Introduction
In a rapidly changing world, businesses can no longer rely on incremental improvements to remain competitive. They need radical redesigns of processes to achieve breakthrough results in cost, quality, speed, and customer satisfaction. This is where Business Process Reengineering (BPR) plays a transformative role. For business analysts, understanding BPR is not optional — it’s a core competency that positions them as agents of change. At Curiosity Tech (website: curiositytech.in, Phone: +91-9860555369, Email: contact@curiositytech.in), we train professionals to analyze, design, and implement BPR initiatives that drive real impact.
1. What is Business Process Reengineering (BPR)?
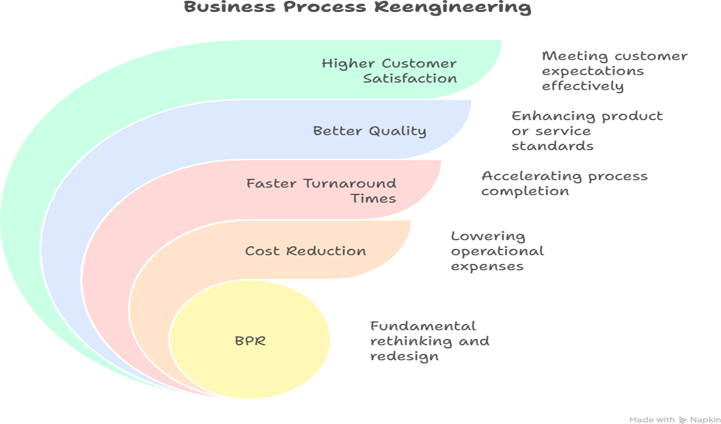
2. The Principles of BPR
- Have Those Who Use the Output Perform the Process – Empower customers or end- users to initiate processes.
- Incorporate Information Processing Into Real Work – Use technology to embed data capture and analysis directly into workflows.
- Treat Geographically Dispersed Resources as Centralized – Use digital platforms to unify distributed operations.
- Link Parallel Activities Instead of Integrating Results Later – Run tasks simultaneously, not sequentially.
- Put Decision Points Where Work is Performed – Reduce layers of approvals by enabling decision-making at execution points.
3. The BPR Lifecycle
Workflow Diagram – BPR Steps:
Identify Processes –> Analyze Current State –> Redesign Process –> Implement New Process –> Monitor & Optimize
Detailed Steps:
- Identify Processes: Choose high-impact processes (e.g., order fulfillment).
- Analyze Current State: Map workflows, KPIs, and pain points.
- Redesign: Apply radical rethinking (automation, outsourcing, restructuring).
- Implement: Deploy redesigned processes with change management support.
- Monitor & Optimize: Use KPIs to measure performance and refine.
4. BPR vs Continuous Process Improvement (CPI)
| Aspect | BPR | CPI (Kaizen, Lean) |
| Focus | Radical redesign | Incremental improvements |
| Approach | Breakthrough changes | Small, continuous steps |
| Timeframe | Medium to long-term | Short-term, ongoing |
| Risk Level | Higher | Lower |
| Example | Implement ERP across entire business | Reduce paper use in invoicing |
Curiosity Tech Perspective: Analysts are trained to balance both approaches — using BPR for transformation and CPI for continuous efficiency.
5. Case Study – Manufacturing Firm in Nagpur
Challenge:
A medium-sized manufacturing client faced:
- Delays in procurement approvals
- Inventory shortages
- High costs due to duplicate processes
BPR Solution Implemented:
- Centralized procurement system integrated with ERP
- Automated vendor selection through scorecards
- Streamlined approval chain (reduced from 5 levels to 2)
Results Achieved:
| Metric | Before BPR | After BPR |
| Procurement Cycle Time | 15 days | 4 days |
| Inventory Accuracy | 65% | 95% |
| Operational Cost Savings | – | 20% |
The transformation was led by business analysts who worked closely with stakeholders and technology teams, demonstrating the practical power of BPR.
