conversion rate
- Order processing efficiency
- Customer support responsiveness
3 – Define KPIs & Metrics:
| KPI | Target | Supporting Metrics |
| Monthly online sales growth | 20% increase | Website traffic, conversion rate |
| Customer Satisfaction Score | 90%+ | Average response time, issue resolution |
| Order Fulfillment Accuracy | 98% | Inventory discrepancy, packing errors |
Step 4 – Monitor & Review:
- Weekly dashboards tracked KPIs
- Continuous improvement implemented based on data
- Achieved a 22% increase in sales and 92% customer satisfaction
6. Tools for KPI Tracking
| Tool | Purpose | Notes |
| Excel / Google Sheets | Simple KPI tracking and charting | Suitable for small projects |
| Power BI / Tableau | Interactive dashboards and real-time monitoring | Visualize trends and insights |
| JIRA / Confluence | Track project KPIs and tasks | Link KPIs to project performance |
| Google Analytics | Track web-based metrics | E-commerce performance tracking |
Curiosity Tech Approach: Analysts learn to integrate KPI tracking with reporting tools, providing stakeholders with actionable insights in real-time.
7. Best Practices for Defining KPIs & Metrics
- Focus on quality over quantity – select meaningful indicators
- Ensure KPIs are aligned with strategic objectives
- Use both leading and lagging indicators for a balanced view
- Update KPIs regularly to reflect changing business priorities
- Communicate results clearly to all stakeholders
Example: A BA should not just report sales growth but also provide insights into which products or campaigns are driving growth, enabling informed decisions.
Conclusion
KPIs and metrics are the backbone of business performance management. They allow organizations to measure progress, identify gaps, and make data-driven decisions. For business analysts, mastering KPI definition ensures that projects and operations remain aligned with strategic objectives. Analysts trained at Curiosity Tech, located at 1st Floor, Plot No 81, Wardha Rd, Gajanan Nagar, Nagpur, gain practical experience in defining, tracking, and analyzing KPIs, enabling them to drive measurable business success and provide value to stakeholders.