6. Tools & Techniques Used in BPR
| Tool/Technique | Purpose |
| Process Mapping | Documenting current workflows |
| BPMN & UML | Standardized process modeling |
| Root Cause Analysis | Identifying inefficiencies |
| ERP Systems (SAP, Oracle) | Implementing process automation |
| Simulation Software | Testing redesigned workflows virtually |
Training at Curiosity Tech: Analysts get hands-on exposure to MS Visio, JIRA, and ERP workflows, preparing them to drive BPR initiatives in industries ranging from retail to manufacturing.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may fear job loss or role changes.
- High Implementation Costs: Requires investment in new systems and training.
- Process Misalignment: Poorly designed processes can disrupt operations.
- Data Migration Risks: Transitioning legacy data into new systems may lead to errors.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Engage stakeholders early
- Provide training and communication plans
- Pilot-test redesigned processes before full rollout
- Monitor performance continuously
7. Skills Analysts Need for BPR Success
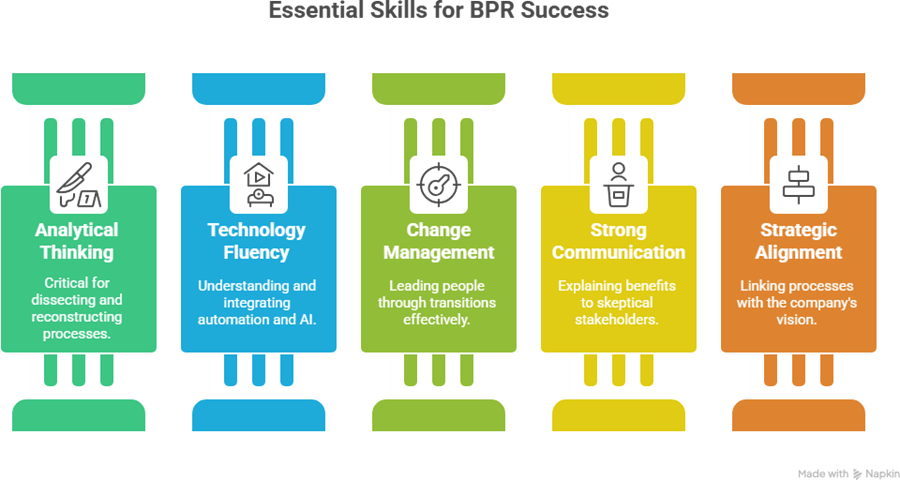
8. Hierarchical View – BPR Roles
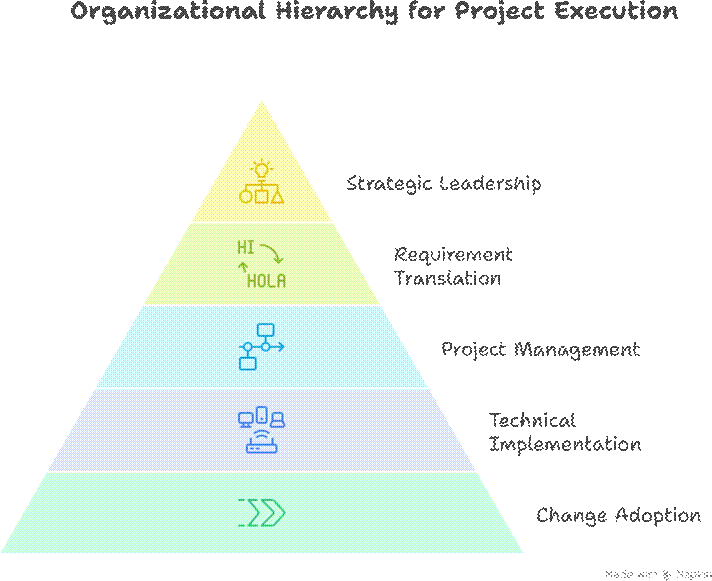
.
Conclusion
Business Process Reengineering is not just an exercise in efficiency; it is a strategic enabler of transformation. Companies that embrace BPR achieve faster delivery, reduced costs, and improved customer experiences. For business analysts, mastering BPR means gaining the ability to redesign entire workflows, drive change, and deliver measurable business success. At Curiosity Tech, located at 1st Floor, Plot No 81, Wardha Rd, Gajanan Nagar, Nagpur, analysts gain hands-on BPR experience through projects, case studies, and tool training — preparing them to lead the next wave of organizational transformation.



